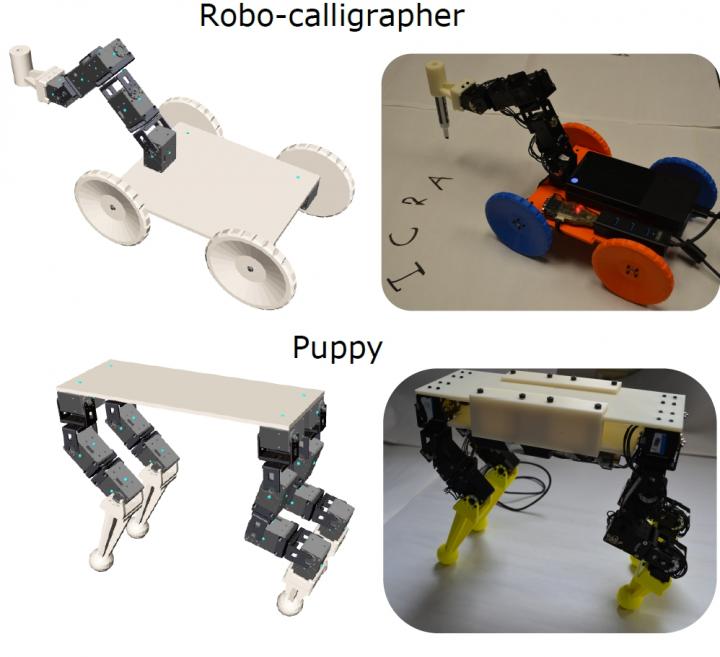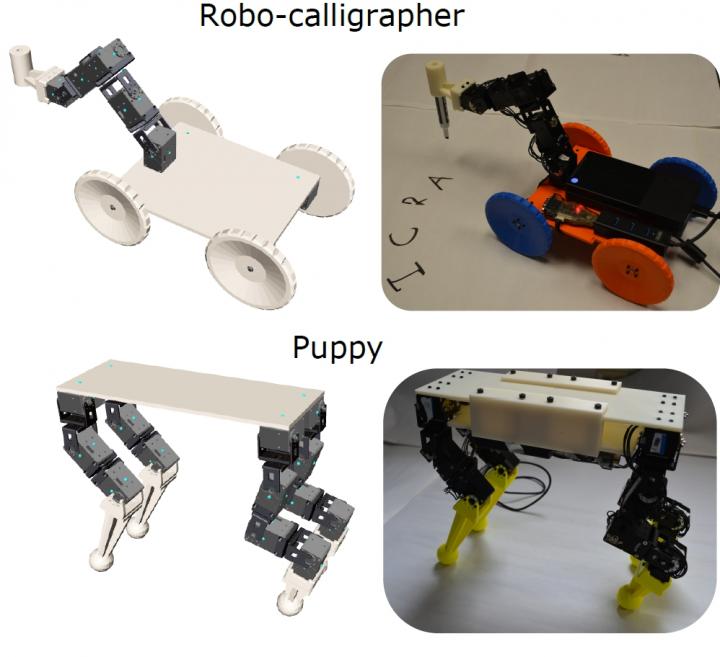
Credit: Carnegie Mellon University
PITTSBURGH – A new interactive design tool developed by Carnegie Mellon University's Robotics Institute enables both novices and experts to build customized legged or wheeled robots using 3D-printed components and off-the-shelf actuators.
Using a familiar drag-and-drop interface, individuals can choose from a library of components and place them into the design. The tool suggests components that are compatible with each other, offers potential placements of actuators and can automatically generate structural components to connect those actuators.
Once the design is complete, the tool provides a physical simulation environment to test the robot before fabricating it, enabling users to iteratively adjust the design to achieve a desired look or motion.
"The process of creating new robotic systems today is notoriously challenging, time-consuming and resource-intensive," said Stelian Coros, assistant professor of robotics. "In the not-so-distant future, however, robots will be part of the fabric of daily life and more people — not just roboticists — will want to customize robots. This type of interactive design tool would make this possible for just about anybody."
Today, robotics Ph.D. student Ruta Desai will present a report on the design tool she developed with Coros and master's student Ye Yuan at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2017) in Singapore.
Coros' team designed a number of robots with the tool and verified its feasibility by fabricating two — a wheeled robot with a manipulator arm that can hold a pen for drawing, and a four-legged "puppy" robot that can walk forward or sideways.
"The system makes it easy to experiment with different body proportions and motor configurations, and see how these decisions affect the robot's ability to do certain tasks," said Desai. "For instance, we discovered in simulation that some of our preliminary designs for the puppy enabled it to only walk forward, not sideways. We corrected that for the final design. The motions of the robot we actually built matched the desired motion we demonstrated in simulation very well."
The research team developed models of how actuators, off-the-shelf brackets and 3D-printable structural components can be combined to form complex robotic systems. The iterative design process enables users to experiment by changing the number and location of actuators and to adjust the physical dimensions of the robot. The tool includes an auto-completion feature that allows it to automatically generate assemblies of components by searching through possible arrangements.
"Our work aims to make robotics more accessible to casual users," Coros said. "This is important because people who play an active role in creating robotic devices for their own use are more likely to have positive feelings and higher quality interactions with them. This could accelerate the adoption of robots in everyday life."
###
The National Science Foundation supported this research.
About Carnegie Mellon University: Carnegie Mellon is a private, internationally ranked research university with programs in areas ranging from science, technology and business, to public policy, the humanities and the arts. More than 13,000 students in the university's seven schools and colleges benefit from a small student-to-faculty ratio and an education characterized by its focus on creating and implementing solutions for real problems, interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation.
Media Contact
Byron Spice
[email protected]
412-268-9068
@CMUScience
http://www.cmu.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag