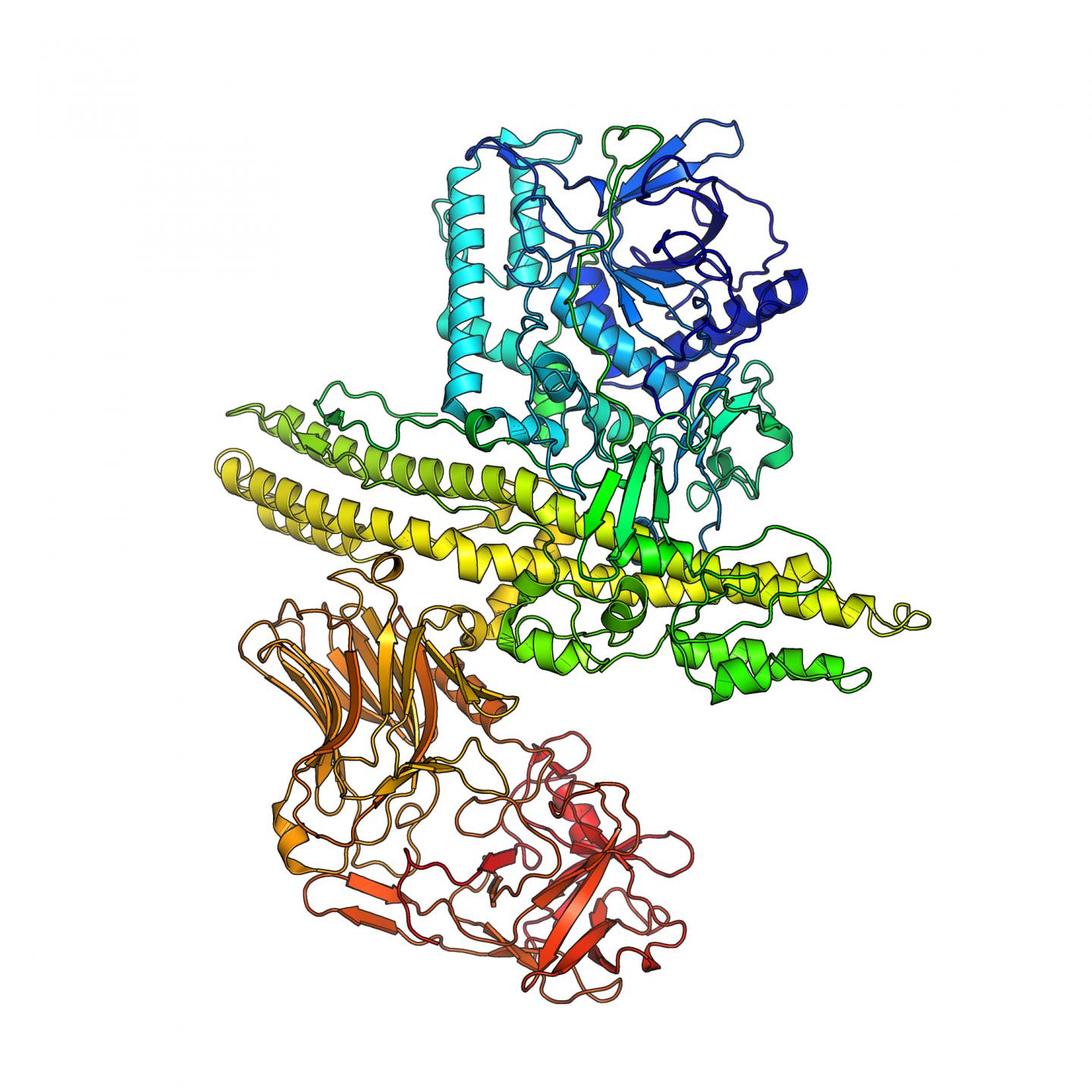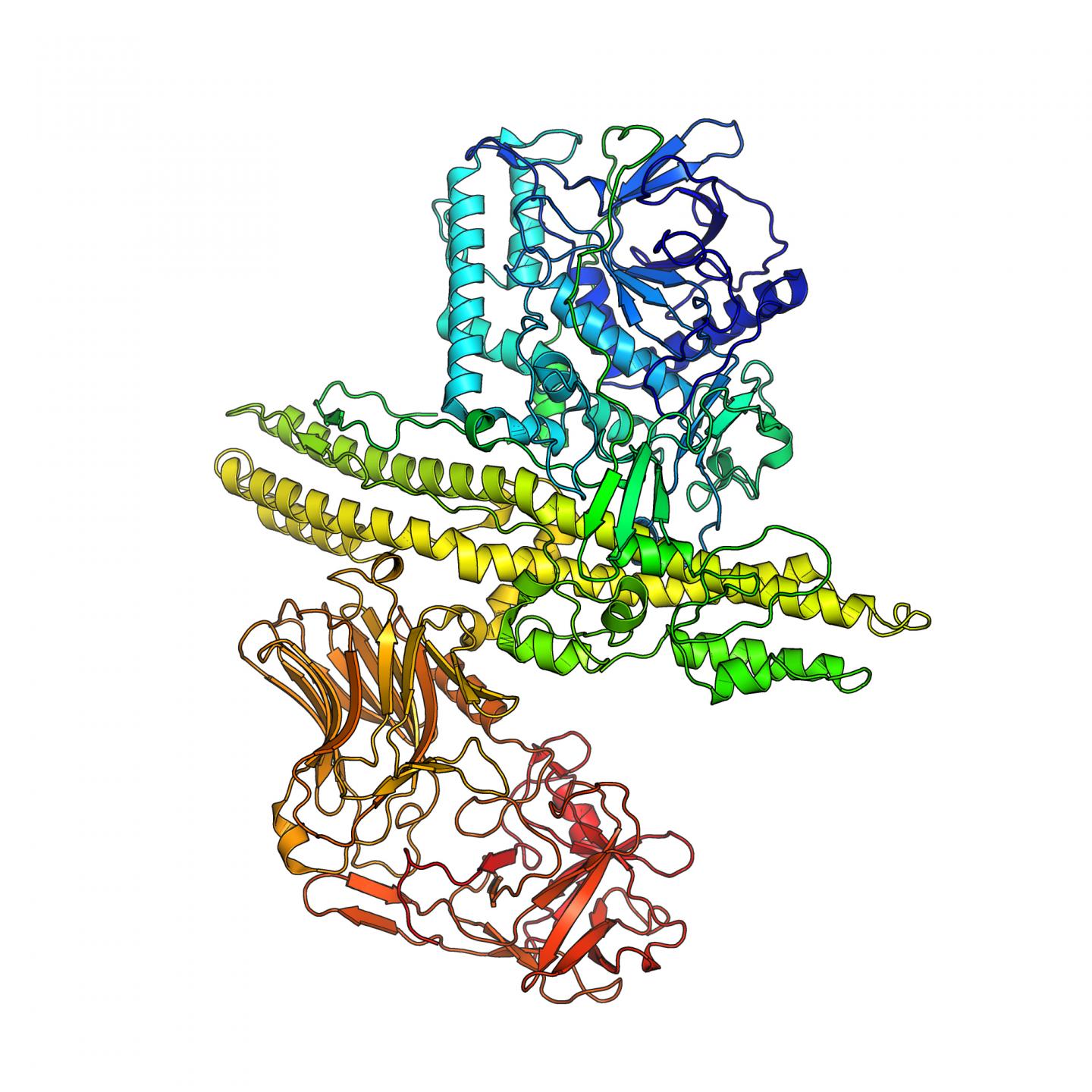
Credit: Pål Stenmark
Botulinum toxins are currently used on more than 80 medical conditions including Muscle spasms, Overactive bladder, Chronic migraine, Cervical dystonia, Sweating and Cerebral Palsy (CP). The new toxin, Botulinum neurotoxin type X (BoNT/X), has the potential to open up a new field of toxin therapeutics related to intracellular membrane trafficking and secretion.
Since Botulinum neurotoxins are the most toxic substances known, the development of detection methods and treatments is very important.
"The discovery of BoNT/X facilitates the development of diagnostics and countermeasures which is important if someone would be exposed to a toxic amount of the substance", says Pal Stenmark, Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Stockholm University.
The research team will now develop antibodies with the ability to detect and inactivate the toxin.
"Within a few months we will have developed ways of detecting if a person has been subject to BoNT/X", says Pal Stenmark.
The researchers will determine the structure of the toxin and investigate how it binds to the nerve cell. They will also investigate how the unique properties of BoNT/X can be best used to develop new therapeutics.
Discovered through an infant in Japan
It all started with an infant in Japan that became ill in 1995. In 2015 the genome of the bacteria isolated from the child was sequenced and deposited in a database. Hidden in the four million letter blueprint of the bacterium, the research team identified the novel toxin.
"When we first discovered this toxin I believed we had made some error in the analysis, but after checking several times it turned out to be correct. This discovery opens a multitude of new exciting research topics that we are eager to explore in collaboration with Dr. Min Dong's research team at Harvard", says Pal Stenmark.
###
Link to the article "Identification and characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin" in Nature Communications: http://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms14130
For further information, please contact Pal Stenmark, Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Stockholm University, e-mail: [email protected], cellphone: +46 739-84 12 16.
Media Contact
Annika Hallman
[email protected]
http://www.su.se/english
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/NCOMMS14130