Credit: Dr. Daniel Yang
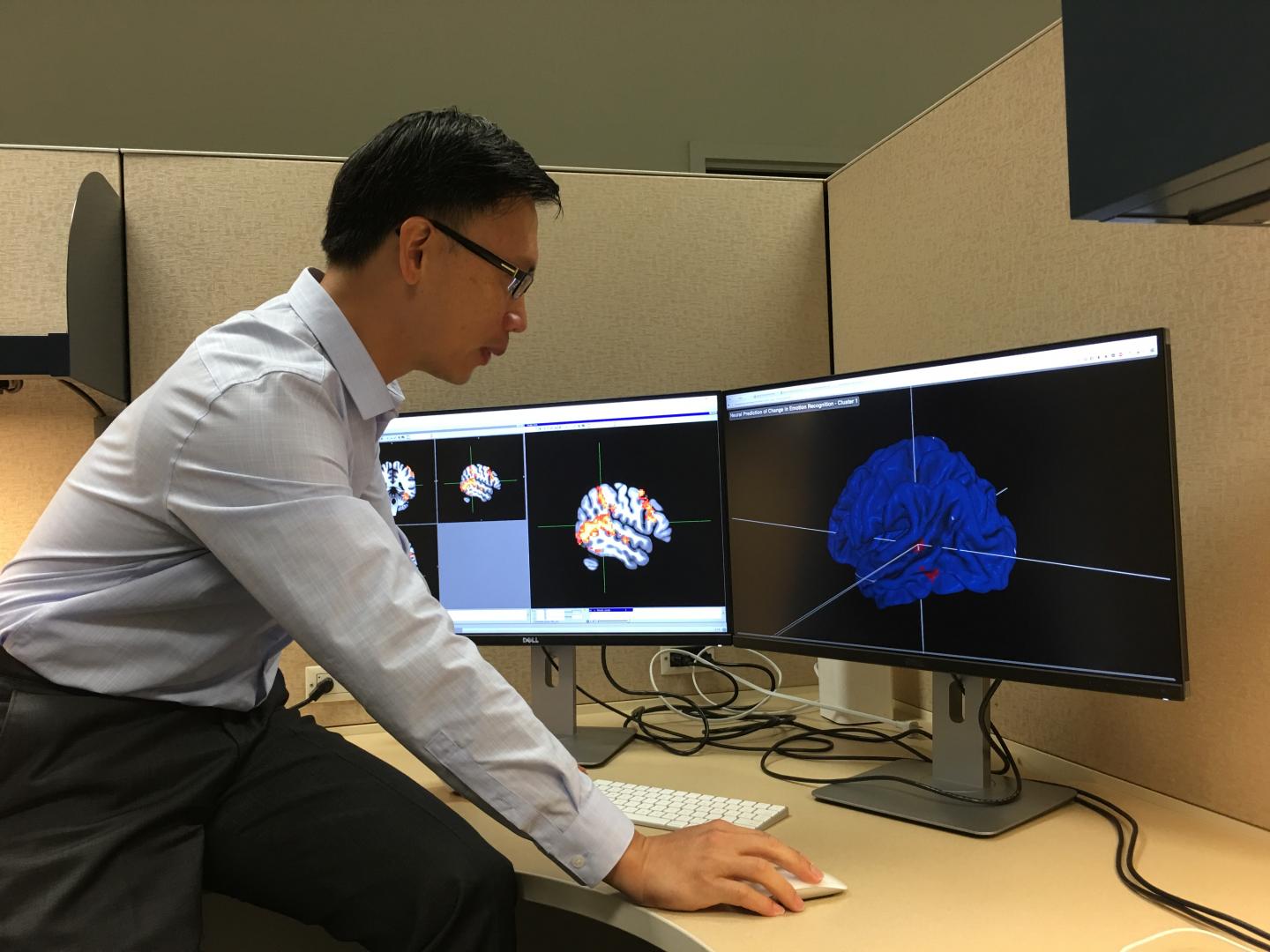
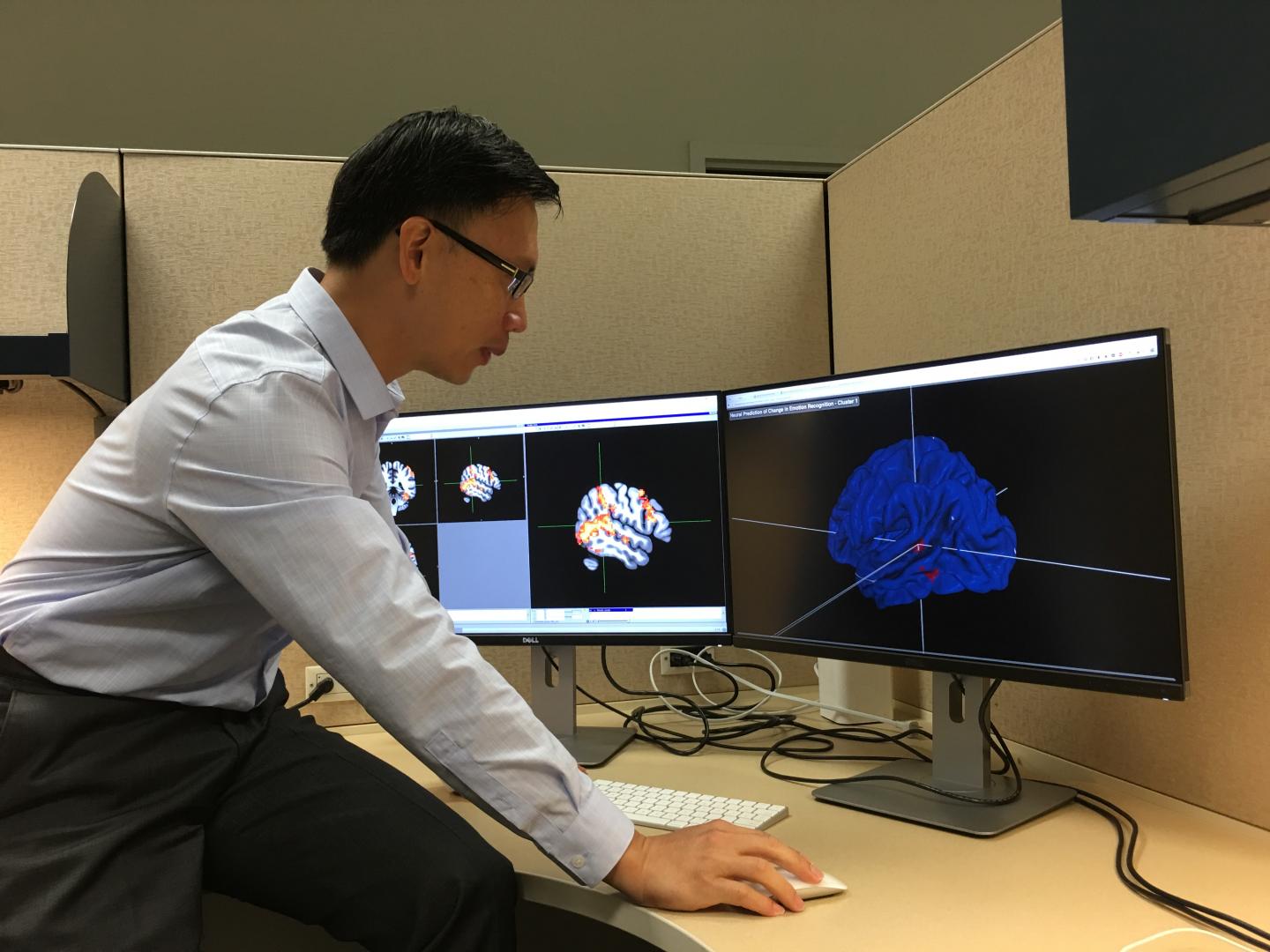
DALLAS, TEXAS, – A collaboration between the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas and the George Washington University created a protocol to predict individual treatment effectiveness for adults on the autism spectrum. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), the researchers identified certain brain regions that significantly correlate with an increase in social abilities following a virtual environment based training program. Adults on the autism spectrum who showed greater activity in the social brain network prior to the training improved more in emotion recognition than those who showed less activity.
"We found that when participants showed more brain activation in certain regions within the social brain network, while viewing digitally represented biological motion – motion that symbolizes something a human might do, such as playing pat-a-cake – the intervention was more beneficial to the participants," explained Dr. Daniel Yang, assistant research professor at the George Washington University and Children's National Health System. "Whereas if these social brain network regions did not show much activation, we observed that the person may not benefit from the intervention at this particular time but, as the brain is constantly changing, could benefit in the future, for example, by increasing pretreatment activation in these regions."
The U.S. Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee (IACC) named Dr. Yang's finding utilizing this predictive method with pediatric populations in a separate study one of the top 20 advances in autism research of 2016.
"This study advances us one step closer toward the goal of targeted, personalized treatment for individuals with autism," said Dr. Yang. "We are very happy that this predictive method may be potentially able to help children, as well as adults on the spectrum, know which training might be worth their time and money based on their current brain function."
For the study, seventeen participants between the ages of 18 and 40 years diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder were recruited from the Center for BrainHealth and the Yale Child Study Center at Yale University where Dr. Yang worked at the study's inception. Participants completed a five-week training program that met twice a week for one hour. The clinician-led, strategy-based intervention allowed participants to role play social interactions in a virtual environment.
"The training focuses on three core social strategies: recognizing others, responding to others and self-assertion," explained Tandra Allen, head of virtual training programs at the Center for BrainHealth, who provided the trainings. "We use avatars to make the complex social situations such as dealing with confrontation, job interviews, or a blind date feel more approachable to practice while still drawing on the same emotions that a person would experience in the real world."
Before the 10 hours of training, participants underwent brain imaging. While in the fMRI scanner, the participant passively viewed a series of animations. Some of the images represented a human in motion, such as a person playing pat-a-cake, while other images were scrambled and did not represent something a human would do.
Two clusters of activity stood out as significantly correlating with training success. The first is an area on the left side of the brain responsible for language processing, specifically conflicts in meanings. The other resides on the right side of the brain and is responsible for processing non-verbal social-emotional cues, for example, being able to look at a person's facial expression and ascertain emotional states such as fear, anger or joy.
Treatment effectiveness was measured by behavioral changes in two distinct domains of social abilities: 1) emotional recognition, or the change in socio-emotional processing abilities and 2) theory of mind, or the change in socio-cognitive processing abilities.
"There is very limited intervention research for adults on the autism spectrum, so being able to help make a leap forward in creating individualized treatment programs for them is very important to the field," said Dr. Yang.
###
ABOUT THE CENTER FOR BRAINHEALTH
The Center for BrainHealth, part of The University of Texas at Dallas, is a research institute committed to enhancing, protecting and restoring brain health across the lifespan. Scientific exploration at the Center for BrainHealth is leading edge, improving lives today and translating groundbreaking discoveries into practical clinical application. By delivering science-based innovations that enhance how people think, work and live, the Center and its Brain Performance Institute™ are empowering people of all ages to unlock their brain potential. Major research areas include the use of functional and structural neuroimaging techniques to better understand the neurobiology supporting cognition and emotion in health and disease.
Media Contact
Lyndie Were
[email protected]
972-883-3281
@BrainHealth
http://www.brainhealth.utdallas.edu/
Original Source
http://www.brainhealth.utdallas.edu/blog_page/study-finds-way-to-predict-treatment-effectiveness-for-adults-with-autism http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2017.03.014
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag