In a groundbreaking development in the battle against breast cancer, researchers have unveiled a novel therapeutic strategy that could redefine treatment paradigms, especially in drug-resistant forms of the disease. The study, led by Luo, Wang, Bui, and colleagues, focuses on a potent CDK2 inhibitor, BLU-222, which demonstrates remarkable synergy when combined with existing CDK4/6 inhibitors. Their work, recently published in Nature Communications, sheds light on the underlying molecular mechanisms, specifically the induction of the cell cycle regulators p21 and p27, providing a beacon of hope for patients facing resistance to conventional therapies.
Breast cancer remains a formidable challenge in oncology, with many subtypes exhibiting complexity that thwarts standard treatments. Over the past decade, CDK4/6 inhibitors have emerged as a cornerstone in managing hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, significantly improving patient outcomes. However, resistance to these inhibitors frequently develops, diminishing their effectiveness and leaving clinicians with limited alternatives. This pressing issue has motivated scientists to explore additional molecular targets within the cell cycle machinery to overcome resistance and extend patient survival.
Central to cell proliferation are cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), enzymes that regulate progression through different phases of the cell cycle by phosphorylating key substrates. CDK4 and CDK6, when activated, facilitate the transition from the G1 to S phase, promoting DNA replication and cell division. Inhibition of these kinases arrests the cycle, suppressing tumor growth. Yet, cancer cells often bypass CDK4/6 inhibition by upregulating CDK2 activity, another pivotal kinase in the G1 to S phase transition. This compensatory mechanism contributes heavily to resistance, making CDK2 an attractive candidate for targeted inhibition.
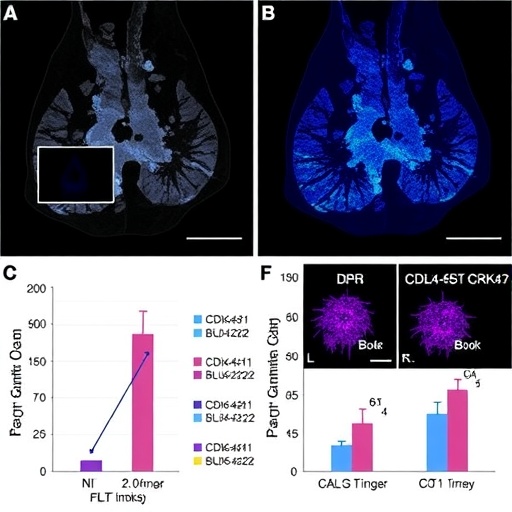
The research team’s investigation into BLU-222, a next-generation CDK2 inhibitor, involved comprehensive in vitro and in vivo analyses. Employing breast cancer models resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors, they discovered that BLU-222 effectively suppressed CDK2 activity, significantly reducing tumor cell proliferation. Intriguingly, when combined with existing CDK4/6 inhibitors, BLU-222 exerted a synergistic effect, enhancing anti-cancer efficacy beyond what each could achieve alone. This synergism underscores a promising therapeutic avenue for patients whose tumors have adapted to evade monotherapy.
Delving deep into the molecular biology of this response, the study elucidated the role of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 (CDKN1A) and p27 (CDKN1B). These proteins act as natural brakes on CDK activity, enforcing checkpoints that halt cell cycle progression in response to DNA damage or oncogenic stress. BLU-222 treatment was shown to induce upregulation of both p21 and p27, amplifying their inhibitory effects on CDKs and consequently reinforcing cell cycle arrest. This induction mechanism appeared critical for the heightened therapeutic impact observed with the BLU-222 and CDK4/6 inhibitor combination.
Mechanistically, the interplay between p21, p27, and CDKs can be viewed as a tightly controlled network, where the balance between kinase activity and inhibitor levels dictates cellular fate. By boosting p21 and p27, BLU-222 not only suppresses CDK2 but also indirectly influences CDK4/6 function, effectively dampening the cell cycle advance at multiple nodes. Such a multipronged blockade could explain the overcoming of resistance phenotypes that typically arise through adaptive rewiring of cancer signaling pathways.
Furthermore, the study utilized sophisticated genomic and proteomic profiling techniques to characterize changes within tumor cells following treatment. These analyses revealed shifts in expression patterns consistent with cell cycle exit and senescence, as well as enhanced apoptosis markers, suggesting that the combination therapy promotes not only growth arrest but also programmed cell death. This dual effect increases the likelihood of durable responses, an essential feature for tackling aggressive and recurrent breast cancer cases.
Animal models bearing patient-derived xenografts of resistant breast tumors validated the translational potential of this therapeutic strategy. Mice receiving the BLU-222 and CDK4/6 inhibitor combo exhibited significant tumor regression compared to controls or single-agent treatments. Importantly, the toxicity profile remained manageable, indicating that the regimen could be feasible for clinical application without undue adverse effects, a critical consideration in cancer therapy development.
The implications of these findings extend beyond breast cancer, as aberrant CDK activity is a hallmark of numerous malignancies. By establishing a framework for dual CDK targeting augmented by endogenous inhibitor induction, this work opens avenues for broad-spectrum oncology approaches. It also invites further exploration into combinations with other targeted therapies or immunomodulatory agents, potentially enhancing efficacy through complementary mechanisms.
From a clinical standpoint, these insights advocate the re-evaluation of treatment algorithms for breast cancer patients exhibiting resistance to standard CDK4/6 inhibitors. Incorporating BLU-222 or related CDK2 inhibitors into therapeutic regimens might offer a new lifeline, especially for those with limited options. Future clinical trials inspired by this research will be critical to confirm safety, dosing parameters, and real-world efficacy, paving the path for regulatory approvals and routine clinical use.
Moreover, the study underscores the importance of precision medicine, emphasizing that understanding specific molecular adaptations within tumors is key to counteracting resistance. By tailoring interventions that target multiple components of the cell cycle machinery, oncologists can devise more robust treatments that anticipate and thwart cancer’s attempts to survive and proliferate.
The discovery also prompts a reconsideration of the tumor microenvironment’s role in moderating response to CDK inhibitors. While the current work focused primarily on tumor-intrinsic mechanisms, the influence of stromal cells, immune populations, and extracellular matrix components on drug sensitivity remains an exciting frontier. Integrating these dimensions may further refine therapeutic strategies and enhance patient outcomes.
In sum, Luo, Wang, Bui, and their colleagues’ investigation represents a significant leap forward in breast cancer therapeutics. By illustrating the synergy of BLU-222 with existing CDK4/6 inhibitors and unraveling the critical role of p21 and p27 induction in overcoming drug resistance, they offer a blueprint for next-generation treatments that could dramatically improve survival and quality of life for many patients battling this formidable disease.
As the oncology community eagerly anticipates subsequent clinical validation, this study will undoubtedly inspire renewed efforts in drug development targeting the cell cycle, heralding a new era in the fight against resistant breast cancer. The integration of innovative small molecules like BLU-222 into combination schemes exemplifies the power of rational drug design grounded in molecular biology, promising to transform outcomes for patients worldwide.
This research also serves as a testament to the relentless pursuit of scientific innovation needed to outpace cancer’s adaptive capacity. It reminds us that by decoding the intricate dance of cellular regulators such as CDKs, p21, and p27, we inch closer to unraveling cancer’s vulnerabilities and crafting therapies that are both potent and precise.
Subject of Research: CDK2 inhibition combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer through the induction of cell cycle inhibitors p21 and p27.
Article Title: CDK2 inhibitor BLU-222 synergizes with CDK4/6 inhibitors in drug resistant breast cancers through p21/p27 induction.
Article References:
Luo, L., Wang, Y., Bui, T. et al. CDK2 inhibitor BLU-222 synergizes with CDK4/6 inhibitors in drug resistant breast cancers through p21/p27 induction. Nat Commun 17, 619 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67865-4
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67865-4