Credit: Alisa Weigandt for Duke Health
DURHAM, N.C. — Long before the Zika virus became a global fear, cytomegalovirus, or CMV, was commonly infecting developing fetuses and causing many of the same brain and developmental impairments.
The virus, one of only a handful known to be transmitted through the mother's placenta to a fetus, infects nearly 1 million infants a year worldwide and is a leading cause of microcephaly, hearing and/or vision loss, and nervous system damage.
With effective interventions lacking, development of a vaccine remains an urgent public health mission. Now researchers from Duke University School of Medicine and Tulane National Primate Research Center report findings in monkeys that demonstrates a vaccine approach that appears to be capable of protecting the animal's fetus from infection.
"The presence of potent antibodies at the time of the mother's primary infection seems to prevent viral transmission and severe disease in the developing fetus, and therefore should be a primary target of vaccines to prevent neonatal infection," said co-senior author Sallie Permar, M.D., Ph.D., professor of pediatrics at Duke and member of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute. Permar and colleagues, including co-senior author Amitinder Kaur, M.D., of Tulane National Primate Research Center, published their findings in the July 6 issue of the journal JCI Insight.
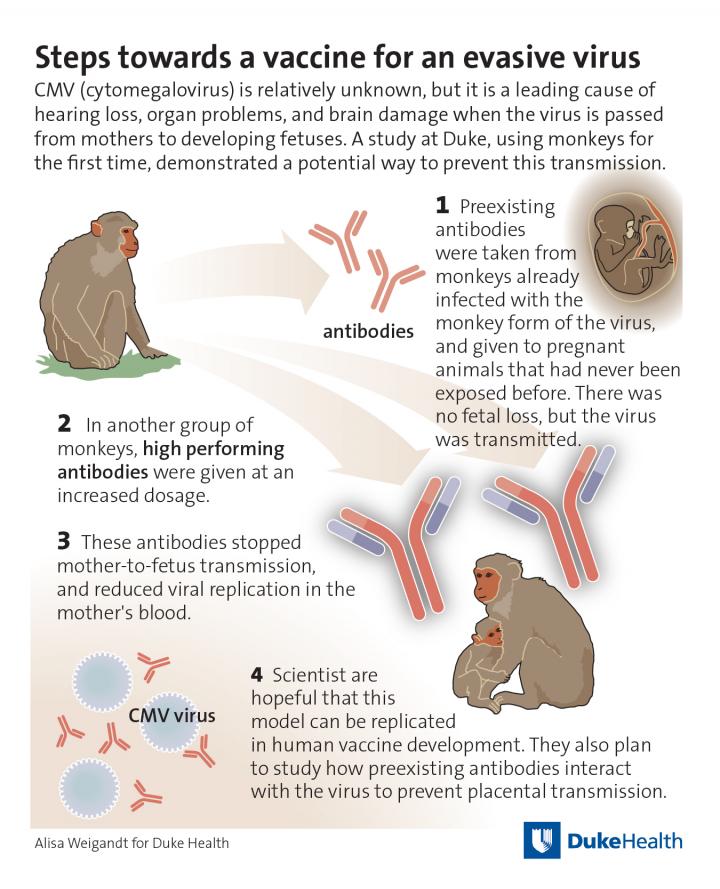
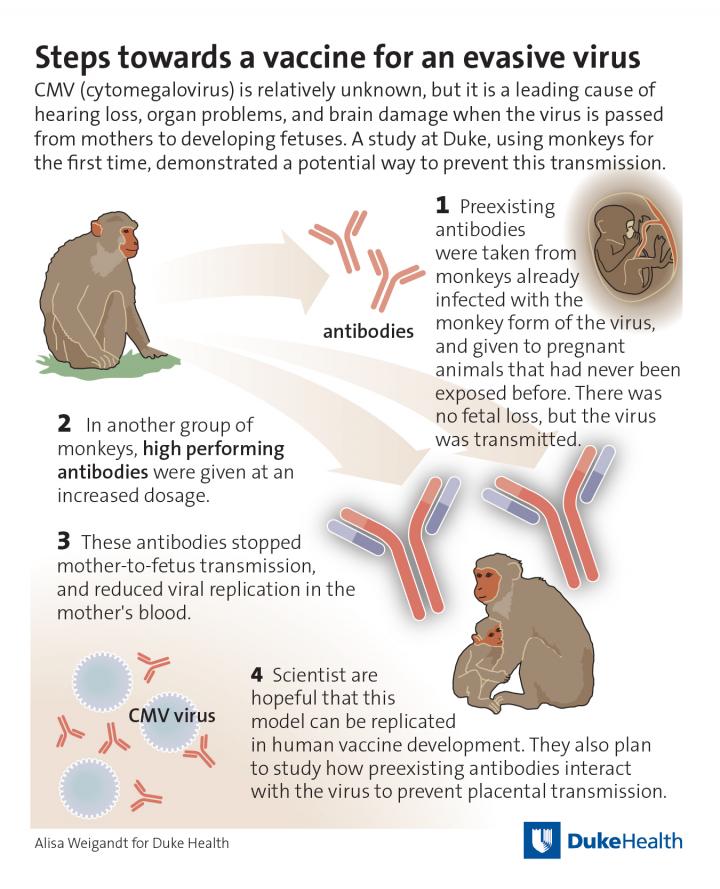
Using rhesus monkeys — a recent advancement in modeling congenital CMV transmission in humans — the researchers tested whether the offspring of mothers exposed for the first time to the rhesus form of CMV (RhCMV) could be protected from infection if the mothers first received RhCMV-specific antibodies.
The question is important, because the answer clarifies the type of immune response a successful vaccine approach should target.
"Ending congenital CMV infection is likely going to require an effective vaccine given before pregnancy, similar to how the rubella vaccine has eradicated congenital rubella syndrome in the Americas," said first author Cody Nelson, a Duke Medical School M.D./Ph.D. student. "It's important to know whether a successful CMV vaccine can rely on antibody responses alone, or whether we need to introduce other immune responses, such as T cells."
In experiments with pregnant monkeys, the RhCMV-specific antibodies protected the mothers from losing the developing fetuses, which is what can happen when the mothers are infected with RhCMV for the first time during pregnancy.
A higher dose of the antibodies completely blocked transmission of the virus in each of the three monkeys that received it, and also reduced the virus's ability to reproduce and mutate.
"Most vaccines on the market today work through an antibody mechanism, so our study demonstrates that a vaccine for CMV can likely go down that traditional path," Permar said.
###
In addition to Permar, Kaur and Nelson, study authors include Diana Vera Cruz, Dollnovan Tran, Kristy M. Bialas, Lisa Stamper, Huali Wu, Margaret Gilbert, Robert Blair, Xavier Alvarez, Hannah Itell, Meng Chen, Ashlesha Deshpande, Flavia Chiuppesi, Felix Wussow, Don J. Diamond, Nathan Vandergrift, Mark R. Walter, Peter A. Barry, Michael Cohen-Wolkowiez and Katia Koelle.
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health Nonhuman Primate Reagent Resource (R24 676 OD010976) The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (HHSN 272201300031C); NIH (DP2HD075699, OD011104, R01AI103960, R01AI63356, F30HD089577).
Media Contact
Sarah Avery
[email protected]
919-660-1306
@DukeHealth
http://www.dukehealthnews.org
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag