In an innovative exploration of the molecular intricacies surrounding high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC), recent research has identified the critical role of the laminin subunit α5. This groundbreaking study, led by researchers Tianli, W., Li, S., and Zhang, R., delves deep into the functional mechanics of laminin α5 and its implications in the progression of HGSOC, a particularly aggressive form of ovarian cancer that poses significant treatment challenges and affects thousands of women globally each year.
The relevance of laminin, a key component in the extracellular matrix (ECM), extends far beyond its structural support role. Laminins are glycoproteins that influence a myriad of cellular behaviors, including adhesion, migration, differentiation, and cellular signaling. In the context of ovarian cancer, the expression profiles of various laminin subunits, particularly α5, have shown a marked correlation with cancer progression and poor patient outcomes. Understanding these relationships could unlock novel therapeutic strategies aimed at curbing the advance of this malignancy.
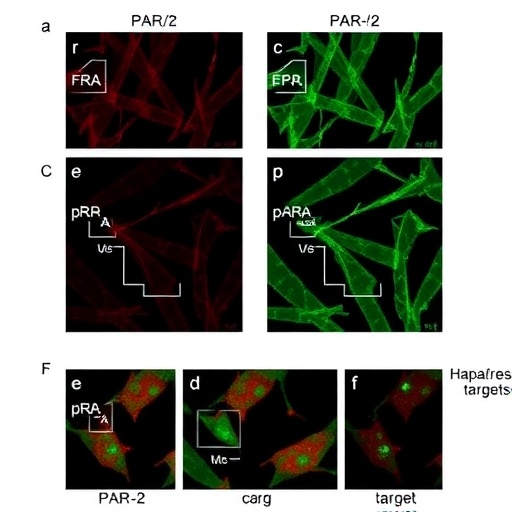
The authors utilized a combination of in vitro and in vivo experiments to elucidate the specific functions of laminin α5 within ovarian cancer cell lines. By employing RNA interference techniques, they successfully downregulated laminin α5 expression and observed the consequent effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The results were striking, revealing that reduced laminin α5 levels resulted in diminished tumorigenic capabilities of the cancer cells. This suggests that laminin α5 is indeed a contributing factor to the invasive characteristics of HGSOC.
Moreover, the interaction between laminin α5 and various integrin receptors was meticulously charted in this study. Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-extracellular matrix adhesion, a fundamental element in tumor metastasis. The exploration of how laminin α5 engages these integrins provides insights into the signaling pathways that may be exploited in therapeutic contexts. The findings indicate that inhibiting this interaction could lead to decreased metastatic potential of HGSOC cells, presenting a promising avenue for targeted therapies.
Another significant revelation from the study is the involvement of laminin α5 in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process that allows epithelial cells to acquire mesenchymal characteristics, enhancing their migratory and invasive properties. The authors noted that higher expression levels of laminin α5 correlated with heightened EMT marker expression in various cancer cell lines. This connection underscores laminin α5’s potential as not only a biomarker for HGSOC progression but also as a target for novel intervention strategies aimed at reversing EMT.
As the authors progressed to evaluate the clinical relevance of their findings, they conducted extensive analyses using patient-derived samples and clinical data. The correlation between laminin α5 expression levels and patient survival rates painted a concerning picture. Elevated laminin α5 levels were associated with poorer prognosis, primarily due to its role in promoting aggressive tumor behavior. These findings could be pivotal in developing diagnostic tools that incorporate laminin α5 as a prognostic biomarker, aiding in early detection and personalized treatment plans.
Moreover, the study delved into the broader implications of laminin α5 not only in HGSOC but also potentially in other malignancies characterized by similar pathology. The researchers emphasized the need for multidisciplinary approaches that consider ECM components like laminin in the broader context of cancer biology. The exploration of laminin subunits, including α5, could pave the way for a new understanding of how cancers evolve and respond to therapies.
In light of these discoveries, the researchers called for additional studies focusing on potential inhibitors of laminin α5. The synthesis of small molecules or monoclonal antibodies targeting this laminin subunit could represent a novel therapeutic class in providing solutions against aggressive ovarian cancer subtypes. Innovations in drug delivery systems specifically tailored to disrupt laminin-integrin interactions might enhance treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
The implications of this research extend beyond the laboratory. By promoting awareness and understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying HGSOC, there is potential for advocacy groups and healthcare providers to initiate discussions around screening and treatment options tailored to laminin α5 profiles. Such discussions could lead to enhanced patient awareness about the importance of early detection and the significance of ongoing research in contributing to improved survival rates.
Bringing the research into the technological sphere also opens opportunities for collaborations with computational biologists and bioinformaticians. The integration of cheminformatics could facilitate the virtual screening of compounds that target laminin α5, streamlining the transition from experimental findings to clinical applications. Through combined efforts, it becomes increasingly feasible to uncover safe and effective therapies that could transform the treatment landscape for ovarian cancer patients.
In summation, the functional study of laminin α5 presents a multifaceted perspective on high-grade serous ovarian cancer, shedding light on the intricate molecular networks that facilitate cancer progression. The direction set forth by Tianli, W., Li, S., and Zhang, R. urges a critical reevaluation of how we approach tumor biology. By comprehensive targeting of extracellular matrix components, particularly laminin, future research and clinical strategies could yield significant advancements in combating ovarian cancer and improving patient outcomes substantially.
This transformative research not only underscores the importance of basic science in understanding complex diseases but also emphasizes the urgent need for continued exploration in cancer biology. The outcome of this study indeed lays a foundation for further research designed to disentangle the complexities of tumor microenvironments and their roles in cancer progression, setting the stage for meaningful clinical innovations in the fight against ovarian cancer.
Subject of Research: Laminin subunit α5 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
Article Title: Functional study of laminin subunit α5 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
Article References:
Tianli, W., Li, S. & Zhang, R. Functional study of laminin subunit α5 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res 18, 157 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-025-01752-w
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: High-grade serous ovarian cancer, laminin α5, tumor microenvironment, extracellular matrix, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, integrins, metastasis, prognostic biomarker, therapeutic target.
Tags: cancer cell adhesion mechanismscellular migration in malignanciesextracellular matrix componentshigh-grade serous ovarian cancer researchin vitro and in vivo cancer experimentslaminin glycoproteins and cancerLaminin α5 in ovarian cancermolecular mechanisms of ovarian cancerovarian cancer treatment challengesRNA interference in cancer studiestherapeutic strategies for ovarian cancertumor progression and patient outcomes