Credit: The Journal of Urology
New York, Jan. 10, 2018 – In a new study published in The Journal of Urology®, researchers determined that men who followed a Mediterranean diet, rich in fish, boiled potatoes, whole fruits, vegetables, legumes, and olive oil, and low consumption of juices had lower risk of aggressive prostate cancer (PC) than those who followed other dietary patterns like Prudent or Western diets.
Although PC is the most common type of cancer in men and can have a high mortality rate, evidence linking PC to specific environmental, occupational, or dietary exposures has been limited. Recent studies have investigated whether certain dietary patterns impact cancer risks, but the results have been inconsistent.
"This study adds important evidence to the scarce information regarding the association of diet with PC, and highlights the relevance of focusing on global dietary patterns," explained lead investigator Beatriz Perez-Gomez, PhD, Cancer and Environmental Epidemiology Unit, National Center for Epidemiology, Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Madrid). "Our results show that a diet oriented towards the prevention of aggressive tumors in the prostate should probably include important elements of the Mediterranean diet such as fish, legumes, and olive oil, and suggest that a high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains might not be enough."
The authors explored the relationship between the risk of having PC and dietary patterns as part of the MCC-Spain study, a Spanish case-control study that involved 733 patients with histologically confirmed PC and 1,229 healthy men with a mean age of 66 years from seven Spanish regions. Anthropometric, epidemiologic, and dietary data were collected.
Adherence to the three dietary patterns of Western, Prudent, and Mediterranean, which characterize the dietary habits of the Spanish population, was evaluated, The Western pattern includes consumption of large amounts of fatty dairy products, refined grains, processed meat, caloric beverages, sweets, fast food, and sauces. The Prudent pattern involves consumption of low-fat dairy products, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and juices. Finally, the Mediterranean pattern consists of high consumption of fish, boiled potatoes, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and olive oil, and low consumption of juices. The diets were graded according to the degree of adherence to each pattern and assigned to four quartiles from lower to higher adherence within each pattern.
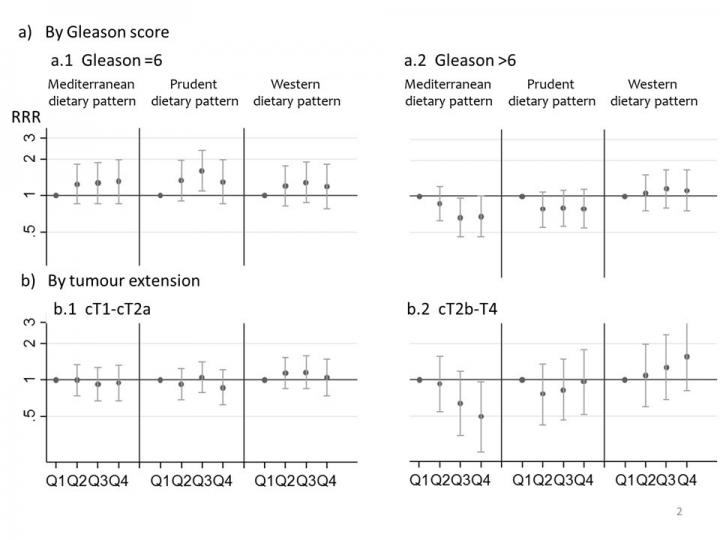
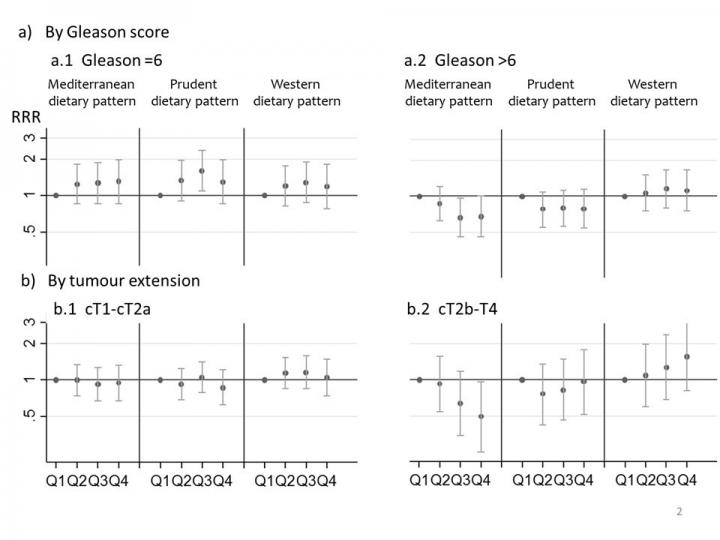
Only a high adherence to Mediterranean dietary pattern appeared to be associated with a lower risk of aggressive PC. Prudent and Mediterranean dietary patterns showed different effects in low and high grade tumors.
PC was assessed using Gleason scores of tumor aggressiveness (6 and stages cT2b to cT4), only high adherence to the Mediterranean diet showed a statistically significant protective effect. All other dietary patterns and tumor characteristics showed little or no correlation and did not achieve statistical significance.
Emphasizing the findings that the degree of adherence to a particular diet can affect the risk for PC, co-author Adela Castelló. PhD, Cancer and Environmental Epidemiology Unit, National Center for Epidemiology, Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Madrid), commented, "There is a striking contrast between the relevance of prostate cancer in terms of public health and the evidence regarding its primary prevention. If other researchers confirm these results, the promotion of the Mediterranean dietary pattern might be an efficient way of reducing the risk of developing advanced PC, in addition to lowering the risk of other prevalent health problems in men such as cardiovascular disease. Dietary recommendations should take into account whole patterns instead of focusing on individual foods."
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
732-238-3628
@elseviernews
http://www.elsevier.com
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.08.087