Credit: Dr. Panagiotis Grammatikopoulos
While nanoparticles sound like a recent discovery, these tiny structures have been used for centuries. The famous Lycurgus cup, made by 4th century Roman artisans, features dichroic glass, with gold and silver nanoparticles sprinkled throughout, producing a green appearance when light is shining on it from the front, and a red appearance when illuminated from behind.
In the centuries since the time of the ancient artisans, researchers have come a long way in understanding nanoparticles. The production of nanocubes has been of particular interest due to their potential applications as biosensors and gas sensors. Nanoparticles can be produced using either physical or chemical methods, though physical methods are advantageous due to the absence of organic contaminants commonly introduced by chemical methods. However, uniformly sized nanocubes are difficult to produce in sufficient quantities by physical methods. Researchers from the Nanoparticles by Design Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) Graduate University have recently discovered a new approach to overcome this problem. Their research was recently published in Advanced Functional Materials.
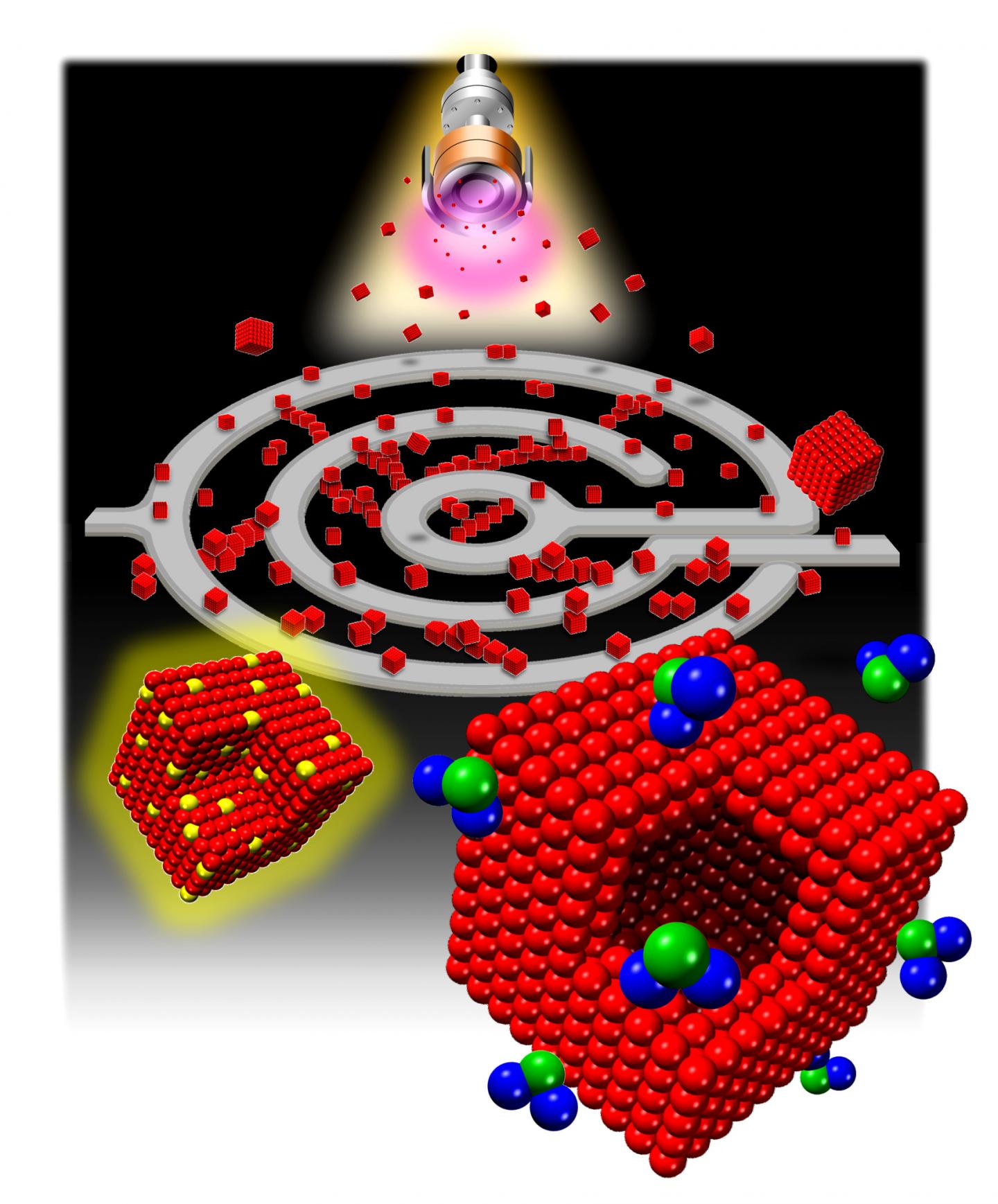
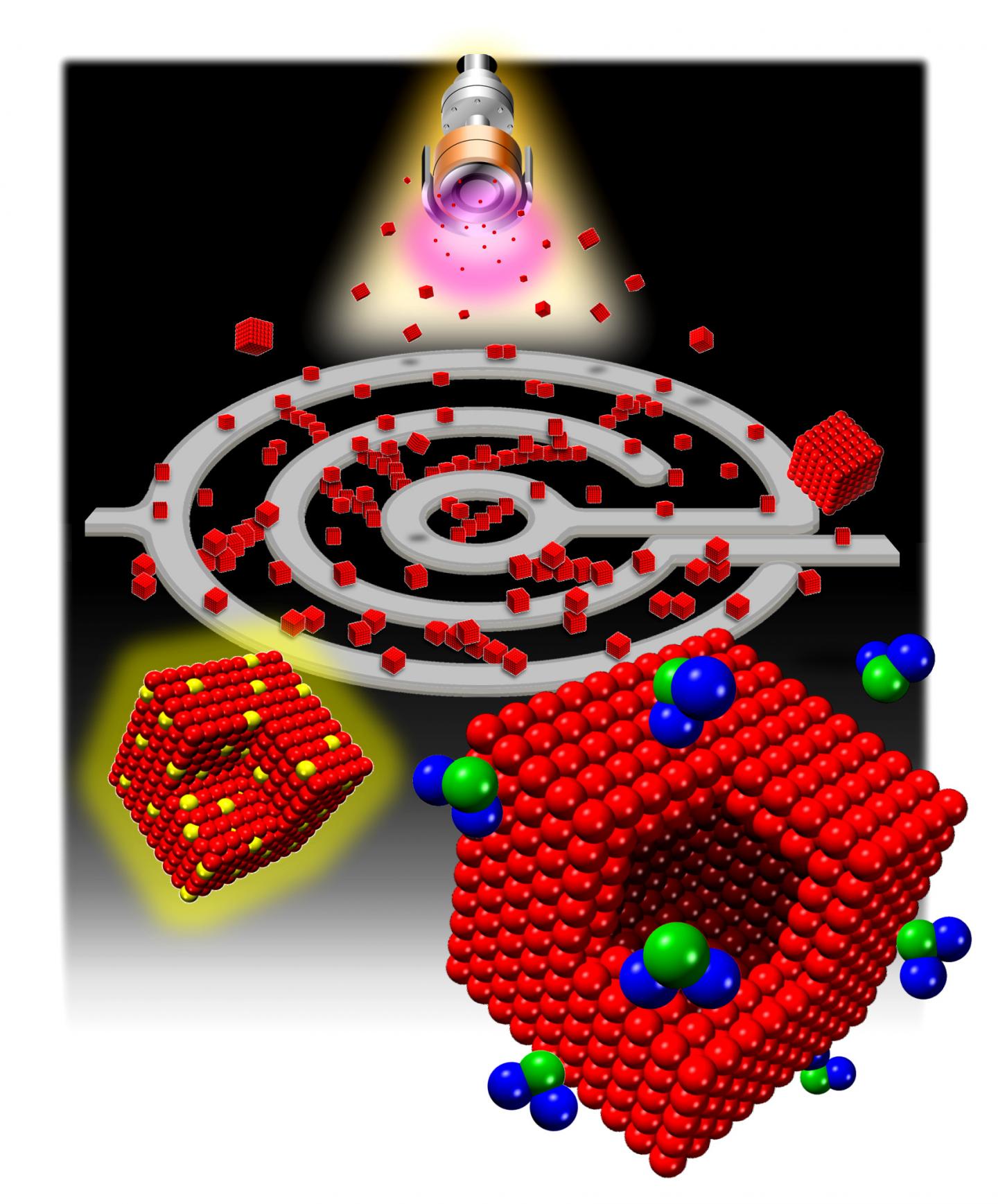
"The cube shape is not the lowest energy structure for iron nanoparticles", explains Dr. Jerome Vernieres, first author of the publication, "thus, we couldn't rely on equilibrium thermodynamics considerations to self-assemble these nanocubes". Instead, the OIST scientists, under the guidance of Prof. Mukhles Sowwan, exploited the possibilities offered by a technique called magnetron-sputtering inert-gas condensation to create their iron nanocubes. With this method, argon gas is first heated up and turned into ionized plasma. Then, a magnet, suitably located behind a target made of the desired material, in this case, iron, controls the shape of the plasma, and ensures that argon ions bombard the target; hence the name "magnetron". As a result, iron atoms are sputtered away from the target, collide with argon atoms and with each other, and form nanoparticles. Accurate control of the plasma via controlling the magnetic field can produce uniform nanocubes. "Uniformity is key in sensing applications. We needed a way to control the size, shape, and number of the nanocubes during their production", explained Dr. Stephan Steinhauer.
To control the size and shape of these cubes, the researchers made a simple but significant observation: iron is magnetic in its own right! In other words, the researchers discovered that they could exploit the intrinsic magnetism of the target itself as an innovative way to modify the magnetic field of the magnetron. This way they managed to manipulate the plasma where the particles are grown, and thus to control the nanocube sizes during formation. "This is the first time uniform iron nanocubes have been made using a physical method that can be scaled for mass production" clarifies Vernieres. To better understand the mechanics of this process, the OIST team collaborated with researchers from the University of Helsinki to make theoretical calculations. "The work relied heavily on both experimental methods and theoretical calculations. The simulations were important for us to explain the phenomena we were observing", illuminates Dr. Panagiotis Grammatikopoulos.
Once the researchers invented a way to produce these uniform iron cubes, the next step was to build an electronic device that can utilize these nanocubes for sensing applications. "We noticed that these cubes were extremely sensitive to the levels of gaseous NO2. NO2 sensing is used for a variety of different purposes, from diagnosis of asthma patients to detecting environmental pollution, so we immediately saw an application for our work", states Steinhauer. The researchers from the Nanoparticles by Design Unit, in collaboration with researchers from the Université de Toulouse, then built a prototype NO2 sensor that measured the change in electrical resistance of the iron nanocubes due to exposure to NO2 gas. Because exposure to even a very tiny amount of NO2 can produce a measurable change in electrical resistance that is considerably larger than for other atmospheric pollutants, the iron nanocube-based sensor is both extremely sensitive and specific. "These nanocubes have many potential uses. The fact that we can produce a relatively large quantity of uniform nanocubes using an increasingly common synthesis method makes this research highly promising for industrial applications," emphasized Vernieres.
###
Media Contact
Kaoru Natori
[email protected]
@oistedu
http://www.oist.jp/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag