Credit: Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), Quantum Wave Microscopy Unit
Professor Tsumoru Shintake at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) yearns for a clean future, one that is affordable and powered by sustainable energy. Originally from the high-energy accelerator field, in 2012 he decided to seek new energy resources — wind and solar were being explored in depth, but he moved toward the sea instead.
That year, Professor Shintake and the Quantum Wave Microscopy Unit at OIST began a project titled "Sea Horse," aiming to harness energy from the Kuroshio ocean current that flows from the eastern coast of Taiwan and around the southern parts of Japan. This project uses submerged turbines anchored to the sea floor through mooring cables that convert the kinetic energy of sustained natural currents in the Kuroshio into usable electricity, which is then delivered by cables to the land. The initial phase of the project was successful, and the Unit is now searching for industry partners to continue into the next phase. But the OIST researchers also desired an ocean energy source that was cheaper and easier to maintain.
This is where the vigor of the ocean's waves at the shoreline comes into play. "Particularly in Japan, if you go around the beach you'll find many tetrapods," Professor Shintake explains. Tetrapods are concrete structures shaped somewhat like pyramids that are often placed along a coastline to weaken the force of incoming waves and protect the shore from erosion. Similarly, wave breakers are walls built in front of beaches for the same purpose. "Surprisingly, 30% of the seashore in mainland Japan is covered with tetrapods and wave breakers." Replacing these with "intelligent" tetrapods and wave breakers, Shintake explains, with turbines attached to or near them, would both generate energy as well as help to protect the coasts.
"Using just 1% of the seashore of mainland Japan can [generate] about 10 gigawats [of energy], which is equivalent to 10 nuclear power plants," Professor Shintake explains. "That's huge."
In order to tackle this idea, the OIST researchers launched The Wave Energy Converter (WEC) project in 2013. It involves placing turbines at key locations near the shoreline, such as nearby tetrapods or among coral reefs, to generate energy. Each location allows the turbines to be exposed to ideal wave conditions that allow them not only to generate clean and renewable energy, but also to help protect the coasts from erosion while being affordable for those with limited funding and infrastructure.
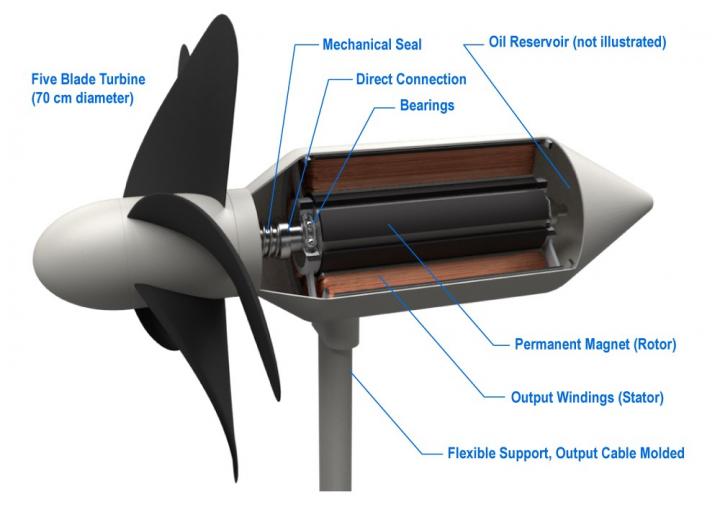
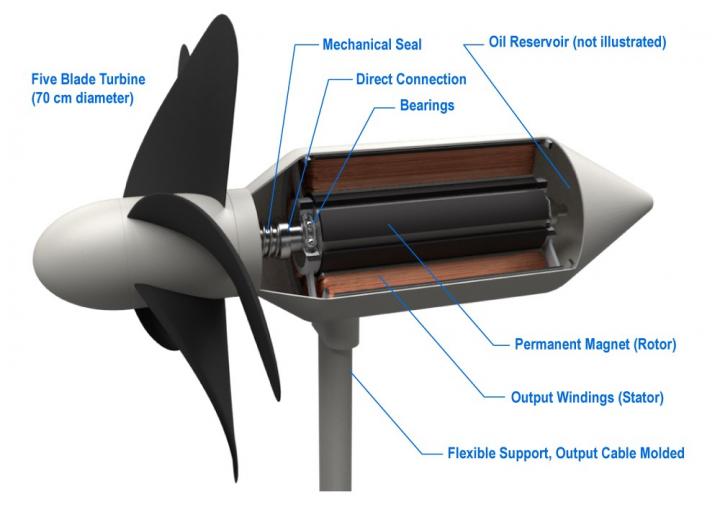
The turbines themselves are built to withstand the forces thrust upon them during harsh wave conditions as well as extreme weather, such as a typhoon. The blade design and materials are inspired by dolphin fins–they are flexible, and thus able to release stress rather than remain rigid and risk breakage. The supporting structure is also flexible, "like a flower," Professor Shintake explains. "The stem of a flower bends back against the wind," and so, too, do the turbines bend along their anchoring axes. They are also built to be safe for surrounding marine life–the blades rotate at a carefully calculated speed that allows creatures caught among them to escape.
Now, Professor Shintake and the Unit researchers have completed the first steps of this project and are preparing to install the turbines–half-scale models, with 0.35-meter diameter turbines–for their first commercial experiment. The project includes installing two WEC turbines that will power LEDs for a demonstration.
"I'm imagining the planet two hundred years later," Professor Shintake says. "I hope these [turbines] will be working hard quietly, and nicely, on each beach on which they have been installed."
###
Media Contact
Kaoru Natori
[email protected]
81-989-662-389
@oistedu
http://www.oist.jp/
Original Source
https://www.oist.jp/news-center/news/2017/9/20/sustainable-future-powered-sea