Credit: © Chenfeng Ke
Using advanced 3-D printing, Dartmouth College researchers have unlocked the key to transforming microscopic nanorings into smart materials that perform work at human-scale.
Nanomachines can already deliver medication and serve as computer memories at the tiny nanometer scale. By integrating a 3-D printing technique pioneered at Dartmouth's Ke Functional Materials Group, researchers may unlock even greater potential for these mini-machines.
The research was published on March 22 in the online edition of Angewandte Chemie, the prestigious journal of the German Chemical Society.
"Up until now, harnessing the mechanical work of nanomachines has been extremely difficult. We are slowly getting closer to the point that the tiny machines can operate on a scale that we can see, touch and feel." said Chenfeng Ke, Assistant Professor for Chemistry at Dartmouth College and principle investigator for the research.
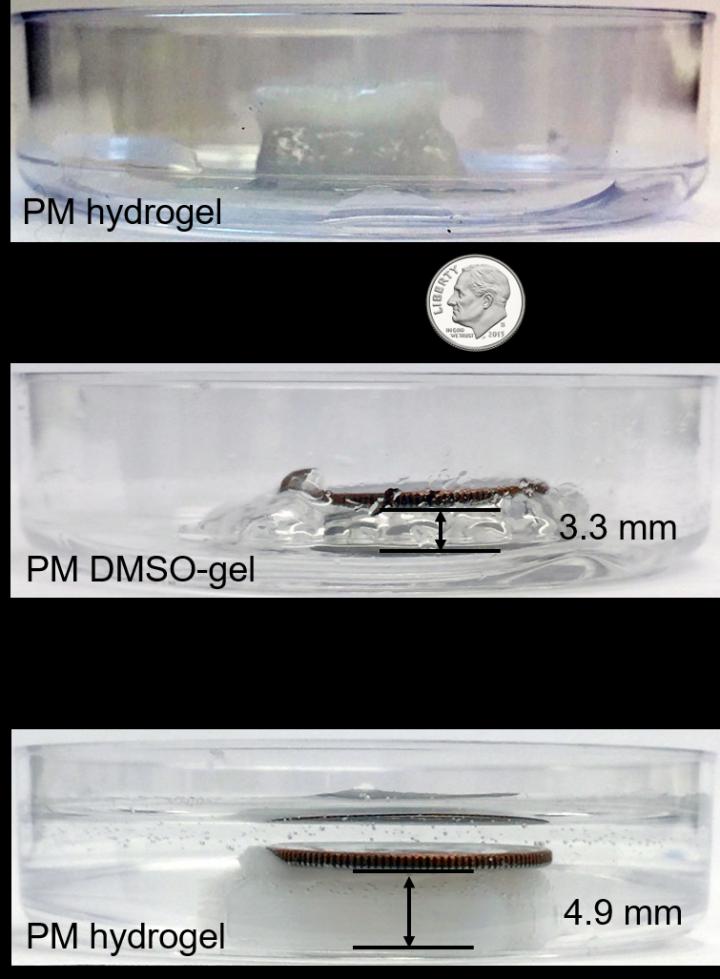
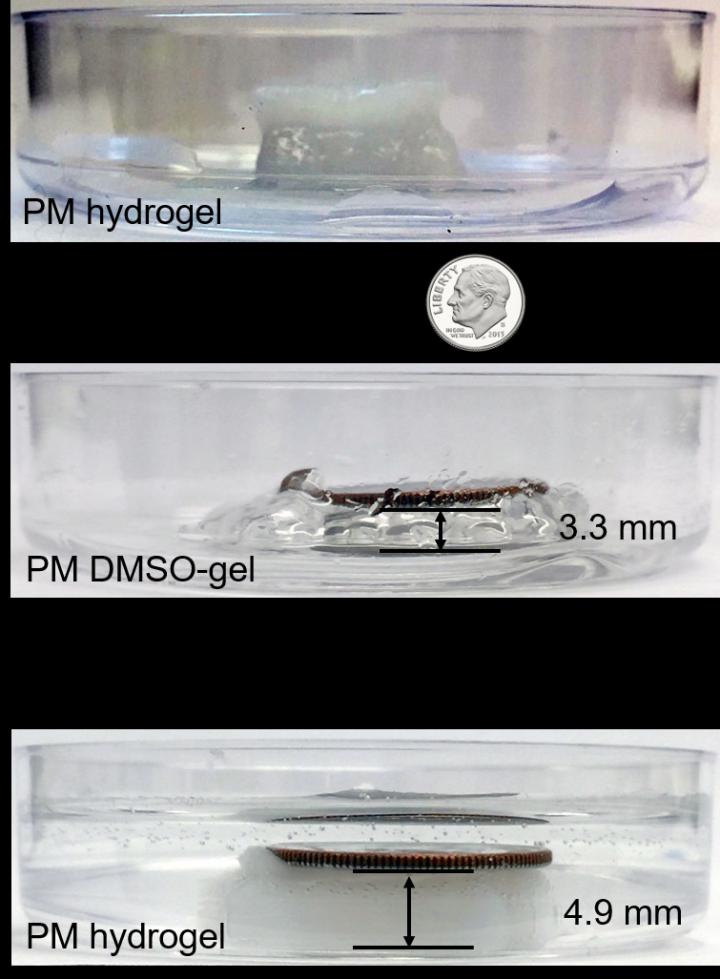
In an example provided by Ke, the first-generation smart material lifted a dime weighing 2.268g. The coin, 15 times the weight of the structure that lifted it, was raised 1.6 mm- the equivalent of a human lifting a car.
"Creating nanomachine-based smart material is still extraordinarily complex and we are only just beginning, but this new technique could allow the design and fabrication of complex smart devices that are currently beyond our grasp," said Ke.
The design of the new material is based on Nobel Prize-winning research that turned mechanically interlocked molecules (MIMs) into work-performing machines at nanoscale. Previously, researchers have shown how light, heat and altered pH levels could force movement within a structure – known as a rotaxane – composed of rings on a molecular axle. Much the same way beads are threaded onto a string, the sliding – or shuttling – of rings along the axle causes the molecules to change shape and store energy.
According to the paper, MIMs are already widely used as molecular shuttles, switches, muscles and pumps. But for years, chemists have been stymied by the problem of ordering their random positions. Establishing such order is critical to keeping the structures from canceling out each other's mechanical movement so that their molecular motions can be amplified.
"Our work provides the first design principle to add 3-D printability to nanomachines. Importantly, we have also transformed molecular motions to macroscale to do useful work," said Ke, who did his post-doctoral research with one of the 2016 Nobel laureates, Sir Fraser Stoddart.
The research group designed and synthesized MIM-based gels with properties desirable for 3-D printing. Utilizing the hydrogen bonding interactions between nanorings, they successfully printed lattice-like 3-D structures. By crosslinking the axles, structures with good 3-D structural integrity and mechanical stability were created.
Researchers found that the complex 3-D architecture of these structures can be reversibly deformed and reformed through solvent exchange that switches the threaded ring structure between random shuttling and stationary states at the molecular level. This shape-changing and recovery behavior was found by to be repeated easily many times.
"Just like moving beads to strengthen or weaken a string, this action is critical because it allows the amplification of molecular motion into macroscopic motion through the conversion of chemical energy input into mechanical work," said Qianming Lin, the first author of the paper and a first-year graduate student in the Department of Chemistry at Dartmouth College.
Ke and his team hopes this advancement will enable scientists to develop smart materials and devices. For example, by adding contraction and twisting to the rising motion, molecular machines could be useful as soft robots that complete complicated tasks similar to a human hand.
###
Media Contact
David Hirsch
[email protected]
@dartmouth
http://www.dartmouth.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag