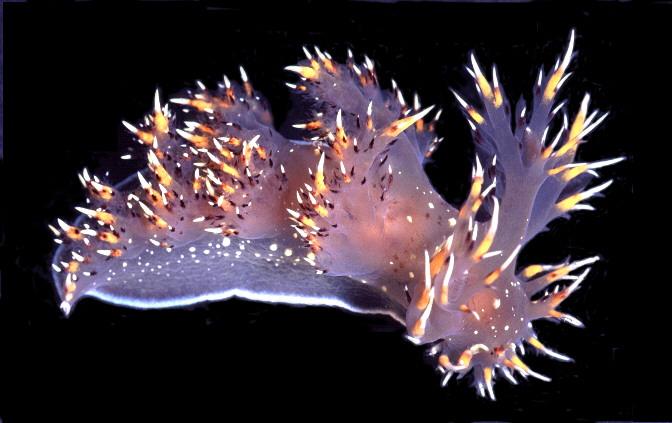
Credit: Courtesy of Ralph and Dale Marie Gonzales
ATLANTA-Scientists at Georgia State University have rewired the neural circuit of one species and given it the connections of another species to test a hypothesis about the evolution of neural circuits and behavior.
Neurons are connected to each other to form networks that underlie behaviors. Drs. Akira Sakurai and Paul Katz of Georgia State's Neuroscience Institute study the brains of sea slugs, more specifically nudibranchs, which have large neurons that form simple circuits and produce simple behaviors. In this study, they examined how the brains of these sea creatures produce swimming behaviors. They found that even though the brains of two species – the giant nudibranch and the hooded nudibranch – had the same neurons, and even though the behaviors were the same, the wiring was different.
The researchers blocked some of the connections in the giant nudibranch using curare, a paralyzing poison used on blow darts by indigenous South Americans. This prevented the brain of the giant nudibranch from producing the pattern of impulses that would normally cause the animal to swim. Then, they inserted electrodes into the neurons to create artificial connections between the brain cells that were based on connections from the hooded nudibranch. The brain was able to produce rhythmic, alternating activity that would underlie the swimming behavior, showing these two species produce their swimming behavior using very different brain mechanisms.
The findings are published in the journal Current Biology.
"Behaviors that are homologous and similar in form would naturally be assumed to be produced by similar neural mechanisms," said Katz, co-author of the study and a Regent's Professor in the Neuroscience Institute at Georgia State. "This and previous studies show that connectivity of the neural circuits of two different species of sea slugs differ substantially from each other despite the presence of homologous neurons and behaviors. Thus, the evolution of microcircuitry could play a role in the evolution of behavior."
The study's results are significant for several reasons. First, they show that over the course of evolution, behaviors might be conserved, but the underlying neural basis for the behaviors could shift.
In addition, other work by these researchers and Katz's lab has underscored the conclusion that neurons are conserved, but differ in function across species. This has implications for extrapolating results across species in general and means caution must be taken in assuming that neural mechanisms are conserved even though brain regions and behaviors are present.
Sakurai is first author of the study and a research scientist in the Neuroscience Institute at Georgia State.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation.
The researchers also recently published results from similar work in the Journal of Neurophysiology. They reported that neural connectivity between the same neurons in two different species of sea slugs varies independently of behavior and the evolutionary history of an organism.
###
Media Contact
Natasha De Veauuse Brown
[email protected]
404-413-3602
@GSU_News
http://www.gsu.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag