Credit: McGill University and Masahiro Morita, Ph.D.
Anti-cancer drugs called mTOR inhibitors slow the growth of cancer cells but show limited ability to cause cancer cell death. New studies explain why.
Masahiro Morita, Ph.D., assistant professor of molecular medicine in the Joe R. & Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine at UT Health San Antonio, contributed to the research. He is an investigator with the university's Sam & Ann Barshop Institute for Longevity & Aging Studies.
Before joining UT Health, Dr. Morita was a postdoctoral fellow at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec.
The cancer drugs act on a cell regulator called mTOR (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin).
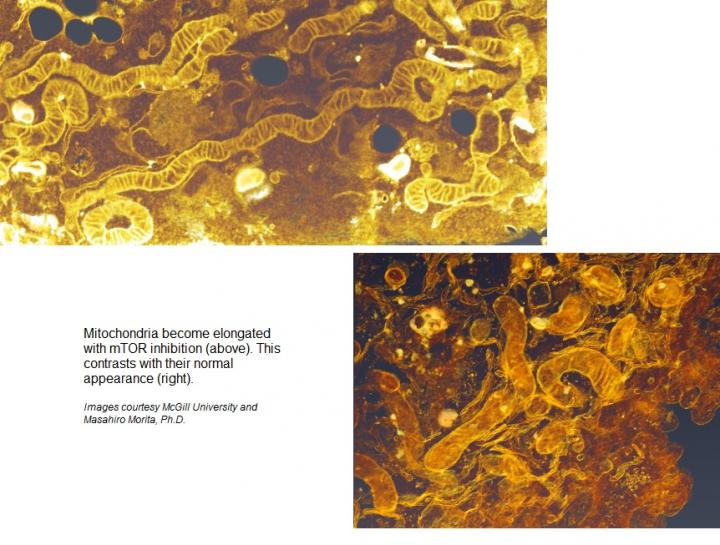
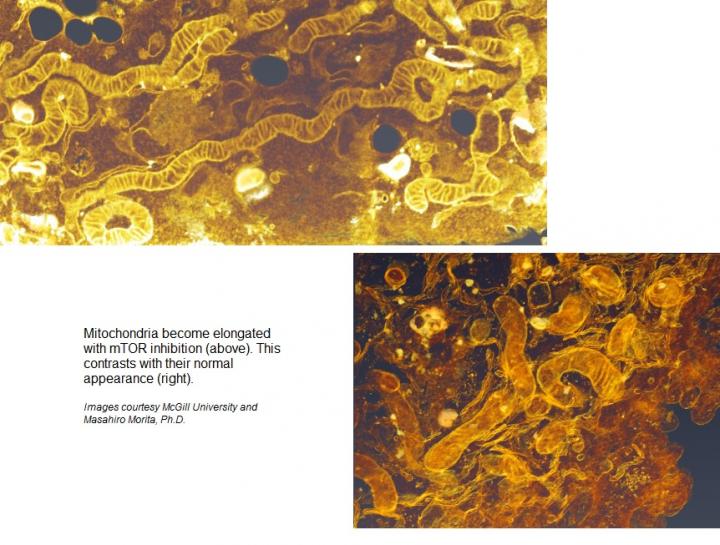
mTOR controls a process that determines how large our cells are and how many cells we have. mTOR also impacts mitochondria, which are the energy centers in our cells.
Mitochondria become elongated when mTOR activity is inhibited, Dr. Morita said. When mTOR is stimulated, these energy centers become fragmented.
"Increased fragmentation of mitochondria is implicated in some cancers," Dr. Morita said.
mTOR controls expression of proteins that alter mitochondrial structure and function in ways that unexpectedly protect cells from death, the team reported.
This is why the cancer cells targeted by mTOR therapy are not dying.
"The next step is to test tandem therapy in cell studies, because it makes sense to combine an mTOR inhibitor with an agent that does kill cancer cells," Dr. Morita said.
The findings are in Molecular Cell.
###
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, with missions of teaching, research and healing, is one of the country's leading health sciences universities and is now called UT Health San Antonio™. UT Health's schools of medicine, nursing, dentistry, health professions and graduate biomedical sciences have produced more than 33,000 alumni who are advancing their fields throughout the world. With seven campuses in San Antonio and Laredo, UT Health San Antonio has a FY 2018 revenue operating budget of $838.4 million and is the primary driver of its community's $37 billion biomedical and health care industry. For more information on the many ways "We make lives better®," visit http://www.uthscsa.edu.
Media Contact
Will Sansom
[email protected]
210-567-2579
@UTHealthSA
http://www.uthscsa.edu/hscnews