Credit: J. Adam Fenster and Prof. A. N. Vamivakas, University of Rochester
Research underway at RIT advances a new kind of sensing technology that captures data with better precision than currently possible and promises cheaper, smaller and lighter sensor designs.
Mishkat Bhattacharya, a theoretical physicist at RIT, is investigating new precision quantum sensing solutions for the U.S. Department of the Navy's Office of Naval Research. The three-year study is supported by $550,000 grant and is a continuation of a previous award. Bhattacharya will test interactions between light and matter at the nanoscale and analyze measurements of weak electromagnetic fields and gravitational forces.
Specialized microscopes measure theoretical predictions that describe matter at the nanoscale in which a nanometer equals one-billionth of a meter and a human hair measures between 80,000-100,000 nanometers, according to the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative.
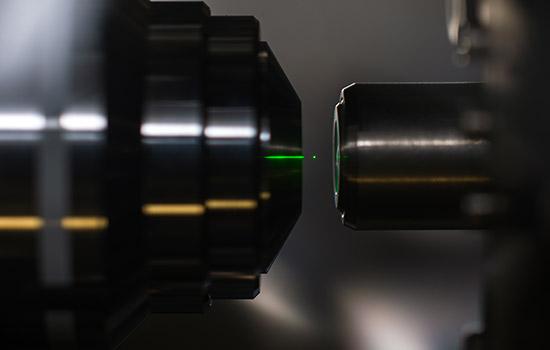
Bhattacharya works in the emerging field of levitated optomechanics, an area of physics that investigates nanoparticles by trapping them in a laser beam. Laser trapping–a method known as "optical tweezers"–tests the limits of quantum effects in isolation and eliminates physical disturbances from the surrounding environment
Using the techniques of laser trapping, Bhattacharya takes quantum mechanics to the next level by probing quantum effects in the nanoparticles, which contain billions of atoms. He investigates where quantum mechanics (which governs the microscopic) butts up against classical physics (which explains the macroscopic) and explores light-matter interaction in macroscopic quantum physics.
"Levitated optomechanical systems provide a clean platform for studying quantum optics, information science, and precision measurement and sensing," said Bhattacharya, an associate professor in RIT's School of Physics and Astronomy and a member of the Future Photon Initiative.
To explore different nanosystems for the Office of Naval Research, Bhattacharya isolates a nanodiamond in a pocket of light. Suspension in laser light turns the particle into a floating probe. Bhattacharya is interested in the signatures carried in the light and the information it reveals about the electromagnetic fields and the gravitational forces surrounding the nanoparticle.
He collaborates with postdoctoral associate Pardeep Kumar and RIT undergraduate physics major Wyatt Wetzel. This summer, a visiting undergraduate from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Peter Mizes, joined his Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics Theory Group. Bhattacharya tests his theoretical predictions in a lab run by his collaborator Nick Vamivakas, an experimental physicist at the University of Rochester's Institute of Optics.
His first study for the Office of Naval Research determined the smallest force that could be detected with a diamond crystal that levitated without spinning. The new project investigates the outcomes of three nanosystems, each using nanoparticles optically trapped under different conditions:
- A particle containing an impurity which acts as a spin sensitive to magnetic fields or as an excess charge sensitive to electric fields;
- A particle moving like a pendulum in three dimensions;
- A particle larger than the wavelength of light entrapping it.
Quantum mechanics is a door to a world on the nanoscale and is governed by a different set of physical laws.
"Unique rules apply in quantum physics," Bhattacharya said. "It is not the day-to-day physical universe familiar to our experience."
Optomechanics explores interactions between light and tiny particles of matter within the nano-realm. Sensing technology advanced at these submicroscopic scale promises finer measurements of physical properties that describe the world, such as electric and magnetic fields, temperature, force, velocity, acceleration, gravitation.
According to Bhattacharya, quantum sensors might someday detect gravitational waves, find dark matter, perfect quantum computing and create precise accelerometers–the technology that rights display screens held at any angle.
###
Media Contact
Susan Gawlowicz
[email protected]
585-475-5061
@ritnews
http://www.rit.edu
Original Source
http://www.rit.edu/news/story.php?id=62861





