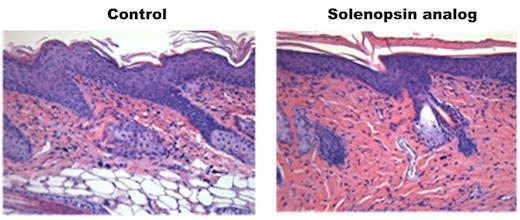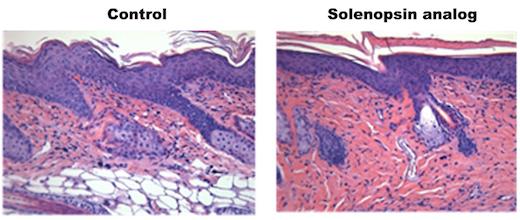
Credit: From Arbiser et al Scientific Reports (2017).
Compounds derived from fire ant venom can reduce skin thickening and inflammation in a mouse model of psoriasis, Emory and Case Western scientists have shown.
The results are scheduled for publication in Scientific Reports.
The findings could lead to new treatments for psoriasis, a common autoimmune skin disease. Topical steroids are now most frequently used for mild to moderate psoriasis, but they have side effects such as skin thinning and easy bruising.
Solenopsins are the main toxic components of fire ant venom. They chemically resemble ceramides, which are lipid-like molecules essential for maintaining for the barrier function of the skin. Ceramides can be found in many skin care products.
Ceramides can act as a double-edged sword, says lead author Jack Arbiser, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at Emory University School of Medicine. Under certain conditions they can be converted by cells into S1P (sphingosine-1-phosphate), an inflammatory molecule.
Arbiser and his colleagues devised two solenopsin analogs that look like ceramides, but can't be degraded into S1P. They then tested them in a mouse model of psoriasis, applying the compounds in a one percent skin cream for 28 days.
The mice treated with solenopsin analogs displayed decreases in skin thickness compared with controls (about 30 percent). The treated mice also had fewer (around 50 percent less) immune cells infiltrating the skin. When applied to immune cells in culture, the compounds decreased the cells' production of the inflammatory signal IL-22 and increased production of anti-inflammatory IL-12.
"We believe that solenopsin analogs are contributing to full restoration of the barrier function in the skin," Arbiser says. "Emollients can soothe the skin in psoriasis, but they are not sufficient for restoration of the barrier."
The scientists also looked at how patterns of gene activity were changed in the skins of the mice after treatment. Solenopsin analog application turned down genes that are turned up by current treatments such as steroids and ultraviolet light.
"This may be compensatory and a mechanism of resistance to anti-psoriasis therapy, and it suggests that the solenopsin compounds could be used in combination with existing approaches," Arbiser says.
His lab has previously shown that solenopsin is an inhibitor of blood vessel growth and has potential as an anticancer agent. Systemic toxicity for the solenopsin derivatives has not been tested, but Arbiser says systemic toxicity would not necessarily preclude use in skin diseases, citing the example of external application of botulinum toxin.
The project was a collaboration with the laboratory of Nicole Ward, PhD at Case Western Reserve, where mouse experiments were performed. Emory and Mercer University have applied for patents for solenopsin derivatives.
###
Research at Emory was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (AR47901) and the Atlanta Clinical & Translational Science Institute (UL1TR000454).
Media Contact
Quinn Eastman
[email protected]
404-727-7829
@emoryhealthsci
http://whsc.emory.edu/home/news/index.html
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10580-y