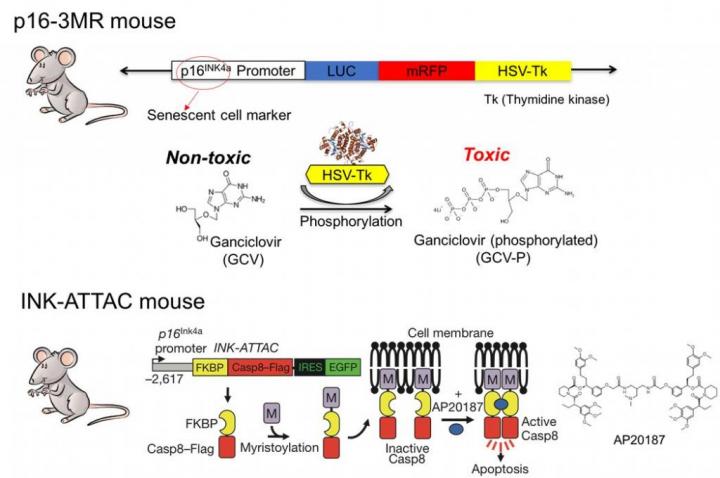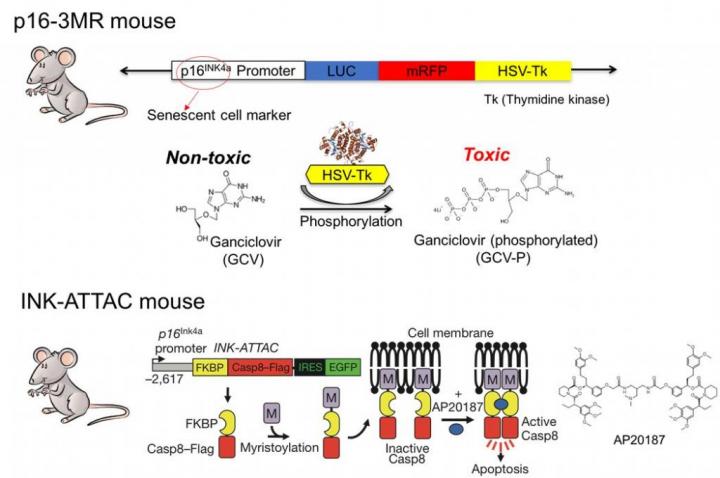
Credit: UNIST
A recent study, led by an international team of researchers confirms that targeted removal of senescent cells (SnCs), accumulated in many vertebrate tissues as we age, contribute significantly in delaying the onset of age-related pathologies.
This breakthrough research has been led by Dr. Chaekyu Kim of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, who is now at UNIST, and Dr. Ok Hee Jeon of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in collaborations with the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, the Buck Institute for Research on Aging, the University Medical Center Groningen, Unity Biotechnology, Inc., and the University of California, Berkeley.
In the study, the research team presented a novel pharmacologic candidate that alleviates age-related degenerative joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis (OA) by selectively destroying SnCs. Their findings, published April 24th in Nature Medicine (Impact Factor: 30.357), suggest that the selective removal of old cells from joints could reduce the development of post-traumatic OA and allow new cartilage to grow and repair joints.
Senescent cells (SnCs) accumulate with age in many vertebrate tissues and are present at sites of age-related pathlogy. Although these cells play an essential role in wound healing and injury repair, they may also promote cancer incidence in tissues. For instance, in articular joints, such as the knee and cartilage tissue, SnCs often are not cleared from the area after injury, thereby contributing to OA development.
To test the idea that SnCs might play a causative role in OA, the research team took both younger and older mice and cut their anterior cruciate ligaments (ACL) to minic injury. They, then, administered injections of an experimental drug, named UBX0101 to selectively remove SnCs after anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) surgery.
Preclinical studies in mice and human cells suggested that the removal of SnCs significantly reduced the development of post-traumatic OA and related pain and created a prochondrogenic environment for new cartilage to grow and repair joints. Indeed, the research team reported that aged mice did not exhibit signs of cartilage regeneration after treatment with UBX0101 injections,
According to the research team, the relevance of their findings to human disease was validated using chondrocytes isolated from arthritic patients. The research team notes that their findings provide new insights into therapies targeting SnCs for the treatment of trauma and age-related degenerative joint disease.
Prior to this study, Johns Hopkins Technology Ventures (JHTV) granted UNITY Biotechnology Inc. the right to use the intellectual property around the senescent cell technology. UNITY is a company aiming to develop therapeutics that address age-related diseases. Last October, the company announced $116 million in Series B funding from some of the big names in venture capital, including Amazon CEO Jeff Bezo's venture fund Bezos Expeditions, Mayo Clinic Ventures, Venrock, and ARCH Venture Partners. UNITY has completed a rigorous screening and preclinical testing process of candidate drugs, discovered in this study, and is launching a new clinical trial to assess its first drug, for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee this year.
###
This study has been also conducted collaboratively by twelve other researchers, including Dr. Jennifer Elisseeff, Director of the Translational Tissue Engineering Center and Morton Goldberg Professor of Ophthalmology at the Johns Hopkins Wilmer Eye Institute, Professor Jan M. Van Deursen's team of the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, and Professor Judith Campisi's team of the Buck Institute for Research on Aging.
Journal Reference
Ok Hee Jeon et al., "Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment," Nature Medicine, (2017).
Media Contact
JooHyeon Heo
[email protected]
82-522-171-223
Original Source
http://news.unist.ac.kr/removal-of-aging-cells-could-extend-human-life/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm.4324
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag