A groundbreaking artificial intelligence-driven technique has been unveiled by researchers that promises to revolutionize how fatty deposits within coronary arteries are detected using optical coherence tomography (OCT). This advancement is particularly significant as lipid-rich plaques in the coronary arteries are intimately linked with the occurrence of heart attacks and other severe cardiac events. By enabling earlier and more precise identification of these dangerous plaques, this novel method could transform preventative cardiology and patient management strategies.
Optical coherence tomography has long been a powerful imaging tool during catheter-based cardiac interventions such as angioplasty and stent placement. Despite its unparalleled capability to render high-resolution images revealing the detailed structure of blood vessels, conventional OCT imaging lacks the biochemical specificity required to discern the composition of vessel walls. This limitation impedes cardiologists’ ability to fully assess the vulnerability of plaques to rupture, a critical factor in predicting heart attack risk.
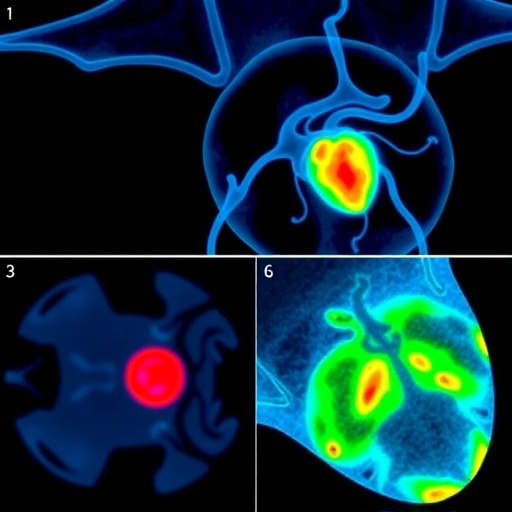
The research team, led by Hyeong Soo Nam from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has devised a new approach that harnesses wavelength-dependent characteristics embedded in OCT signals. By integrating these spectral insights with advanced artificial intelligence, their system can non-invasively detect and map the distribution of lipid deposits inside coronary arteries. This ability to identify lipid content provides a previously inaccessible level of detail crucial for evaluating patient risk.
Published in Biomedical Optics Express, the study details a sophisticated methodology for extracting subtle spectral information from standard OCT images. Unlike traditional modifications requiring specialized hardware, this AI-driven solution works seamlessly with the OCT systems already deployed in clinical settings. It reflects a major innovation in computational imaging, leveraging deep learning for automated, quantitative tissue characterization without additional equipment costs or procedural changes.
This AI-powered advancement is poised to enhance clinical decision-making during coronary interventions. By offering real-time, objective data on lipid presence, the tool can aid physicians in assessing risks more accurately, tailoring procedural strategies, and monitoring treatment responses. The ultimate benefit lies in enabling individualized patient care plans that reduce the likelihood of adverse cardiac events and improve long-term health outcomes.
A core technical achievement of the research is the sophisticated extraction and analysis of spectral data from OCT signals, which IIllustrates tissue-specific light-tissue interactions. Lipids, fibrous tissue, and calcifications each exhibit distinct optical absorption and scattering properties across different wavelengths of light. The AI model effectively learns to detect these unique patterns, enabling an automated and robust identification of lipid-rich plaque areas throughout the vessel wall.
This approach uniquely combines weakly supervised deep learning with spectroscopic OCT. Importantly, it reduces the annotation burden that often hampers AI model training. Instead of requiring detailed pixel-level annotations of lipid regions—an arduous and subjective manual task—the system learns from simpler frame-level labels indicating the presence or absence of lipids. This strategy enhances practicality and scalability, facilitating real-world clinical adoption.
To validate their model’s accuracy and clinical relevance, the team applied the method to intravascular imaging data from a rabbit model of atherosclerosis. They rigorously compared the AI-derived lipid detection outcomes against conventional histopathology using lipid-specific staining techniques. The results demonstrated high accuracy in classifying lipid presence and strong spatial correspondence between AI-highlighted regions and histologically confirmed lipid deposits.
The research heralds a new era in the application of AI to intravascular imaging. Beyond OCT, the framework offers potential for extension to other optical or vascular imaging modalities where subtle spectral variations remain underutilized. This adaptability suggests a broad future impact, encouraging the development of AI-integrated diagnostic tools for a variety of cardiovascular diseases and other pathologies.
Looking forward, the team is focused on optimizing the system for speed and robustness, key factors for implementation in the fast-paced clinical environment. Further validation with human coronary artery data will be crucial to confirm translatability and determine best practices for integration into existing clinical workflows. Ensuring that the technology complements physician workflows without disruption will be critical to its adoption and success.
This innovative AI method represents a substantial leap forward in cardiovascular diagnostics, pairing the sophisticated physics of spectroscopic OCT with state-of-the-art computational techniques. The ability to non-invasively, accurately, and rapidly detect lipid-rich plaques offers a powerful new tool in combating the global burden of heart disease. With further development, it has the potential to save countless lives through earlier intervention and personalized treatment.
The study not only exemplifies the promise of AI-enhanced medical imaging but also underscores the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration—in this case, merging expertise in optical physics, clinical imaging, pathology, and machine learning. Such convergences are driving the future of precision medicine, enabling physicians to unlock new dimensions of insight from existing diagnostic technologies.
For clinicians and researchers alike, this work marks a pivotal step towards safer, more effective management of coronary artery disease. As healthcare increasingly embraces AI-driven innovations, tools like this herald a transformative shift towards predictive, preventive, and personalized care—factors essential to addressing one of the leading causes of global mortality.
Subject of Research: Artificial intelligence-based detection of lipid-rich plaques within coronary arteries using spectroscopic optical coherence tomography.
Article Title: Automated lipid detection in spectroscopic optical coherence tomography using a weakly supervised deep learning network.
News Publication Date: Information not provided.
Web References:
– Biomedical Optics Express journal: https://www.osapublishing.org/boe/home.cfm
– DOI link: https://opg.optica.org/boe/abstract.cfm?doi=10.1364/BOE.585222
– KAIST: https://www.kaist.ac.kr/en/
References:
J. H. Hwang, W. Lee, J. H. Kim, R. H. Kim, D.O. Kang, J. W. Kim, H. Yoo, H. S. Nam, “Automated lipid detection in spectroscopic optical coherence tomography using a weakly supervised deep learning network,” Biomed. Opt. Express, 17, 1279-1292 (2026). DOI: 10.1364/BOE.585222
Image Credits: Hyeong Soo Nam, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Keywords
Artificial intelligence, Cardiac arrest, Optical coherence tomography, Medical imaging
Tags: advanced cardiac imaging techniquesAI and OCT integrationAI-based lipid-rich plaque detectionAI-driven cardiovascular diagnosticscatheter-based cardiac intervention enhancementscoronary artery plaque imagingearly detection of heart attack risklipid deposit mapping in arteriesnon-invasive coronary artery assessmentoptical coherence tomography in cardiologypreventing coronary artery diseasespectral analysis in OCT imaging