In a pioneering development for the biomedical field, a research team led by Yuanjin Zhao from Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China, has published a research article in Engineering. The article, titled “Controllable Histotomy Based on Hierarchical Magnetic Microneedle Array Robots,” introduces a novel technique for tissue slicing and cultivation that could revolutionize the way primary tissues are handled in clinical settings.
Credit: Xiaoxuan Zhang et al.
In a pioneering development for the biomedical field, a research team led by Yuanjin Zhao from Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China, has published a research article in Engineering. The article, titled “Controllable Histotomy Based on Hierarchical Magnetic Microneedle Array Robots,” introduces a novel technique for tissue slicing and cultivation that could revolutionize the way primary tissues are handled in clinical settings.
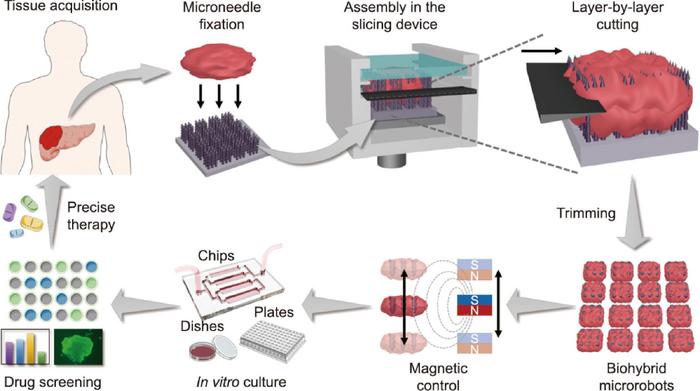
The in vitro cultivation of patient-derived tissues is crucial for accurate diagnosis, precision medication, individualized therapy, and tissue engineering. However, current tissue slicing and cultivation techniques often fall short of clinical requirements. The research team’s innovative approach addresses these challenges by introducing a controllable histotomy strategy that utilizes hierarchical magnetic microneedle array robots.
This strategy involves a three-dimensionally printed, mortise-tenon-structured slicing device, coupled with a magnetic-particle-loaded and pagoda-shaped microneedle array scaffold. The multilayered structure of the microneedles allows for the effective fixation of tissue specimens, avoiding tissue slipping during the slicing process. Moreover, the encapsulated magnetic microneedle fragments enable the tissue pieces to act as magnetically responsive biohybrid microrobots, facilitating their separation, transportation, and dynamic culture through magnetic fields.
The team demonstrated the technique’s efficacy by tailoring primary pancreatic cancer tissues into tiny pieces and culturing them in multilayered microfluidic chips for high-throughput drug screening. The results indicate the promising future of this technique in clinical settings, offering a significant step forward in the precision medicine landscape.
“The development of this controllable histotomy technique marks a significant advancement in the field of tissue engineering and drug screening,” said Jiaming Wu, the editor of Engineering. “By leveraging the capabilities of magnetic microneedle array robots, researchers have been able to create a more efficient and precise method for tissue manipulation and analysis.”
The research article also discusses the potential for further improvements to the technique, such as automating the horizontal sectioning and production of tissue cubes, and scaling up the microtomy device for higher throughput. Additionally, the team envisions the application of this technology beyond cancer research, to other types of patient-derived primary tissues, and its potential for long-term tissue cultivation and observation.
The innovative work by Yuanjin Zhao’s team not only pushes the boundaries of current tissue analysis techniques but also opens up new possibilities for personalized medicine and the development of more effective treatments. As the technology matures, it is expected to play a pivotal role in the advancement of biomedical research and clinical applications.
The paper “Controllable Histotomy Based on Hierarchical Magnetic Microneedle Array Robots,” authored by Xiaoxuan Zhang, Hanxu Chen, Taiyu Song, Jinglin Wang, Yuanjin Zhao. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.05.004. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
Journal
Engineering
DOI
10.1016/j.eng.2024.05.004
Article Title
Controllable Histotomy Based on Hierarchical Magnetic Microneedle Array Robots
Article Publication Date
21-May-2024




