Credit: Yale University
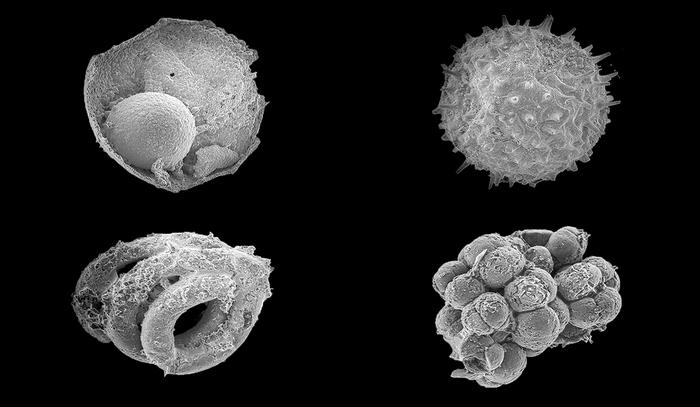
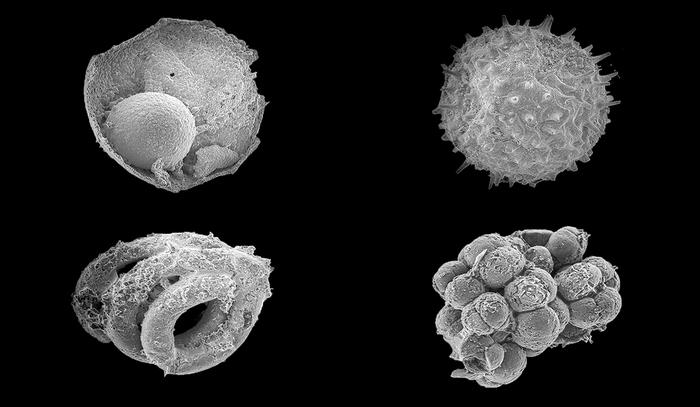
New Haven, Conn. – A Yale-led research team has discovered a cache of embryo-like microfossils in northern Mongolia that may shed light on questions about the long-ago shift from microbes to animals on Earth.
Called the Khesen Formation, the site is one of the most significant for early Earth fossils since the discovery of the Doushantuo Formation in southern China nearly 20 years ago. The Dousantuo Formation is 600 million years old; the Khesen Formation is younger, at about 540 million years old.
"Understanding how and when animals evolved has proved very difficult for paleontologists. The discovery of an exceptionally well-preserved fossil assemblage with animal embryo-like fossils gives us a new window onto a critical transition in life's history," said Yale graduate student Ross Anderson, first author of a study in the journal Geology.
The new cache of fossils represents eight genera and about 17 species, comprising tens to hundreds of individuals. Many of them are spiny microfossils called acritarchs, which are roughly 100 microns in size — about one-third the thickness of a fingernail.
The Khesen Formation is located to the west of Lake Khuvsgul in northern Mongolia. "This site was of particular interest to us because it had the right type of rocks — phosphorites — that had preserved similar organisms in China," Anderson said.
The discovery may help scientists confirm a much earlier date for the existence of Earth ecosystems with animals, rather than just microbes. For two decades, researchers have debated the findings at the Doushantuo Formation, with no resolution. If confirmed as animals, these microfossils would represent the oldest animals to be preserved in the geological record.
The other authors of the study are Derek Briggs, Yale's G. Evelyn Hutchinson Professor of Geology and Geophysics and curator at the Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History; Sean McMahon, a postdoctoral fellow in the Briggs lab; Francis Macdonald of Harvard; and David Jones of Amherst College.
The researchers said the Khesen Formation should provide scientists with additional information for years to come.
"This study is only the tip of the iceberg, as most of the fossils derive from only two samples," Anderson said. Since the original discovery, the Yale team has worked with Harvard and the Mongolian University of Science and Technology to sample several additional sites within the formation.
###
Media Contact
Jim Shelton
[email protected]
203-432-3881
@yale
http://www.yale.edu