The Rising Burden of Sepsis Among Cancer Patients in China: A Nationwide Analysis
Sepsis represents a critical public health challenge worldwide, characterized by the body’s extreme response to infection, resulting in tissue damage, organ failure, and potentially death. This bitter reality resonates particularly within the realm of oncology. Cancer patients are inherently at greater risk for sepsis, as the very treatments that may extend life—such as chemotherapy and radiation—can also induce profound immune suppression, leaving them vulnerable to infections. Recent findings from a nationwide observational study in China have unveiled alarming trends regarding sepsis incidence and mortality rates among hospitalized non-child cancer patients between 2017 and 2019.
The study, diligently led by esteemed researchers including Prof. Bin Du, Li Weng, and Hongda Chen, drew from data collected across China’s expansive healthcare network, encapsulating the clinical experiences of over 1.1 million cancer patients. This extensive dataset encompassed 3975 hospitals, offering a comprehensive view of the trends associated with sepsis in an environment where cancer serves as one of the leading public health crises. It is sobering to note that cancer accounts for around 30% of global cancer-related fatalities, highlighting the pressing need to address the secondary complications frequently associated with cancer care, including sepsis.
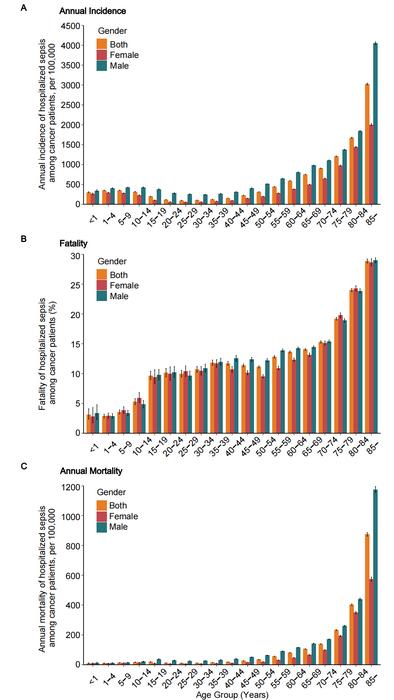
From 2017 to 2019, the occurrence of sepsis among the study population demonstrated a staggering 35.3% increase, elevating the rates from 4111.20 to 5564.42 cases per 100,000 admissions. This significant rise sends a clear message regarding the burgeoning infection rates in a demographic already grappling with compromised health due to cancer. Notably, the incidence of sepsis was markedly higher in older patients—particularly those aged 85 and above—demonstrating that age continues to play a crucial role in determining health outcomes for cancer patients.
The connection between advancing age and increased sepsis risk cannot be overstated. Older adults are well-documented to have physiological changes that alter their immune response, reducing their ability to mount an effective defense against infections. Moreover, the study revealed that hospital mortality rates surged from sepsis, with a stark 53% rise in related mortality observed over the three-year span analyzed. Despite such dire statistics, the case fatality rate (CFR) did exhibit a slight decline, suggesting that while more patients may be succumbing to sepsis, the improvements in critical care practices may also be aiding survival among some patients.
Underlying these trends are the multifaceted challenges posed by cancer-related treatments. The risk of infection is exacerbated in patients undergoing intense chemotherapy regimens or those who have recently had surgical interventions. These patients often face prolongation in hospital stays entailed by necessary medical interventions, hence increasing their exposure to potential pathogens, which can induce sepsis.
In analyzing the results of this nationwide study, researchers pointed to several factors that contribute to healthcare disparities across different regions in China. Limited resources, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and variances in regional medical practices all contribute to uneven sepsis outcomes. The recognition of these disparities is vital, as it underscores the need for targeted interventions that address both the prevention and early detection of infections in cancer patients, especially in underserved areas.
The findings from this study resonate not only within China but also carry implications for global healthcare practices. As sepsis remains a significant cause of mortality in cancer patients, clinicians must prioritize early recognition and management to enhance patient outcomes. Key elements such as infection control practices, timely antibiotic therapy, and an awareness of patient vulnerability must be integrally woven into the fabric of oncologic care.
Furthermore, the need for ongoing surveillance and research into sepsis trends in cancer patient populations is evident. This calls for a collaborative approach among healthcare institutions, policymakers, and researchers to foster an environment where data sharing leads to improved treatment strategies and patient care protocols. By ensuring that healthcare providers are educated about the risks and management of sepsis in cancer patients, it is possible to reduce the mortality rates associated with this severe condition.
While this study offers critical insights into the sepsis landscape facing cancer patients in China, it simultaneously emphasizes the pressing need for proactive healthcare measures. The healthcare system must adapt to address the complex interplay of cancer treatment and sepsis prevention. Patients deserve a care continuum that integrates infection risk assessment and management into the overall cancer care strategy, thereby improving both quality of life and survival outcomes.
In conclusion, while progress in cancer treatment and management is commendable, it must not overshadow the accompanying risks of secondary complications such as sepsis. By melding ongoing research with dedicated interventions focusing on infection prevention, early diagnosis, and prompt treatment, the healthcare community can aim to mitigate the lethal impact of sepsis among its most vulnerable patients. The insights garnered from this study are a clarion call for action, urging stakeholders at all levels to take a comprehensive approach in combating this pervasive threat within the oncology sphere.
Subject of Research: The Burden of Sepsis Among Hospitalized Cancer Patients in China
Article Title: The Rising Burden of Sepsis Among Cancer Patients in China: A Nationwide Analysis
News Publication Date: [Insert Publication Date]
Web References: [Insert any related web references]
References: [Insert any citations or references]
Image Credits: ©Science China Press
Keywords: Sepsis, cancer patients, mortality, healthcare disparities, infection prevention, China, observational study.
Discover more from Science
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.