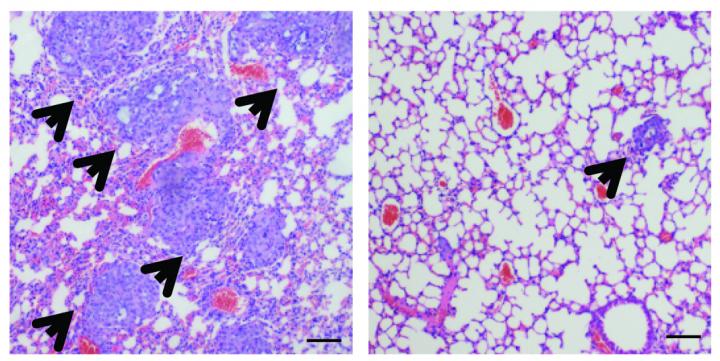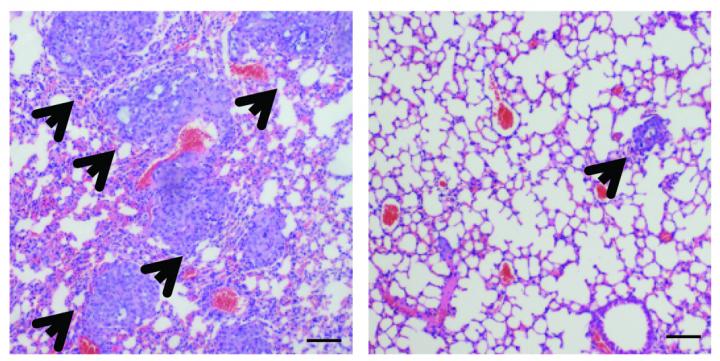
Credit: Wu et al., 2017
Researchers in China have discovered that a metabolic enzyme called AKR1B1 drives an aggressive type of breast cancer. The study, "AKR1B1 promotes basal-like breast cancer progression by a positive feedback loop that activates the EMT program," which has been published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine, suggests that an inhibitor of this enzyme currently used to treat diabetes patients could be an effective therapy for this frequently deadly form of cancer.
Around 15-20% of breast cancers are classified as "basal-like." This form of the disease, which generally falls into the triple-negative breast cancer subtype, is particularly aggressive, with early recurrence after treatment and a tendency to quickly spread, or metastasize, to the brain and lungs. There are currently no effective targeted therapies to this form of breast cancer, which is therefore often fatal.
Crucial to basal-like breast cancer's aggressiveness is a process called epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), in which the cancer cells become more motile and acquire stem cell-like properties that allow them to resist treatment and initiate tumor growth in other tissues.
Chenfang Dong and colleagues at the Zhejiang University School of Medicine in Hangzhou, China, found that the levels of a metabolic enzyme called AKR1B1 were significantly elevated in basal-like and triple-negative breast cancers and that this was associated with increased rates of metastasis and shorter survival times.
The researchers discovered that AKR1B1 expression was induced by Twist2, a cellular transcription factor known to play a central role in EMT. AKR1B1, in turn, elevated Twist2 levels by producing a lipid called prostaglandin F2 that activates the NF-B signaling pathway. This "feedback loop" was crucial for basal-like cancer cells to undergo EMT; reducing AKR1B1 levels impaired the cells' ability to migrate and give rise to cancer stem cells.
Knocking down AKR1B1 also inhibited the growth and metastasis of tumors formed by human basal-like breast cancer cells injected into mice. "Our data clearly suggests that AKR1B1 overexpression represents an oncogenic event that is responsible for the aggressive behaviors of basal-like breast cancer cells," Dong explains.
Moreover, epalrestat, a drug that inhibits AKR1B1 and is approved in Japan to treat peripheral neuropathies associated with diabetes, was similarly able to block the growth and metastasis of human basal-like breast cancer cells. "Since epalrestat is already on the market and has no major adverse side effects, our study provides a proof of principle that it could become a valuable targeted drug for the clinical treatment of basal-like breast cancer," Dong says.
###
Wu et al., 2017. J. Exp. Med. http://jem.rupress.org/cgi/doi/10.1084/jem.20160903?PR
About The Journal of Experimental Medicine
The Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) features peer-reviewed research on immunology, cancer biology, stem cell biology, microbial pathogenesis, vascular biology, and neurobiology. All editorial decisions are made by research-active scientists in conjunction with in-house scientific editors. JEM provides free online access to many article types from the date of publication and to all archival content. Established in 1896, JEM is published by The Rockefeller University Press. For more information, visit jem.org.
Visit our Newsroom, and sign up for a weekly preview of articles to be published. Embargoed media alerts are for journalists only.
Follow JEM on Twitter at @JExpMed and @RockUPress.
Media Contact
Ben Short
[email protected]
212-327-7053
@RockUPress
http://www.rupress.org/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag