Credit: Dr. Hidetoshi Arima
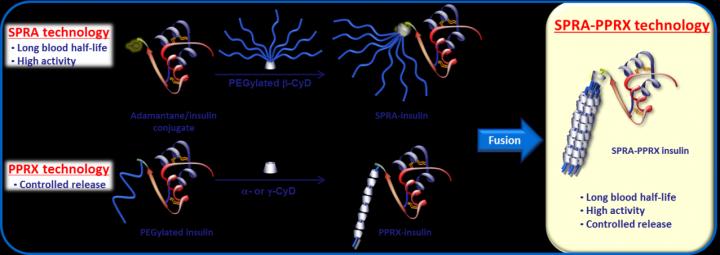
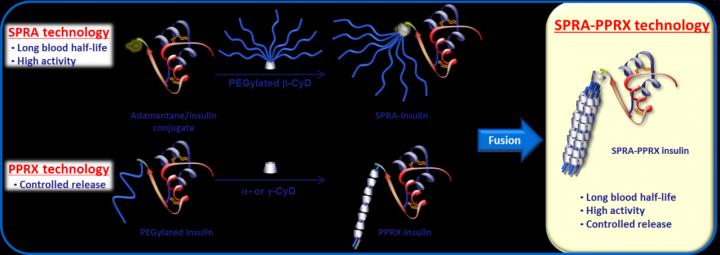
The prevalence of diabetes has grown around the world over the past three decades. In 2016, the World Health Organization estimated that 422 million people had the disease as the rate of obesity also increased. Aside from proper diet and exercise, the best treatment for diabetes is the delivery of insulin into the body that is both controllable and sustainable over time to manage blood glucose levels. Working toward the development of a better insulin delivery system, a research group from Kumamoto University in Japan has been experimenting with polyethylene glycol (PEG) modification (PEGylation) of protein drugs through a host-guest interaction between cyclodextrin (CyD) and adamantane to improve the stability and lifetime of insulin, calling the results of their work "SPRA technology". Their current research focuses on combining SPRA technology with another development of their own that allows for better control of insulin release, "polypseudorotaxane (PPRX) technology". Their goal in combining the two technologies was to develop a sustained and controllable insulin release system.
Using mono- or multi-SPRA-insulin solutions and alpha- or gamma-cylodextrin (CyD), the researchers developed four types of SPRA-insulin/CyD PPRXs, mono-SPRA-insulin/alpha-CyD, mono-SPRA-insulin/gamma-CyD, multi-SPRA-insulin/alpha-CyD, and multi-SPRA-insulin/gamma-CyD PPRX. Alpha-CyDs were found to form PPRXs with a single PEG molecule of SPRA-insulin, whereas gamma-CyD formed them with two molecules. The multi-SPRA-insulin was expected to remain in the blood supply for a relatively long period of time, and the use of different concentrations of CyDs allowed researchers to control insulin release through the CyD and PEG equilibrium reaction.
The hypoglycemic effects of the insulin type with the highest CyD safety profile (multi/gamma) was then assessed in vivo. Two gamma-CyD concentrations, 116 mg/ml and 232 mg/ml, of multi-SPRA-Insulin/gamma-CyD PPRX were tested against a control of multi-SPRA-insulin. "We found that 232 mg/ml gamma-CyD PPRX provided for a longer blood glucose reduction time than the 116 mg/ml PPRX and the control. This is quite important since it shows that both sustained and controlled insulin release can be achieved, which is necessary for the treatment of diabetes," said lead researcher Dr. Hidetoshi Arima. "Furthermore, a blood chemistry safety analysis of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, aspartate aminotransferase, and alanine aminotransferase were found to be unchanged by the insulin injections. Our SPRA-PPRX injections appear to be a safe and reliable insulin release system."
A limitation of this study is the low number of experimental subjects, only 3 rats per group. Also, it was unclear whether or not a diabetic animal model was used in the experiments.
In future work, the researchers plan to combine other forms of insulin with gamma-CyD PPRX with the hope of further improving diabetes treatment. The current findings be found online in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers at ScienceDirect.com.
###
[Reference]
T. Hirotsu, T. Higashi, K. Motoyama, and H. Arima, "Cyclodextrin-based sustained and controllable release system of insulin utilizing the combination system of self-assembly PEGylation and polypseudorotaxane formation," Carbohydrate Polymers, vol. 164, pp. 42-48, Jan. 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.074
Media Contact
J. Sanderson
[email protected]
http://ewww.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/en/news/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag