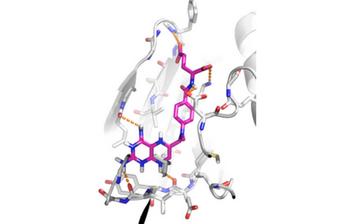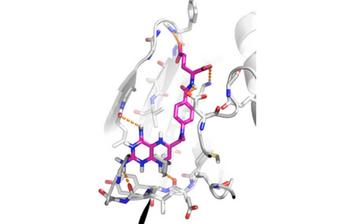
Credit: University of Sheffield
- University of Sheffield scientists discover drug used for arthritis could be used to treat blood cancer
- Polycythemia Vera, a type of blood cancer, affects 3,000 people a year
- Breakthrough offers an affordable and effective treatment
Blood cancer sufferers could be treated with a simple arthritis drug, scientists at the University of Sheffield have discovered.
Every year 3,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with Polycythemia Vera (PV), a type of blood cancer which causes an overproduction of red blood cells. Patients suffer with itching, headaches, weight loss, fatigue and night sweats.
Current treatments do not slow the disease progression and provide little relief from symptoms.
Dr Martin Zeidler, from the University of Sheffield's Department of Biomedical Science, working with colleagues from the Department of Haematology at the Royal Hallamshire Hospital, and funded by the Medical Research Council (MRC) have discovered that methotrexate (MTX) – a drug on the World Health Organisation list of essential medicines and commonly used to treat arthritis – works by directly inhibiting the molecular pathway responsible for causing disease.
Initial tests were carried out on fruit fly cells to screen for small molecules that modulate JAK/STAT signalling – a signalling pathway whose misregulation is central to the development in humans of Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), the collective term for progressive blood cancers like PV.
Further testing in human cells showed that methotrexate acts as a potent suppressor of JAK/STAT pathway activation – even in cells carrying the mutated gene responsible for MPNs in patients.
Dr Martin Zeidler said the latest tests on mice were entirely consistent with the cell-based studies.
The tests showed low-dose MTX suppresses JAK/STAT pathway activity and is able to normalise both the raised blood counts and the increase in spleen size associated with the disease in these mice.
"We have now shown pretty conclusively that we can use this approach to treat mouse models of human MPNs, results which provide a much more tangible prospect of success in humans," he said.
"Repurposing MTX has the potential to provide a new, molecularly targeted treatment for MPN patients within a budget accessible to healthcare systems throughout the world – a development that may ultimately provide substantial clinical and health economic benefits."
MTX has been used for 35 years to treat inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and psoriasis. Even though the mechanisms by which MTX acts in these diseases had not previously been understood, the safety and effectiveness of MTX is well documented and many millions of patients regularly take the drug. Strikingly, diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis all feature inflammatory processes driven by JAK/STAT activity and the effectiveness of MTX in these inflammatory diseases may well be a consequence of its ability to dampen the JAK/STAT pathway.
The team now hope to go on to a full clinical trial early next year.
The research paper Low-dose methotrexate in myeloproliferative neoplasm models was published in Haematologica, the journal of the European Hematology Association and the Ferrata Storti Foundation.
###
Media Contact
Kirsty Bowen
[email protected]
44-114-222-1034
@sheffielduni
http://www.shef.ac.uk
Original Source
https://www.sheffield.ac.uk/news/nr/blood-cancer-athritis-1.720503