The study uncovers a unique reparative function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the process of fracture healing, a discovery that adds a new dimension to our understanding of the immune response in tissue regeneration. Tregs, a subset of T cells known for their role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity, are now shown to play a critical part in the intricate interplay between the immune system and bone repair.
The study uncovers a unique reparative function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the process of fracture healing, a discovery that adds a new dimension to our understanding of the immune response in tissue regeneration. Tregs, a subset of T cells known for their role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity, are now shown to play a critical part in the intricate interplay between the immune system and bone repair.
Fracture healing is a complex process that involves a sequence of events, including inflammation, repair, and remodeling. While the initial inflammatory phase is crucial for setting the stage for repair, an excessive or unresolved inflammatory response can impair the healing process. The research highlights how Tregs can modulate this inflammatory response, thereby facilitating the transition to the repair phase.
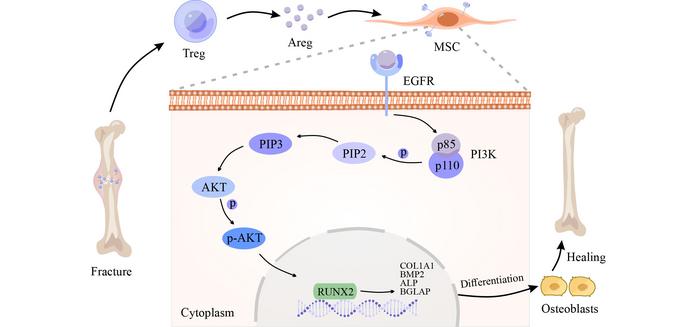
The study uses a combination of in vivo experiments and in vitro analyses to investigate the role of Tregs in fracture healing. It demonstrates that the presence of Tregs at the site of injury is associated with improved healing outcomes. Tregs are shown to exert their reparative effects by secreting specific cytokines that promote the resolution of inflammation and enhance the activity of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation.
Furthermore, the research reveals that Tregs can directly interact with other immune cells, such as macrophages, to modulate their activity. This interaction is important for shifting the wound environment from a pro-inflammatory state to one that is more conducive to tissue repair. The study also examines the molecular mechanisms by which Tregs influence the behavior of osteoblasts, identifying a signaling pathway that is activated by Treg-derived cytokines and leads to increased bone matrix production.
The findings suggest that Tregs have a distinct “repair” role in fracture healing, distinct from their well-known immunosuppressive functions. This dual role of Tregs in both regulating immune responses and promoting tissue regeneration could have significant implications for the development of therapeutic strategies to improve fracture healing, particularly in cases where the healing process is delayed or impaired.
The study also acknowledges the complexity of the immune environment in wound healing and the need for further research to fully understand the interactions between different immune cell types and their contributions to the healing process. It calls for a more nuanced approach to modulating the immune response in clinical practice, one that takes into account the potential for immune cells to promote tissue repair as well as maintain immune homeostasis.
In conclusion, the research provides compelling evidence for the reparative role of Tregs in fracture healing. By enhancing our understanding of the crosstalk between the immune system and bone regeneration, the study opens up new avenues for the development of targeted therapies to promote healing and improve outcomes for patients with fractures. The findings also contribute to the broader field of regenerative medicine, highlighting the potential of modulating immune responses to enhance tissue repair and recovery.
Journal
Frontiers of Medicine
DOI
10.1007/s11684-023-1024-8
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
A distinct “repair” role of regulatory T cells in fracture healing
Article Publication Date
15-Jun-2024