Credit: Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST)
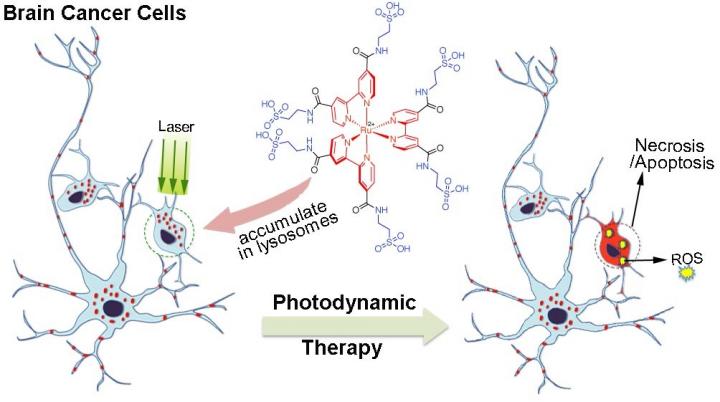
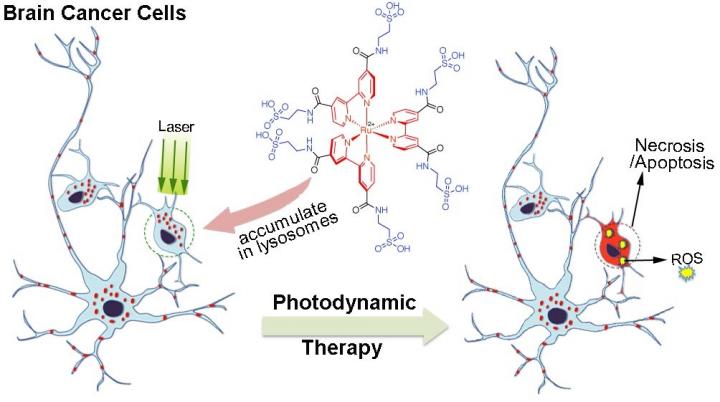
Photodynamic therapy is often used to treat brain tumors because of its specificity — it can target very small regions containing cancerous cells while sparing the normal cells around it from damage. It works by injecting a drug called a photosensitizer into the bloodstream, where it gathers in cells, and then exposing the drug-filled cells to light. When the photosensitizer is exposed to this light, it emits what is known as a reactive oxygen species (ROS) that causes the cells to die. The method is precise because photosensitizers preferentially gather in cancerous cells over normal cells. As such, when they are exposed to the light, the normal cells will be spared from damage.
This method is far from perfect, however. Although the chemical components used to build the photosensitizer, such as polypyridyl Ru-complexes, are stable, biocompatible, and highly efficient in emitting ROS — and more ROS means more effective tumor cell death — the additional components added to it to boost emissions lead to poor solubility in water. Thus the compound is difficult to wield for effective drug delivery since the molecules tend to clump together rather than dissolve uniformly and thus move cleanly through blood, which is over 90% water. As such, there is room to improve the photodynamic therapy method, and researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have posited a new way of constructing a photosensitizer by adding the natural amino acid taurine into the Ru-complex's chemical makeup. The study is published in the journal Chemical Communications.
Taurine is one of most abundant amino acids in the central nervous system, and is known to assist in essential functions such as transmitting signals through the brain. Inspired by taurine's important relationship with the brain as well as the fact that it is biocompatible and naturally soluble in water, the OIST research team, including first author on the paper Dr. Enming Du, used it to modify Ru-complexes. Their research was carried out in specialized cell flasks with either citrate buffer, which is a solution that mimics the inside of cells where the photosensitizer accumulates, or phosphate-buffered saline, a different solution that mimics a cell's natural pH.
"Taurine-modification is pretty simple," OIST Professor Ye Zhang from the Bioinspired Soft Matter Unit, explains. By simple chemistry, it can be added to the Ru-complexes to create a new type of photosensitizer.
After observing the effects of this new photosensitizer on cancer cells, the OIST researchers found that the taurine-modified Ru-complexes were able to enter cells effectively and that they generated a large amount of ROS when exposed to light, all without compromising inherent advantages. In addition, they found that the modified complexes were particularly effective in destroying brain cancer cells, as opposed to other types of cancer cells.
For years, researchers have been exploring different chemical components to create an effective photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy, yet no one method has yielded optimal results. The taurine-modified photosensitizer created by the OIST research team is a promising new avenue of exploration — with further modification, it could reveal that elusive optimality that would allow for better brain cancer treatment with photodynamic therapy.
###
Media Contact
Kaoru Natori
[email protected]
81-989-662-389
@oistedu
http://www.oist.jp/
Original Source
https://www.oist.jp/news-center/news/2017/6/23/unique-amino-acid-brain-cancer-therapy http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C7CC03337K
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag