In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unveiled a fascinating aspect of ovarian biology that has far-reaching implications for reproductive health and fertility treatments. The research, conducted by an innovative team, focused on the effects of mouse serum on the development of ovarian follicles. What sets this work apart is its assertion that mouse serum can influence the expansion of the follicular cavity, promoting further growth regardless of the phase of the estrous cycle. This finding not only sheds light on ovarian physiology but also opens doors for new therapeutic approaches in reproductive medicine.
The intricate world of ovarian follicles has always been a subject of great interest within the scientific community. Ovarian follicles are essential structures that house developing eggs and produce hormones crucial for female reproduction. Each follicle goes through a precise journey, starting from primordial stages and advancing to mature antral follicles. However, the factors that regulate the growth and development of these follicles remain complex and multifaceted. This recent study provides a new angle on the interplay between hormones, serum components, and follicular development, contributing to our overall understanding of reproductive biology.
One of the most striking elements of the study is how mouse serum appears to facilitate follicular cavity expansion at various stages of the estrous cycle. The estrous cycle itself is a dynamic process characterized by fluctuating hormone levels that signal the maturation of ovarian follicles. Researchers observed that irrespective of the stage in this cyclical process, mouse serum had a consistent capacity to enhance the growth of the follicular cavity. Such a finding suggests that there are underlying mechanisms in play that allow serum components to take charge of follicular dynamics.
At the heart of this research is the characterization of the serum itself. The study meticulously examined the protein and hormonal composition of mouse serum, identifying specific factors that correlate with enhanced follicular development. Some of these components are known to influence cellular mechanisms such as growth factor signaling and steroidogenesis. Understanding how these serum constituents affect follicular behavior will be crucial for future applications in reproductive science. It raises pertinent questions about the potential for harnessing these biological agents within fertility treatments, potentially boosting ovarian response in women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies.
The implications of this research extend beyond the immediate findings. By documenting how mouse serum can modulate ovarian activity, this study paves the way for a potential translational approach to human reproductive health. If similar serum factors can be identified and reproduced in humans, it might lead to novel fertility therapies designed to enhance ovarian response during critical times of reproductive interventions. As researchers probe deeper into the mechanisms of serum-induced changes, there could be new insights into how best to support ovarian function in women facing fertility challenges.
Additionally, this study serves as a reminder of the vital role that animal models play in biomedical research. Mouse models, in particular, remain invaluable tools for investigating human reproductive health due to their genetic and physiological similarities. Through such studies that explore mouse serum’s effects, scientists can gain a clearer understanding of biological processes that may be conserved across species, providing a strong platform for further investigation into human ovarian function and fertility.
Yet, while the findings are undoubtedly promising, they caution against premature conclusions. The physiological and biochemical differences between mice and humans require careful consideration when translating these findings. Future studies will be needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of any serum-based treatments in human models, and researchers will need to navigate the regulatory and ethical landscape surrounding such innovations. Nonetheless, the journey has begun, and with it, a multitude of questions and avenues for further exploration arise.
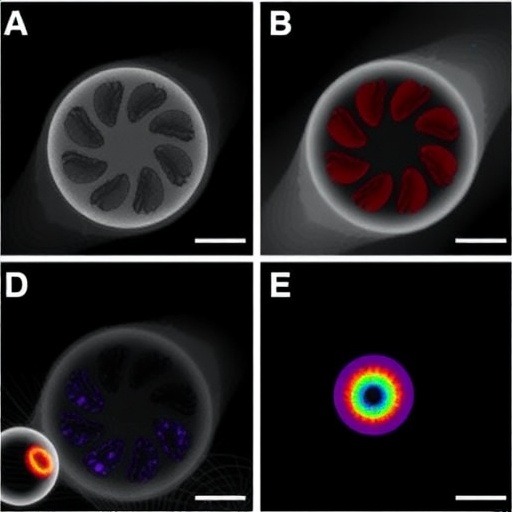
Experiments conducted within the study employed meticulous methodologies to ensure the reliability of the conclusions drawn. The researchers utilized sophisticated imaging techniques to visualize changes in follicular structure in response to mouse serum. They monitored the expansion of the follicular cavity over time, documenting a clear progression that aligns with their hypothesis. Such rigorous experimental design is a hallmark of high-quality research, providing confidence in the results and their implications.
Moreover, the study draws attention to the environment in which ovarian follicles develop. It highlights how serum, as part of the extracellular matrix, can create a supportive milieu that promotes optimal conditions for ovum growth and maturation. This stands in stark contrast to previous assumptions that focused predominantly on hormonal signals. The newfound emphasis on serum composition invites a broader inquiry into how the ovarian microenvironment influences follicular health, an area ripe for innovative research.
Cumulatively, these findings encourage a more integrated perspective on reproductive biology. Rather than viewing ovarian development as a linear process limited to hormonal regulation, the influence of serum and its components suggests a complex interplay of internal and external factors. As the research continues to evolve, it may facilitate the development of more holistic approaches to fertility—treatments that consider not just hormones, but the entire array of biological signals at play.
In conclusion, this study on mouse serum and its facilitation of follicular cavity expansion marks a significant contribution to our understanding of ovarian biology. It opens the door for potentially revolutionary advances in fertility treatment and sheds light on the importance of a supportive microenvironment for ovarian health. The journey from basic research to therapeutic application is often long and filled with challenges, but the prospect of enhancing reproductive health through a better understanding of these mechanisms offers hope and excitement for both scientists and patients alike.
Through such innovative research, the scientific community is poised not only to broaden the horizons of reproductive health but also to unravel the sophisticated tapestry of ovarian physiology, helping countless individuals facing fertility challenges on their journey toward parenthood. As we balance scientific pursuit with responsible application, it is essential to remain committed to exploring the multifaceted nature of female reproduction, ensuring that discoveries in the laboratory translate into practical solutions in the clinic.
Ultimately, this study serves as a testament to the power of research in uncovering the intricate details of life itself. The finding that mouse serum promotes follicular cavity expansion regardless of the estrous cycle phase stands as a reminder that even small variations in our biological makeup can yield impactful outcomes. As scientists continue to roll up their sleeves and dive into the unknown, the potential for discovery within the realm of reproductive health remains vibrant and brimming with promise.
Subject of Research: The influence of mouse serum on ovarian follicle development.
Article Title: Mouse serum facilitates the expansion of the follicular cavity regardless of the estrous cycle phase.
Article References:
Cao, MT., Sun, CX., Luo, WQ. et al. Mouse serum facilitates the expansion of the follicular cavity regardless of the estrous cycle phase. J Ovarian Res 18, 280 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-025-01869-y
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-025-01869-y
Keywords: ovarian follicles, mouse serum, estrous cycle, reproductive health, fertility treatments.
Tags: estrous cycle influence on reproductionfollicular cavity expansion mechanismshormonal regulation of follicular developmentimplications for reproductive health researchinnovative research in reproductive biologymouse models in reproductive studiesmouse serum effects on ovarian folliclesovarian biology and fertility treatmentsovarian physiology and egg developmentserum components in follicular growththerapeutic approaches in reproductive medicineunderstanding female reproductive systems