Russian scientists at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT), the Joint Institute for High Temperatures of the Russian Academy of Sciences (JIHT RAS), and Gamaleya Research Centre of Epidemiology and Microbiology found that treating cells with cold plasma leads to their regeneration and rejuvenation. This result can be used to develop a plasma therapy program for patients with non-healing wounds. The paper has been published in the Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics.
Non-healing wounds make it more difficult to provide effective treatment to patients and are therefore a serious problem faced by doctors. These wounds can be caused by damage to blood vessels in the case of diabetes, failure of the immune system resulting from an HIV infection or cancers, or slow cell division in elderly people. Treatment of non-healing wounds by conventional methods is very difficult and in some cases impossible.
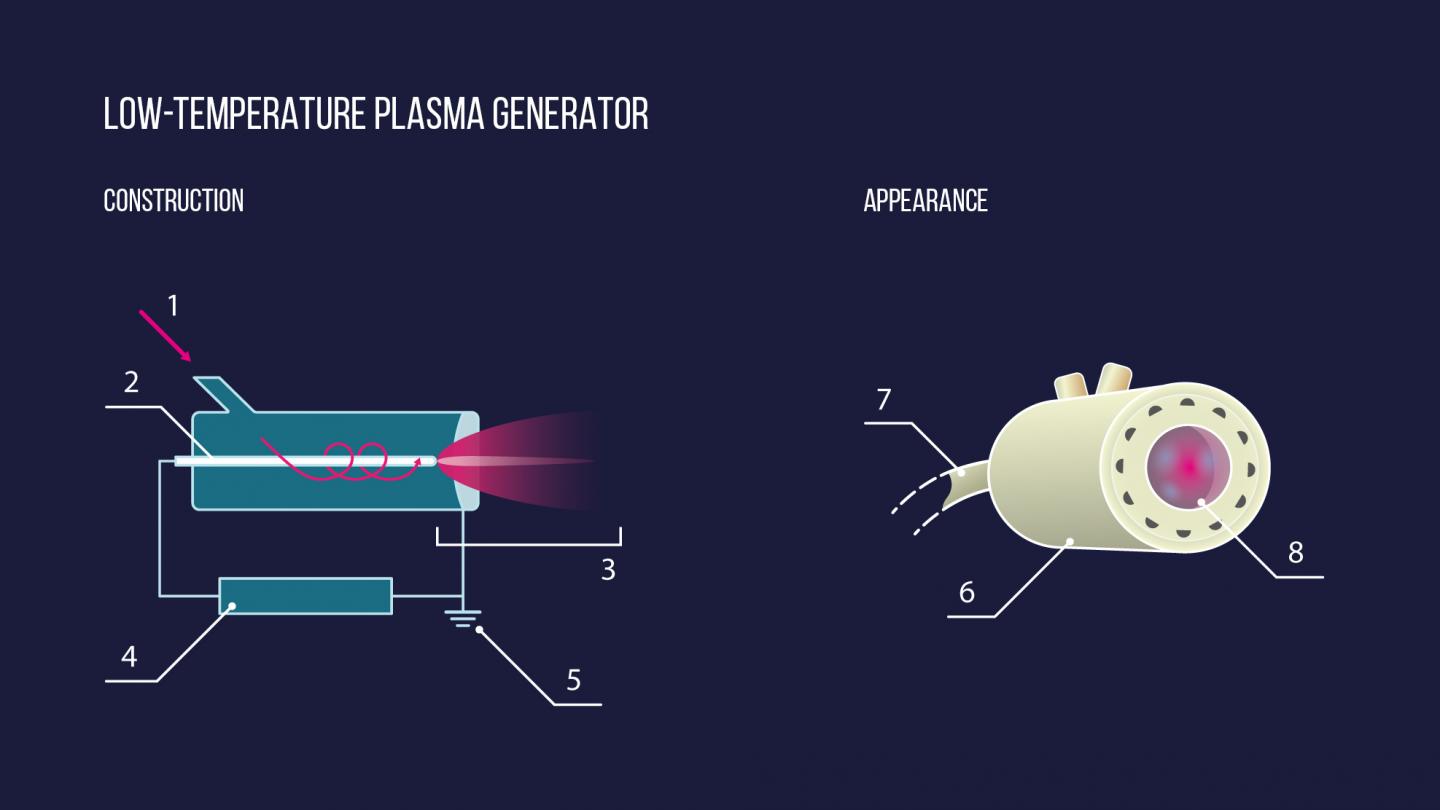
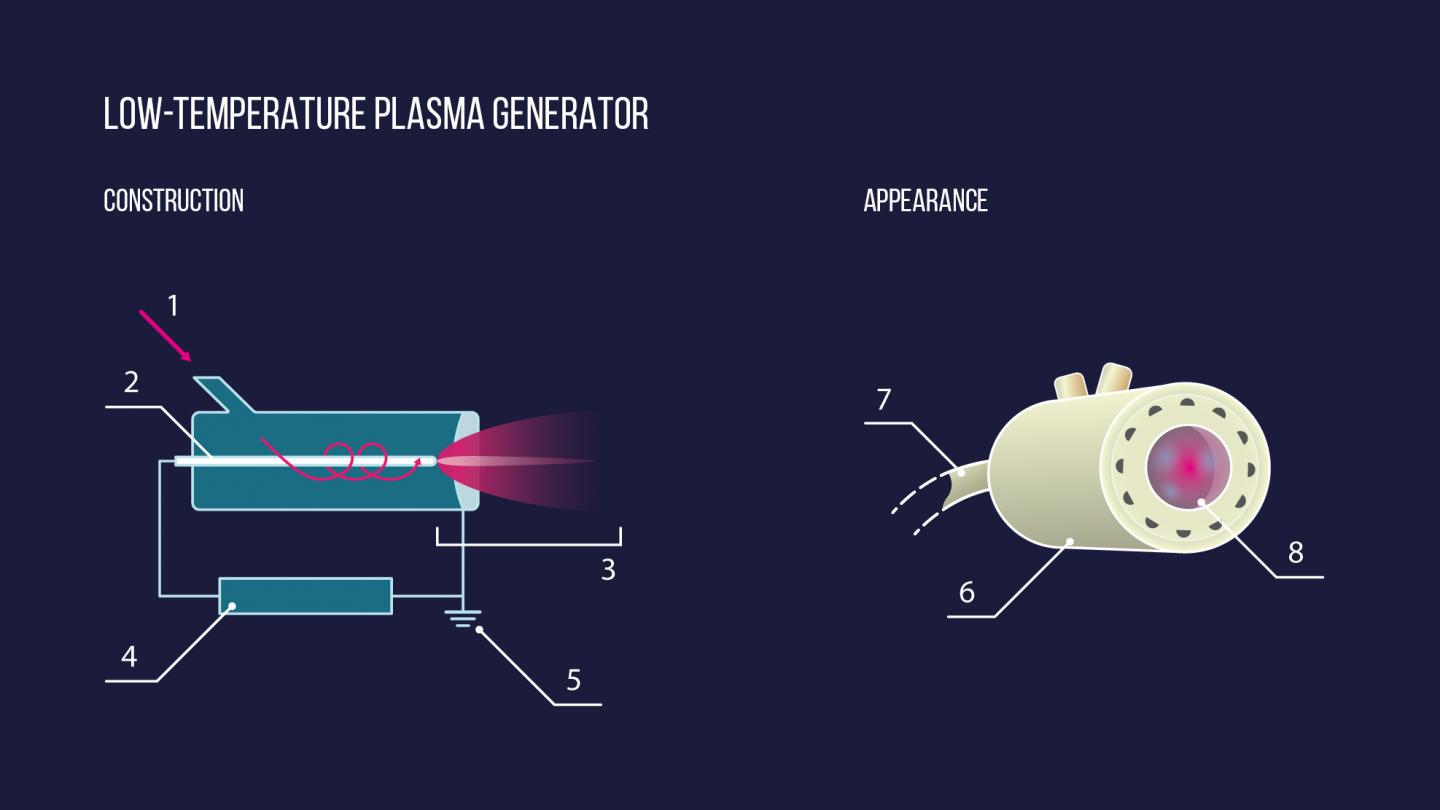
Cold atmospheric-pressure plasma refers to a partially ionized gas (the proportion of charged particles in the gas being close to 1?%) with a temperature below 100,000 K. Its application in biology and medicine has been made possible by the advent of plasma sources generating jets at 30-40?°C.
An earlier study established the bactericidal properties of low-temperature plasma, as well as the relatively high resistance of cells and tissues to its influence. The results of plasma treatment of patients with non-healing wounds varied from positive to neutral. The authors’ previous work prompted them to investigate the possibility that the effect of plasma treatment on wound healing could depend on application pattern (the interval between applications and the total number of applications).
Two types of cells were used in this study, viz. fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) and keratinocytes (epithelial cells). Both play a central role in wound healing.
The effect of plasma treatment on cells was measured. In fibroblast samples, the number of cells increased by 42.6?% after one application (A) and by 32.0?% after two applications (B), as compared to the untreated controls. While no signs of DNA breaks were detected following plasma application, an accumulation of cells in the active phases of the cell cycle was observed, alongside a prolonged growth phase (30 hours). This means that the effect of plasma could be characterized as regenerative, as opposed to harmful.
The proliferation of cells that had been treated daily over a period of three days (group C) was reduced by 29.1?% relative to the controls. Keratinocytes did not show noticeable changes in proliferation.
The researchers also performed an assay of the senescence-associated β-galactosidase, which is measured at pH 6.0. The concentration of this enzyme in a cell increases with age. Plasma treatment significantly reduced the content of this substance in the samples. This, together with a prolonged exponential growth phase of the culture, suggests a functional activation of cells–their rejuvenation.
‘The positive response to plasma treatment that we observed could be linked to the activation of a natural destructive mechanism called autophagy, which removes damaged organelles from the cell and reactivates cellular metabolic processes,’ says Elena Petersen, a co-author of the paper and the head of the Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Technologies at MIPT.
The scientists are planning additional research into the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of plasma on cells. They also aim to determine the influence of a patient’s age on the effectiveness of plasma therapy.
###
Media Contact
Asya Shepunova
[email protected]
@phystech
https://mipt.ru/english/