Credit: (Photo: KIT)
Nothing works without proteins in the body, they are the molecular all-rounders in our cells. If they do not work properly, severe diseases, such as Alzheimer's, may result. To develop methods to repair malfunctioning proteins, their structure has to be known. Using a big data approach, researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now developed a method to predict protein structures.
In the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), the researchers report that they succeeded in predicting even most complicated protein structures by statistical analyses irrespective of the experiment. Experimental determination of protein structures is quite cumbersome, success is not guaranteed. Proteins are the basis of life. As structural proteins, they are involved in the growth of tissue, such as nails or hairs. Other proteins work as muscles, control metabolism and immune response, or transport oxygen in the red blood cells.
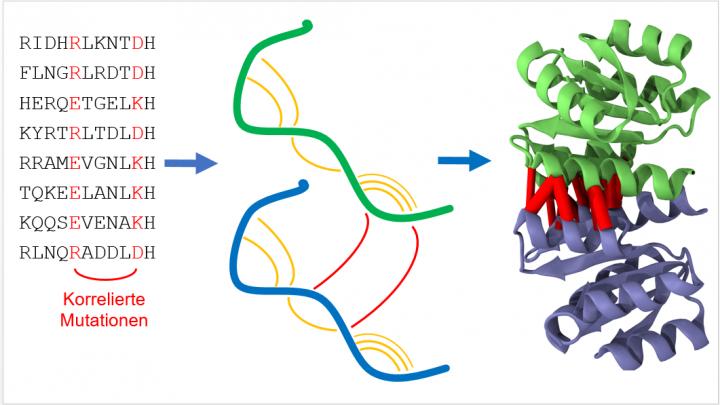
The basic structure of proteins with certain functions is similar in different organisms. "No matter whether human being, mouse, whale or bacterium, nature does not constantly invent proteins for various living organisms anew, but varies them by evolutionary mutation and selection," Alexander Schug of the Steinbuch Centre for Computing (SCC) says. Such mutations can be identified easily when reading out the genetic information making up the proteins. If mutations occur in pairs, the protein sections involved mostly are located close to each other. With the help of a computer, the data of many spatially adjacent sections can be composed to an exact prediction of the three-dimensional structure similar to a big puzzle. "To understand the function of a protein in detail and to influence it, if possible, the place of every individual atom has to be known," Schug says.
For his work, the physicist uses an interdisciplinary approach based on methods and resources of computer science and biochemistry. Using supercomputers, he searched the freely available genetic information of thousands of organisms, ranging from bacteria to the human being, for correlated mutations. "By combining latest technology and a true treasure of datasets, we studied nearly two thousand different proteins. This is a completely new dimension compared to previous studies," Schug adds. He emphasizes that this shows the high performance of the method that promises to be of high potential for applications ranging from molecular biology to medicine. Although present work is fundamental research according to Schug, the results may well be incorporated in new treatment methods of diseases in the future.
###
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
Media Contact
Monika Landgraf
[email protected]
49-721-608-47414
@KITKarlsruhe
http://www.kit.edu/index.php
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag





