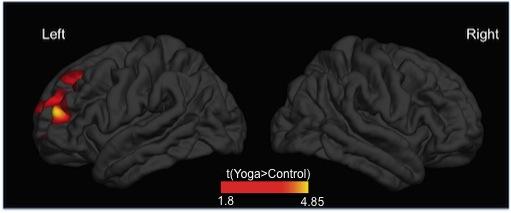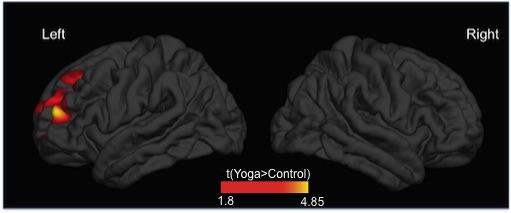
Credit: Afonso RF, Balardin JB, Lazar S, Sato JR, Igarashi N, Santaella DF, Lacerda SS, Amaro E Jr. and Kozasa EH (2017) Greater Cortical Thickness in Elderly Female Yoga Practitioners–A Cross-Sectional…
Scientists in Brazil have imaged elderly female yoga practitioners' brains and found they have greater cortical thickness in the left prefrontal cortex, in brain areas associated with cognitive functions like attention and memory. The results suggest that yoga could be a way to protect against cognitive decline in old age.
As we age, the structure and functionality of our brains change and this often leads to cognitive decline, including impaired attention or memory. One such change in the brain involves the cerebral cortex becoming thinner, which scientists have shown is correlated with cognitive decline. So, how can we slow or reverse these changes?
You might think medication would be required, but surprisingly, the answer could lie in contemplative practices like yoga. Yoga practitioners consciously maintain postures, and perform breathing exercises and meditation.
"In the same way as muscles, the brain develops through training," explains Elisa Kozasa of Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein in São Paulo, Brazil, a researcher involved in the study, which was recently published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. "Like any contemplative practice, yoga has a cognitive component in which attention and concentration are important."
Previous studies have suggested that yoga can have greater health benefits than similar aerobic exercises, and yoga practitioners have shown improved awareness, attention and memory. Older adults with mild cognitive impairment have also shown improvements after a short yoga training program.
But can practicing yoga over several years significantly shape your brain and if so, could it offset some of the changes that happen in the aging brain? The research team wanted to see if elderly long-term yoga practitioners had any differences in terms of brain structure compared with healthy elderly people who had never practiced yoga.
They recruited 21 female yoga practitioners (also known as yoginis) who had practiced yoga at least twice a week for a minimum of 8 years, although the group had an average of nearly 15 years of yoga practice. The researchers compared the yoginis with another group of 21 healthy women, who had never practiced yoga, meditation or any other contemplative practices, but who were well-matched to the yoginis in terms of their age (all the participants were 60 or over) and levels of physical activity. For more consistent results, the researchers only recruited women, and the participants completed surveys to see if there were any other factors at work that could affect brain structure, such as depression or level of formal education.
The researchers scanned the participants' brains using magnetic resonance imaging to see if there were any differences in brain structure. "We found greater thickness in the left prefrontal cortex in the yoginis, in brain regions associated with cognitive functions such as attention and memory," says Rui Afonso, another researcher involved in the study. As the groups were well-matched in terms of other factors that can change brain structure, such as education and levels of depression, yoga practice appears to underlie the yoginis' different brain structure.
The results suggest that practicing yoga in the long-term can change the structure of your brain and could protect against cognitive decline in old age. However, the team plan to carry out more studies to see if these brain changes result in enhanced cognitive performance in elderly yoginis.
Another possibility is that people with these brain features are more likely to be attracted to yoga. "We have compared experienced yoginis with non-practitioners, so we do not know if the yoginis already had these differences before they started yoga," explains Afonso. "This can only be confirmed by studying people for a few years from the time they start yoga."
###
Media Contact
Melissa Cochrane
[email protected]
0041-787-246-393
@frontiersin
http://www.frontiersin.org
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00201