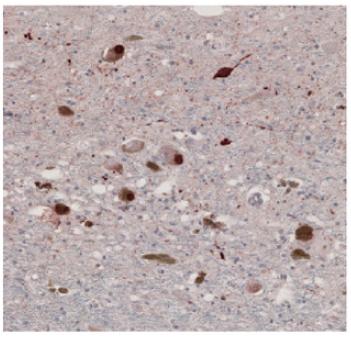
Credit: From Zhang et al NSMB (2017).
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are not the same. They affect different regions of the brain and have distinct genetic and environmental risk factors.
But at the biochemical level, these two neurodegenerative diseases start to look similar. That's how Emory scientists led by Keqiang Ye, PhD, landed on a potential drug target for Parkinson's.
In both Alzheimer's (AD) and Parkinson's (PD), a sticky protein forms toxic clumps in brain cells. In AD, the troublemaker inside cells is called tau, making up neurofibrillary tangles. In PD, the sticky protein is alpha-synuclein, forming Lewy bodies.
Ye and his colleagues had previously identified an enzyme (asparagine endopeptidase or AEP) that trims tau in a way that makes it more sticky and toxic. Drugs that inhibit AEP have beneficial effects in Alzheimer's animal models.
In a new Nature Structural and Molecular Biology paper, Emory researchers show that AEP acts in the same way toward alpha-synuclein.
"In Parkinson's, alpha-synuclein behaves much like Tau in Alzheimer's," Ye says. "We reasoned that if AEP cuts Tau, it's very likely that it will cut alpha-synuclein too."
A particular chunk of alpha-synuclein produced by AEP's scissors can be found in samples of brain tissue from patients with PD, but not in control samples, Ye's team found.
In control brain samples AEP was confined to lysosomes, parts of the cell with a garbage disposal function. But in PD samples, AEP was leaking out of the lysosomes to the rest of the cell.
The researchers also observed that the chunk of alpha-synuclein generated by AEP is more likely to aggregate into clumps than the full length protein, and is more toxic when introduced into cells or mouse brains. In addition, alpha-synuclein mutated so that AEP can't cut it is less toxic.
Ye cautions that AEP is not the only enzyme that cuts alpha-synuclein into various toxic pieces, and the full-length alpha-synuclein protein is still able to aggregate and cause harm. Nevertheless, he says his team is moving on to testing drugs that inhibit AEP in Parkinson's animal models.
###
First author Zhentao Zhang, MD, PhD, a former postdoc with Ye, is now at Wuhan University in China.
At Emory, the laboratories of P. Michael Iuvone, PhD in the Department of Ophthalmology and Nick Seyfried, PhD in the Department of Biochemistry contributed to the paper. Lingjing Jin, MD at Shanghai Tongji Hospital and Jian-Zhi Wang, MD, Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education of China for Neurological Disorders also contributed to the paper.
The research was supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Eye Institute (P30EY006360 and R01EY004864).
Media Contact
Holly Korschun
[email protected]
404-727-3990
@emoryhealthsci
http://whsc.emory.edu/home/news/index.html
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3433
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag





