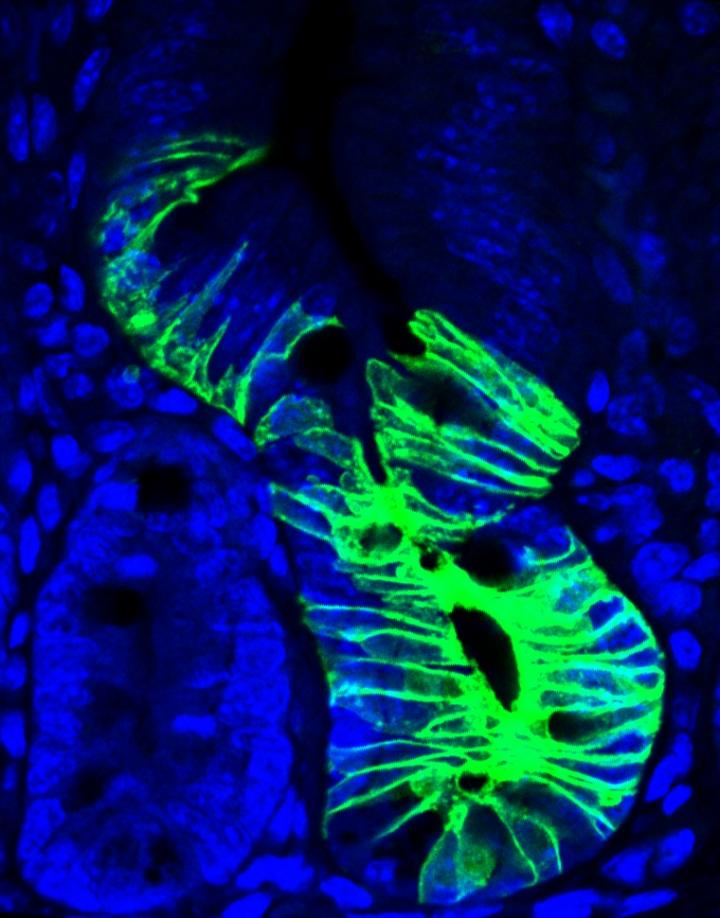
Credit: Franscisco Barriga, IRB Barcelona
The intestine has a high rate of cellular regeneration due to the wear and tear originated by its function degrading and absorbing nutrients and eliminating waste. The entire cell wall is renewed once a week approximately. This explains why the intestine holds a large number of stem cells in constant division, thereby producing new cell populations of the various types present in this organ.
Researchers at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) headed by ICREA investigator Eduard Batlle, head of the Colorectal Cancer Laboratory, have discovered a new group of intestinal stem cells with very different characteristics to those of the abundant and active stem cells already known in this organ. Performed in collaboration with the Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico (CNAG-CRG), the study has been published in Cell Stem Cell. These new group of stem cells are quiescent, that is to say, they do not proliferate and are apparently dormant.
The researchers describe them as a reservoir of stem cells–it is estimated that there is one quiescent cell for every 10 active intestinal stem cells. In healthy conditions, these cells have no apparent relevant function. However, they are important in situations of stress, , for example, after chemotherapy, in inflammatory processes, and in tissue infections–all conditions in which the population of "normal/active" stem cells is depleted. These quiescent cells would serve to regenerate the organ by giving rise to the various types of cells present in the intestine, renewing the population of "normal/active" stem cells, and restoring balance to the tissue.
Eduard Batlle explains that the discovery of quiescent stem cells in the intestine reveals that stem cell biology is more complex that previously appreciated and that it does not follow ahierarchical model of cell organisation. "In intestinal cell hierarchy, there are no cells above others, so the two populations are in a continual balance to ensure the proper function of the organ".
Most drugs against cancer have a secondary effect on the cells that are dividing in our tissues. "Because quiescent stem cells divide infrequently, they are resistant to many types of chemotherapy and they regenerate the tissue that this treatment has damaged," explains Eduard Batlle, head of one of the labs of international prestige in research into intestinal stem cells and their involvement in colorectal cancer.
Quiescent cells are present in many kinds of tissue. However, in spite of their relevance in tissue regeneration, increasing evidence points to their involvement in tumour development. "It is difficult to study these cells, mainly because they are scarce and there are technical limitations with respect to monitoring, straining and distinguishing them from the others," explains Francisco Barriga, first author of the study and current postdoctoral fellow at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Using advanced techniques, such as genetic tracing of cell lineages and transcriptomic analysis of individual cells, performed by CNAG-CRG and the Bioinformatics and Biostatistics Unit at IRB Barcelona, the group has identified the distinct genetic programme used by quiescent stem cells with respect to normal intestinal ones. This work has been done over six years.
The researchers have labelled this cell population with a specific marker, the Mex3a protein, which has allowed them to track it over time. "We intend to continue studying quiescent stem cells in health and disease and to discover the function of the genes that distinguish them in the colon and in other organs," says Batlle.
###
Reference article:
Francisco M. Barriga, Elisa Montagni, Miyeko Mana, Maria Mendez-Lago, Xavier Hernando-Momblona , Marta Sevillano, Amy Guillaumet-Adkins,Gustavo Rodriguez-Esteban, Simon J. A. Buczacki, Marta Gut, Holger Heyn, Douglas J. Winton, Omer H. Yilmaz, Camille Stephan-Otto Attolini, Ivo Gut, and Eduard Batlle
Mex3a marks a slowly dividing subpopulation of Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells
Cell Stem Cell (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.02.007
Media Contact
Sònia Armengou
[email protected]
34-934-037-255
http://www.irbbarcelona.org
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag