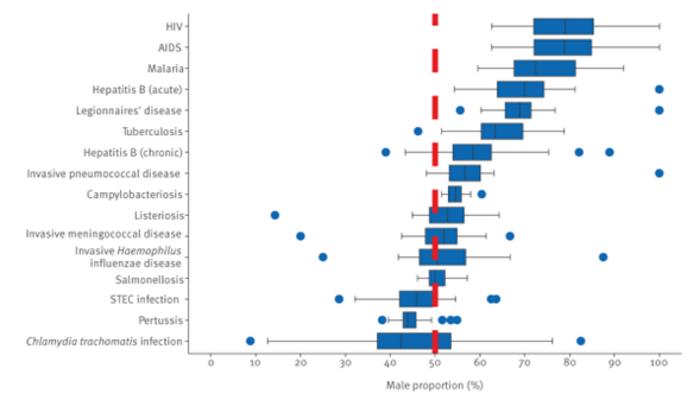
A study published in Eurosurveillance analysing 5.5 million cases of infectious diseases in the European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) over 10 years has found important differences in the relative proportion of notified male versus female cases for several diseases. The proportion of males ranged on average from 40-45% for pertussis and Shiga toxin-producing Escherischia coli (STEC) infections to 75-80% for HIV/AIDS.
A study published in Eurosurveillance analysing 5.5 million cases of infectious diseases in the European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) over 10 years has found important differences in the relative proportion of notified male versus female cases for several diseases. The proportion of males ranged on average from 40-45% for pertussis and Shiga toxin-producing Escherischia coli (STEC) infections to 75-80% for HIV/AIDS.
“Although this study was not able to fully explain the differences observed across countries and diseases, it offers some interesting leads,” said Julien Beauté, principal expert in general surveillance at the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and co-author of the study.
“Based on possible explanation(s) for these differences, public health professionals should further investigate whether this could apply to their setting to eventually design sex-specific interventions for infectious disease prevention and control.”
Methodology
Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis of surveillance data on cases reported between 2012 and 2021 for 16 infectious diseases notifiable at the EU level, and included data from 30 countries.
“Surveillance data at EU/EEA level provide a unique opportunity to compare epidemiological patterns and testing or screening policies across countries,” said Julien Beauté.
The study recorded male proportions of cases for each disease, which were also computed by country, year and six age groups (< 5, 5–14, 15–24, 25–44, 45–64, and ≥ 65 years). The number of reporting countries ranged from 24 (Chlamydia trachomatis infection and hepatitis B) to 30 (HIV/AIDS, invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease, Legionnaires’ disease and tuberculosis). Cases reported with sex recorded as ‘other’ were excluded.
Results
For campylobacteriosis, acute hepatitis B, Legionnaires’ disease, malaria and HIV/AIDS, the male proportion was above 50% in all countries. Only two diseases, pertussis and STEC infection, had a male proportion below 50% in most countries.
The proportion of males did not vary significantly between most countries, which could indicate common drivers for sex differences across countries. Most outliers were countries reporting few cases. Country-specific screening policies could also explain male proportions observed in countries that diverged from the EU/EEA average.
Possible sex- and gender-related factors and public health implications
The role of biological sex and gender in the transmission of infectious diseases is complex, and depends on context and disease. While the study could not completely explain the sex differences observed in the data, it did provide some insights.
Some STIs and blood-borne diseases such as HIV and hepatitis B had a higher proportion of male cases, likely reflecting the higher risk of infection associated with certain modes of transmission. The higher male proportion for malaria could be due to higher exposure in males, with one previous study suggesting women are less likely to be infected by vector-borne diseases.
Other differences could be related to risk and testing. For example, the lower proportion of males with C. trachomatis infections was mostly explained by testing policies, as chlamydia prevalence is likely to be similar in both sexes, but screening programmes often target sexually active young women.
Findings underscored the relevance of characteristics of surveillance systems in interpreting data. Julien Beauté said:
“The study highlighted the importance of documenting some key characteristics of surveillance systems or variables to help interpret surveillance data, including case detection policy (e.g. screening of asymptomatic people), variables related to a specific setting of infection (e.g. travel, occupation) or mode of transmission (e.g. sex between men), that may drive a sex difference, and information on both sex and gender for some diseases such as sexually-transmitted infections.”
These would help better identify differences related to sex and gender, which would then inform and improve the design of targeted public health interventions.
Journal
Eurosurveillance
DOI
10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2024.29.33.2300655
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Differences between males and females in infectious diseases notifications in the EU/EEA, 2012 to 2021
Article Publication Date
15-Aug-2024
COI Statement
None declared.