Title: Revolutionary Anti-Melanoma Treatment: The Power of Green-Produced Silver Nanoparticles
Melanoma remains one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, notorious for its rapid progression and high mortality rates once metastasis occurs. As a consequence, research has continually sought innovative therapeutic strategies to combat this devastating disease effectively. Among the novel approaches emerging in this realm are metal nanoparticles, particularly silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), which have garnered significant attention as potential anti-cancer agents due to their unique properties. Recent research has demonstrated the remarkable efficacy of AgNPs, especially when conjugated with chlorhexidine, in targeting melanoma cells while minimizing damage to normal tissues.
The study that has sparked interest in the medical community involved investigating the anti-tumor activities of silver nanoparticles and their conjugates. Researchers synthesized these nanoparticles using a green technology approach, leveraging the natural properties of Camellia sinensis, commonly known as green tea. This eco-friendly method not only avoids the use of toxic reagents but also produces nanoparticles with enhanced antimicrobial and anti-tumor properties, making them a promising candidate for clinical applications.
Silver nanoparticles are known for their broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, but their potential as anti-cancer agents has only recently come into focus. The unique characteristics of AgNPs such as size, shape, and surface charge play a crucial role in their biological interactions and subsequent effectiveness in cancer therapy. Notably, nanoparticles with a negative charge and spherical shape have shown to be less toxic than their positively charged counterparts. However, they might possess lower anti-cancer potency, highlighting the delicate balance required in nanoparticle design for optimal therapeutic applications.
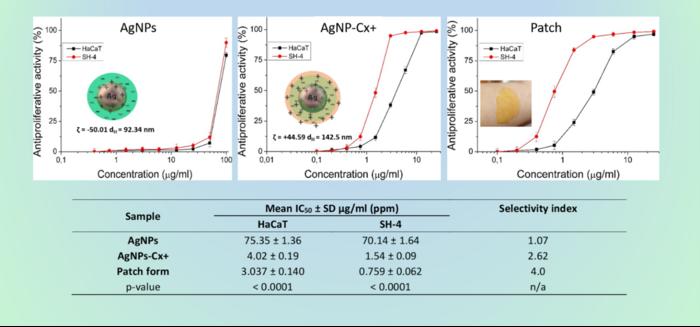
The research highlighted the notable improvements achieved through the synthesis of chlorhexidine-silver nanoparticle conjugates (AgNP-Cx+). These complexes exhibited a staggering 18-fold increase in anti-melanoma activity compared to non-functionalized AgNPs. This enhancement in efficacy is attributed to the synergistic effects of the antimicrobial properties of chlorhexidine and the inherent capacities of silver nanoparticles, resulting in a highly selective approach to targeting melanoma cells without adversely affecting normal cells.
A significant breakthrough in this research was the development of a topical dosage form in the form of an adhesive patch integrating the AgNP-Cx+ complex. This prototype not only serves as a practical application of the synthesized nanoparticles but also exhibits an innovative method of drug delivery that could revolutionize treatment protocols for melanoma patients. The use of polymers like Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and Eudragit® RS in the adhesive patch formulation ensured compatibility with the active agents, facilitating sustained release of the therapeutic components and enhancing the selectivity of the treatment against tumor cells.
The study also conducted comprehensive evaluations of the pharmacological properties of the AgNP-Cx+ complex, measuring crucial parameters such as hydrodynamic diameter and zeta potential. Understanding these characteristics is essential, as they dictate how the nanoparticles interact with different biological environments. Through meticulous experimentation, researchers have been able to demonstrate that these nanoparticles can effectively penetrate tumor tissue, targeting cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, thus paving the way for safer cancer treatments.
To ensure the credibility and reproducibility of the findings, the experimental setup used in this study adhered to rigorous scientific methodologies. Multiple repetitions were conducted to establish reliability in data, and statistical analyses were employed to support claims regarding the effectiveness of the AgNP-Cx+ complexes. Remarkably, the use of a selectivity index allowed researchers to quantify the therapeutic potentials of these nanoparticles, providing a clearer understanding of their application in clinical settings.
The promise of the AgNP-Cx+ complexes extends beyond its efficacy against melanoma; they offer insights into the future of personalized medicine. As research progresses, the goal is to tailor treatments based on individual patient profiles, utilizing nanoparticle technology to provide customized therapeutic solutions that optimize outcomes while reducing side effects.
Moreover, the findings from this research provide a blueprint for future studies aiming to explore the utility of different nanoparticles in oncology. Combining various metallic nanoparticles with other chemotherapeutic agents could lead to devising more advanced strategies to combat not only melanoma but other types of cancer, further broadening the scope of applications for nanoparticle technology in medicine.
In conclusion, the advancements presented in this study signify a crucial leap forward in the fight against melanoma. The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles conjugated with chlorhexidine underscores an era where environmental considerations harmonize with medical innovations. As researchers continue to unlock the potential benefits of these novel treatment modalities, it becomes increasingly evident that nanoparticles could form the core of next-generation therapies, allowing for more effective, targeted, and safer treatment options for cancer patients worldwide.
Subject of Research: Anti-melanoma activity of green-produced nanosilver-chlorhexidine complex
Article Title: Anti-melanoma activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and chlorhexidine-silver nanoparticles conjugates (AgNP-Cx+) against melanoma
News Publication Date: 30-Jan-2025
Web References: http://dx.doi.org/10.3897/pharmacia.72.e143419
References: Ivanova NA (2025) Anti-melanoma activity of green-produced nanosilver-chlorhexidine complex. Pharmacia 72: 1-7
Image Credits: Credit: Nadezhda Ivanova
Keywords: Silver nanoparticles, melanoma, chlorhexidine, nanotechnology, cancer therapy, green synthesis, targeted treatment, drug delivery, antimicrobials, personalized medicine.
Tags: anti-melanoma treatmentantimicrobial properties of AgNPsCamellia sinensis in medicinechlorhexidine conjugateseco-friendly cancer therapiesgreen-synthesized silver nanoparticlesinnovative cancer treatment strategiesmetal nanoparticles in cancer researchnanoparticles in oncologyreducing toxicity in cancer therapiestargeting melanoma cellstherapeutic applications of silver nanoparticles