Credit: UTSA
Ruyan Guo, Robert E. Clark Endowed Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA), has received a $50,000 I-Corps grant from the National Science Foundation to commercialize a chip that can make lower power electronics, like cell phones, work more efficiently.
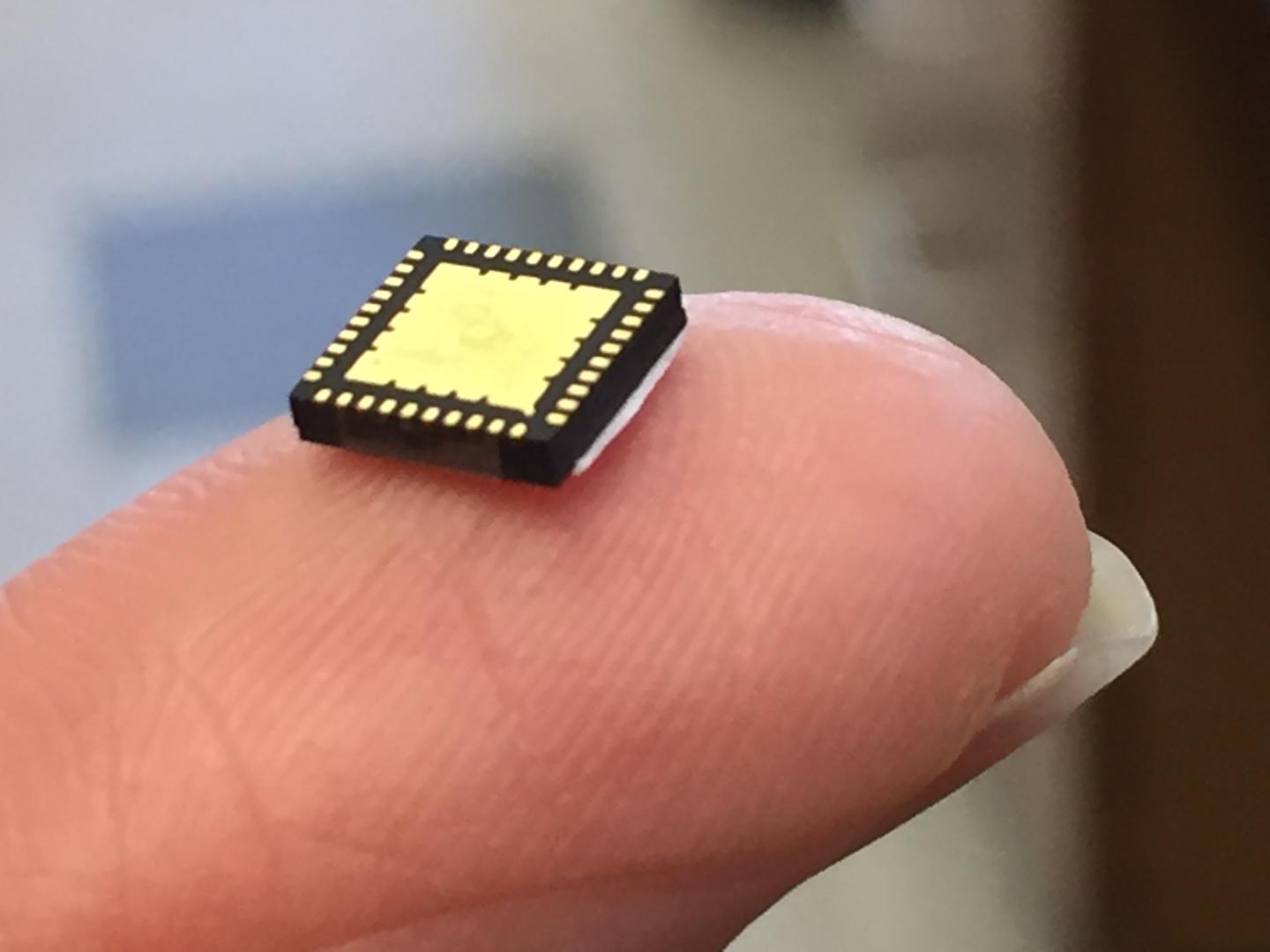
Guo's team developed the technology, which is about the size of a pin's head, with UTSA researcher Shuza Binzaid in the UTSA Multifunctional Electronic Materials and Devices Research Laboratory alongside graduate student Avadhood Herlekar.
"The purpose of this grant is better identify the commercial opportunities for technology created at universities," Guo said.
Guo and Binzaid are currently working with marketplace experts, as well as UTSA technology and IP management specialist Neal A. Guentzel, to understand the needs of consumers so they can determine which industry their chip is best suited for. It's an odd problem to have, since the device is applicable to several different uses, from every day electronics to medical apparatuses.
"This chip can be used with anything that runs on a battery," said Binzaid. "It manages power so that the device can last longer."
Cell phone users in desperate need of a charge, for example, put their devices on low power mode and reduce its regular functions to extend the battery life of their phones. The chip can keep a phone working at top functionality with much less power. Moreover, it facilitates the use of smaller batteries, since the object itself is so small.
The chip also tackles another common annoyance for electronics users: how hot devices get when they're being used for several minutes.
"The heat is a result of a lot of power being used," Guo said. "It's a nuisance, but with our device there is less power consumption, which means the heat will be much less of an issue."
Guo noted that as the "internet of things" becomes more integrated into the average person's daily life, battery power will continue to become a valuable resource. Beyond lower power devices such as cell phones, the chip could be used in fire sensors, fitness monitors and even medical apparatuses.
"We hope to make a significant leap forward in defibrillators and pacemakers," she said. "Invasive surgeries to replace medical devices that are running out of power could become much less frequent."
For now, Guo's team is focusing on developing the chip for customized sensors, with more possibilities on the horizon.
###
Media Contact
Joanna E Carver
[email protected]
210-243-4557
@utsa
http://www.utsa.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag