Credit: Source: Christian Böhler, Maria Asplund
Complex neurotechnological devices are required to directly select and influence brain waves inside the skull's interior. Although it has become relatively easy to implement the devices, researchers are still faced with challenges when trying to keep them running properly in living organisms over time. But that could be changing now, thanks to a new method from Freiburg. A research team was able to create a microprobe that grows into the neural tissue without inflammation and with the help of a medicinal coating. Even after twelve weeks it is still able to deliver strong signals. Now that such implants are no longer required to be replaced as often, they are able to open the doors for better diagnoses while making life easier for the chronically ill — such as Parkinson's patients that need to be treated with brain stimulation methods. The study has appeared in the journal „Biomaterials" and is based on the group's earlier research on conductive and absorbent plastics.
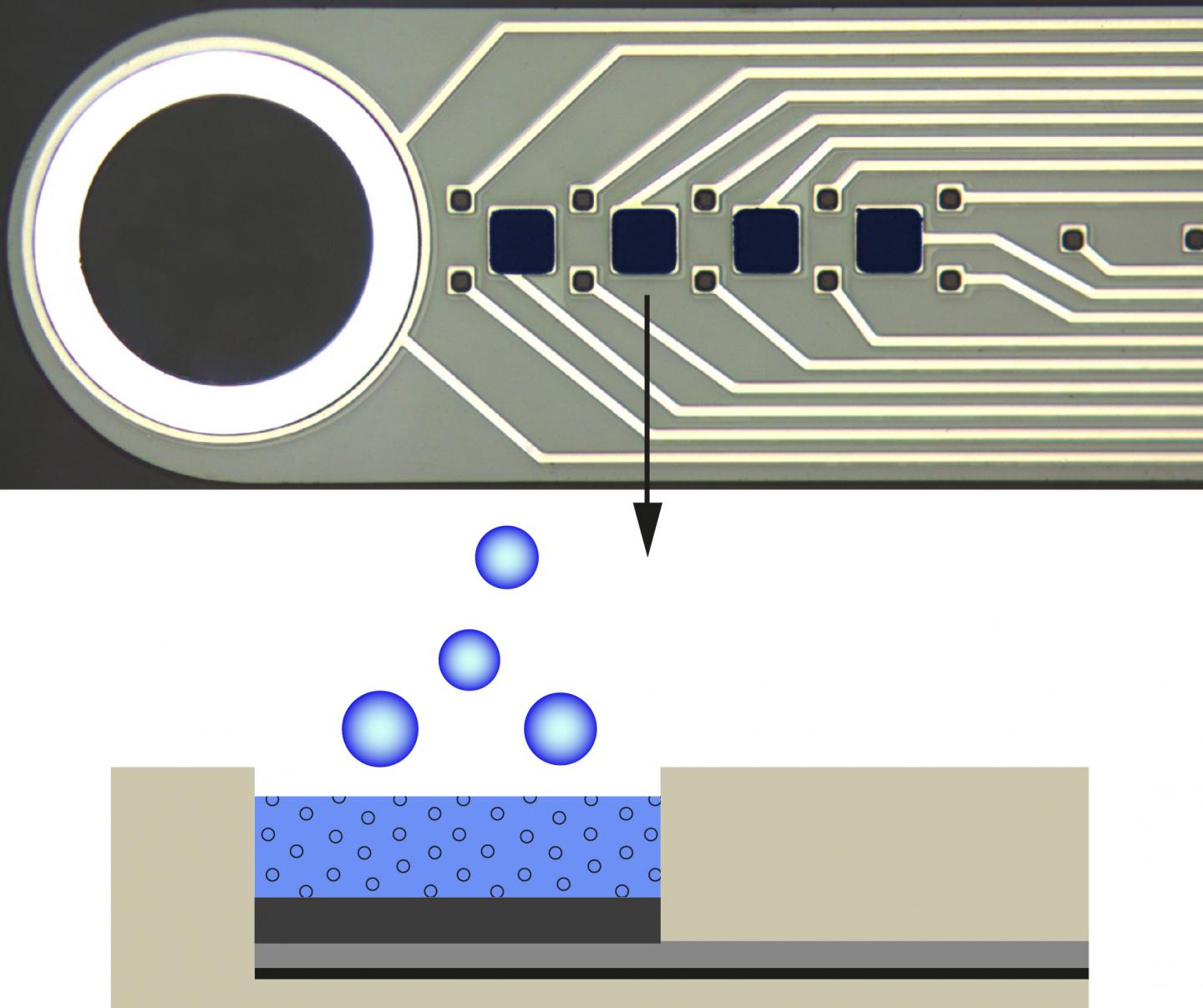
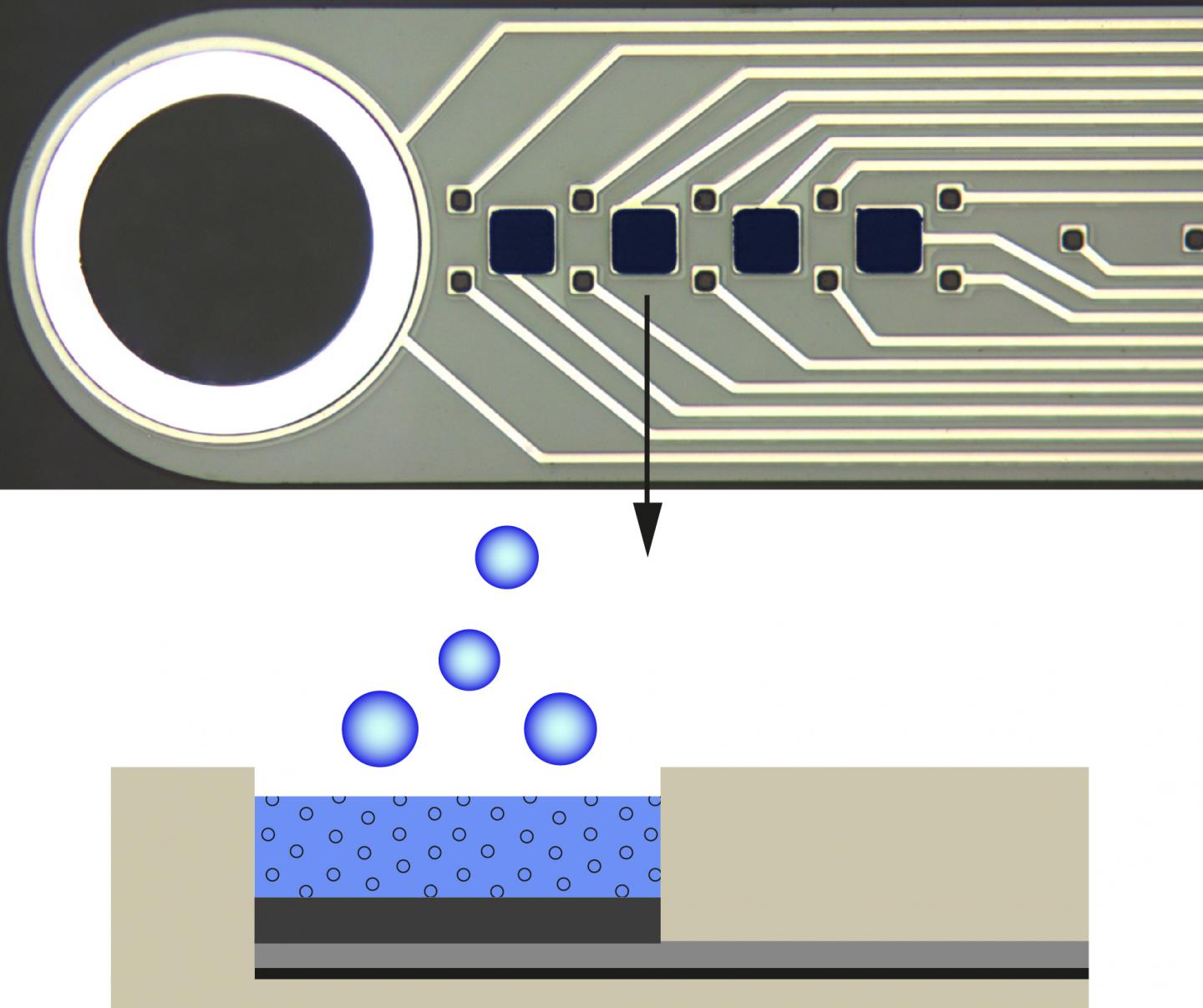
The microsystems engineer Christian Böhler from Dr. Maria Asplund's junior research group in the Cluster of Excellence BrainLinks-BrainTools, Prof. Dr. Thomas Stieglitz, chair for biomedical microtechnology at the Institute for Microsystem Technology and Prof. Dr. Ulrich G. Hofmann, the section for neuroelectronic systems in the Department of Neurology at the University Hospital Freiburg have participated in the research. „After a while, the immune system tends to treat most of the bidirectional neural implants – that is, those that are implanted for measuring and stimulating simultaneously – as a foreign object. That is the reason their functionality becomes so limited. After a few weeks they barely give off any signals at all," says Böhler. The junior research group has shown that flexible microprobes made of so-called polyimides offer distinct advantages over implants made of silicon, for instance. „At the same time, inflammatory reactions can arise that make the electrodes unserviceable or that ultimately lead to the implant's removal," adds Asplund. In their study, the researchers show that, based on an animal model, these side effects can be delayed longer by using a special coating on the electrodes placed on the polyimide implant.
The electrodes' coating is made from the polymer PEDOT that absorbs medicine and, when applying negative voltage, releases it again – in this case, the anti-inflammatory compound dexamethasone. „In this way, we can pour the medicine directly around the implant, regulate the dosage and determine the time it is administered," explains Böhler. Compared to traditional methods for drug administering, a much lower dosage can be used. It also makes it possible to limit the effects to a specific area. In that way, undesirable side effects from the medicine can be reduced. As early as the beginning of 2016 the team showed that PEDOT has ideal characteristics as a drug carrier.
„We are able to reinforce the flexible microprobes' superior nature over other designs with our study," Asplund summarizes. The implant from the Freiburg microsystems technology even holds together longer: „We are on the cusp of a breakthrough in a new generation of neuronal interfaces. We can finally build microprobes with a longer shelf life through our coating method." Of that Böhler is certain. Many more promising avenues for long-term treatments with, for instance, deep brain stimulation can be explored with this system. Patients whose nervous system requires not only regular stimulation but also close measurements and monitoring, such as those with Parkinson's or epilepsy as well as people with obsessive-compulsive disorders or severe depression.
###
Original publication:
C. Böhler, C. Kleber, N. Martini, Y. Xie, I. Dryg, T. Stieglitz, U.G. Hofmann & M. Asplund (2017): Actively Controlled Release of Dexamethasone from neural microelectrodes in a chronic in vivo study, In: Biomaterials 129, pp. 176-187.
Caption:
In the upper part of the image you can see an enlarged picture of the microprobe manufactured in Freiburg for stimulating and simultaneously gathering data. Below there is a cross section oft he coating made from the polymer PEDOT that has stored an anti-inflammatory medicine that can be released by applying negative voltage.
Source: Christian Böhler, Maria Asplund
Contact:
Junior Research Group BioEPIC
Laboratory for Biomedical Microtechnology – IMTEK
University of Freiburg
E-Mail: [email protected]
Levin Sottru
Science Communicator
Cluster of Excellence
BrainLinks-BrainTools
University of Freiburg
Tel.: 0761/203-67721
E-Mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Christian Böhler
49-761-203-67375
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag