Credit: © Till Korten, Cornelia Kowol
Crashing computers or smartphones and software security holes that allow hackers to steal millions of passwords could be prevented if it were possible to design and verify error-free software. Unfortunately, to date, this is a problem that neither engineers nor supercomputers can solve. One reason is that the computing power required to verify the correct function of a many types of software scales exponentially with the size of the program, so that processing speed, energy consumption and cooling of conventional microelectronic processors prevent current computers from verifying large programs.
The recently launched research project aims to develop a biocomputer that can overcome the two main obstacles faced by today's supercomputers: first, they use vast amounts of electric power – so much that the development of more powerful computers is hampered primarily by limitations in the ability to cool the processors. Second, they cannot do two things at the same time. The EU now funds a project that will develop a computer based on highly efficient molecular motors that will use a fraction of the energy of existing computers, and that can tackle problems where many solutions need to be explored simultaneously.
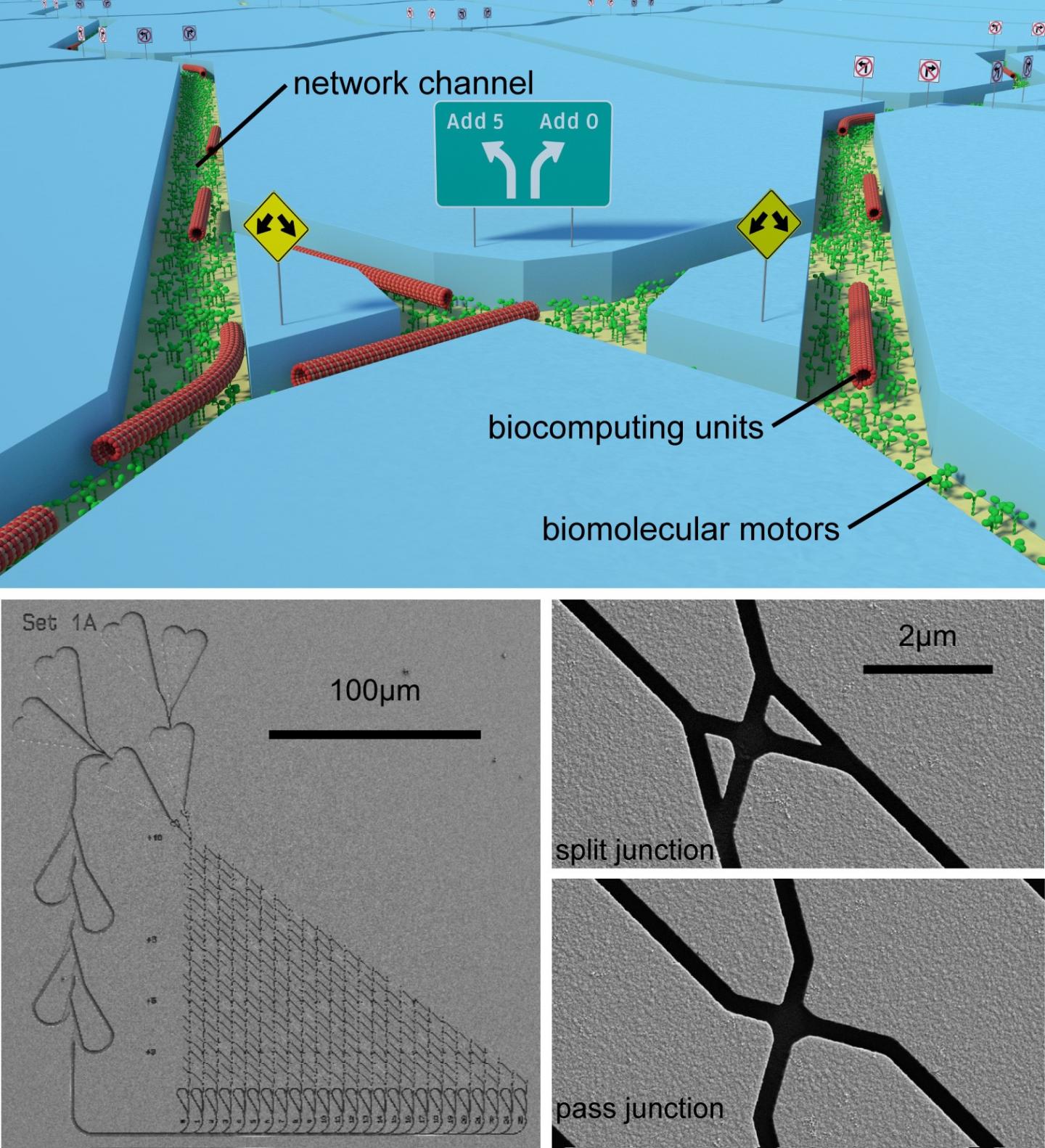
The potential impact of the project results is not limited to the design of error-free software: "Practically all really interesting mathematical problems of our time cannot be computed efficiently with our current computer technology." says Dan V. Nicolau, Ph.D. M.D., from the UK-based enterprise Molecular Sense, who had the original idea of using biomolecular motors as computers. This is the limit that the new project aims to push by using biomolecular motors as computing units: The idea is that biomolecular machines, each only a few billionth of a meter (nanometers) in size, can solve problems by moving through a nanofabricated network of channels designed to represent a mathematical algorithm (see fig. 1); an approach the scientists in the project termed "network-based biocomputation". Whenever the biomolecules reach a junction in the network, they either add a number to the sum they are calculating or leave it out. That way, each biomolecule acts as a tiny computer with processor and memory. While an individual biomolecule is much slower than a current computer, they are self-assembling so that they can be used in large numbers, quickly adding up their computing power. The researchers have demonstrated that this works in a recent publication in the Proceedings of the National Academy of the USA (PNAS). "We are using molecular motors of the cell that have been optimized by a billion years of evolution to be highly energy efficient nanomachines.", says Prof. Stefan Diez who is heading the participating TU Dresden research team, "and the biological computing units can multiply themselves to adapt to the difficulty of the mathematical problem." adds Dr. Till Korten from TU Dresden, co-coordinator of the Bio4Comp project and equally contributing first author of the PNAS publication.
The research consortium will focus on developing the technology required to scale up network-based biocomputers to a point at which they are able to compete with other alternative computing approaches such as DNA computing and quantum computing. In the process, they aim to attract a larger scientific and economic community that will focus on developing the technology into a viable alternative computing approach. To do so, they have received 6.1 Million € from the Future & Emerging Technologies (FET) programme of the EU to run a highly interdisciplinary research project touching mathematics, biology, engineering, and computation. Of this funding, 1.1 million € will go to the research group of Stefan Diez, Professor for BioNanoTools at B CUBE, a TU Dresden research institute focusing on Molecular Bioengineering, and fellow at the Max Planck Institute of Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) Dresden. The role of the group will be to modify the properties of motor proteins, such as kinesin, in order to optimize them for biocomputation, as well as to integrate them into nanofabricated devices. This work will strongly benefit from synergies and collaborations with the Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed), one of the current Clusters of Excellence at TU Dresden. "Optimizing the motors not only gives us ideal tools for nanotechnology, but at the same time we learn a great deal about how they work and what they do inside the cell.", Diez says. These insights will be useful beyond the specific project goals, for example to elucidate the roles of these proteins in serious diseases such as cancer and dementia.
###
The project Bio4Comp (2017-2021) is funded by Horizon 2020, the EU framework program for Research and Innovation under under Grant Agreement No 732482. More information can be found on the research consortium's webpage: http://www.bio4comp.eu.
Media Inquiries:
Stefan Diez, Professor for BioNanoTools
B CUBE – Center for Molecular Bioengineering
Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
Tel.: +49 (0) 351 463-43010
[email protected]
http://www.tu-dresden.de/bcube
Contact list of project partners:
Partner 1: Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Heiner Linke, Professor of Nanophysics; Director of NanoLund
Tel.: +46 (0) 46 222 4245
[email protected]
Kristina Lindgärde, Pressansvarig vid Kommunikation och Samverkan, LTH
Tel.: +46 (0) 46 222 0769
[email protected]
http://www.nano.lu.se/
Partner 2: Linné-University Kalmar, Kalmar, Sweden
Alf Månsson, professor i fysiologi
Tel.: +46 (0) 70 886 6243
Annika Sand, pressansvarig
Tel.: +46 (0) 76 830 0105
https://lnu.se/en/research/searchresearch/the-molecular-motor-and-bionano-group/
Partner 3: Molecular Sense Ltd., Oxford, U.K.
Dan V. Nicolau, PhD. MD.
https://molecularsense.com/
Partner 4: Bar-Ilan University, Ramat Gan, Israel
Dr. Hillel Kugler
Tel.: +972 (0) 3 7384437
[email protected]
http://www.eng.biu.ac.il/hillelk/
Partner 5: Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Wissenschaften e.V.
Prof. Stefan E. Schulz
Tel.: +49 (0) 371 45001-232
[email protected]
https://www.fraunhofer.de/
Links
To PNAS paper: http://www.pnas.org/content/113/10/2591.full?sid=5d9e45c4-6338-461e-9c93-a74c5ca7b6ed
To web-site: http://www.bio4comp.eu
Media Contact
Stefan Diez
[email protected]
49-035-146-343-010
@tudresden_de
http://tu-dresden.de/en
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag