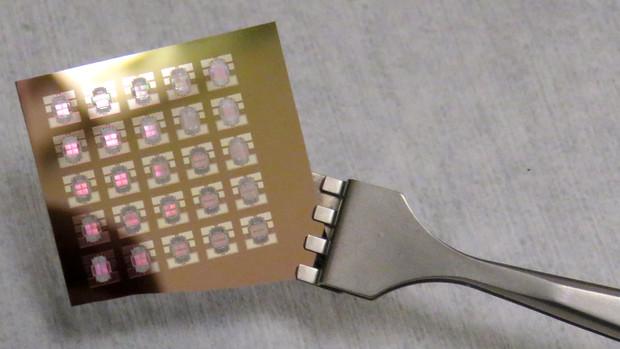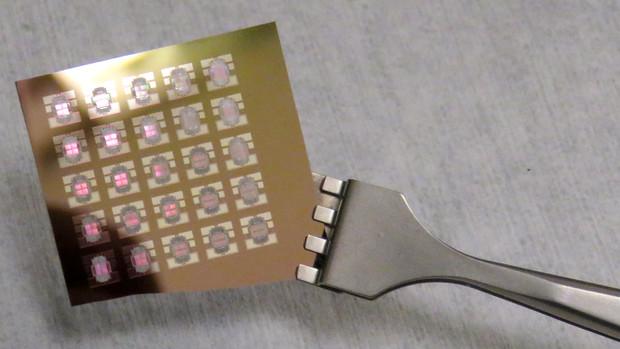
Credit: Karl Vogel | University of Nebraska-Lincoln Engineering
One of the biggest problems with computers, dating to the invention of the first one, has been finding ways to keep them cool so that they don't overheat or shut down.
Instead of combating the heat, two University of Nebraska-Lincoln engineers have embraced it as an alternative energy source that would allow computing at ultra-high temperatures.
Sidy Ndao, assistant professor of mechanical and materials engineering, said his research group's development of a nano-thermal-mechanical device, or thermal diode, came after flipping around the question of how to better cool computers.
"If you think about it, whatever you do with electricity you should (also) be able to do with heat, because they are similar in many ways," Ndao said. "In principle, they are both energy carriers. If you could control heat, you could use it to do computing and avoid the problem of overheating."
A paper Ndao co-authored with Mahmoud Elzouka, a graduate student in mechanical and materials engineering, was published in the March edition of Scientific Reports. In it, they documented their device working in temperatures that approached 630 degrees Fahrenheit.
Ndao said he expects the device could eventually work in heat as extreme as 1,300 degrees Fahrenheit, which could have major implications in many industries.
"We are basically creating a thermal computer," Ndao said. "It could be used in space exploration, for exploring the core of the earth, for oil drilling, (for) many applications. It could allow us to do calculations and process data in real time in places where we haven't been able to do so before."
By taking advantage of an energy source that has long been overlooked, Ndao said, the thermal diode could also help limit the amount of energy that gets wasted.
"It is said now that nearly 60 percent of the energy produced for consumption in the United States is wasted in heat," Ndao said. "If you could harness this heat and use it for energy in these devices, you could obviously cut down on waste and the cost of energy."
The next step is making the device more efficient and making a physical computer that could work in the highest of temperatures, Ndao said.
Though the researchers have filed for a patent, Elzouka said there is still work to be done to improve the diode and its performance.
"If we can achieve high efficiency, show that we can do computations and run a logic system experimentally, then we can have a proof-of-concept," Elzouka said. "(That) is when we can think about the future."
Yet Ndao has even bigger ambitions for his group's research.
"We want to to create the world's first thermal computer," he said. "Hopefully one day, it will be used to unlock the mysteries of outer space, explore and harvest our own planet's deep-beneath-the-surface geology, and harness waste heat for more efficient-energy utilization."
###
Media Contact
Sidy Ndao, mechanical and materials engineering
[email protected]
402-472-1623
@UNLNews
http://www.unl.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag