Credit: Youhei Takeda
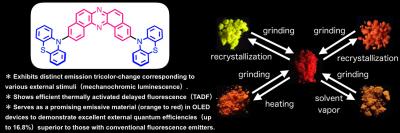
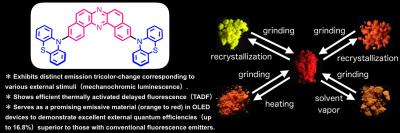
Mechanochromic luminescent (MCL) materials change their color in response to a change in their environment, like pressure and temperature. To date, most MCL materials only change between two colors, limiting their applications. The international research team comprising of chemists at Osaka University and physicists at Durham University has developed tricolor-changing MLC materials. Not only that, the developed materials exhibited efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) and allowed high performance organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) devices. The findings can be read about in Chemical Science.
"Most MCL materials generate two colors by switching between a stable state and one metastable state. To realize multi-color MCL, more metastable states are necessary," explain Professors Youhei Takeda and Satoshi Minakata at the Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering of Osaka University. To create these states, the chemist team led by Takeda and Minakata designed a new molecule by applying a conformationally-switchable phenothiazine (PTZ) as the donor.
"By making the use of a promising and unique acceptor, dibenzophenazine (DBPHZ), which we previously developed, we made a PTZ-DBPHZ-PTZ triad," said Takeda. "In this structure, the PTZ moiety could take two distinct conformers, which therefore in principle creates in total four metastable states as a whole molecule."
In response to heating, fuming, and grinding, the molecule switched its color between yellow, red and orange. The team found that the three colors derive from different conformers in which each PTZ takes either an equatorial or axial conformation relative to the DBPHZ core.
"For red, both of PTZ units take an equatorial-equatorial conformer, for orange, PTZ had an equatorial-axial conformer, and for yellow, PTZ had an axial-axial conformer."
Most OLEDs devices with high energy conversion efficiencies depend on expensive precious metals. TADF light emitting devices, on the other hand, can achieve equal or better efficiency at much lower cost, which is why they have gained popularity for the design of displays in daily electronics like smart phones.
In collaboration with the physicists team at Durham University, the United Kingdom, led by Dr Data and Professor Monkman, they successfully made highly efficient OLED devices by applying the newly developed MCL-TADF molecule as an emissive material. Incorporating the PTZ-DBPHZ-PTZ triad into a light emitting device resulted in an efficiency three times higher than the theoretical maximum of conventional fluorescent materials.
Takeda says that, "Our molecule could become a basis for efficient light-emitting devices and pressure- and temperature-responsive sensors in the future."
###
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag