Clathrate hydrates are complex water structures that contain foreign guest molecules inside a host water-molecule shell. A predicted clathrate hydrate phase structure has been stably synthesized in the lab and may play an important role in future material science research.
Credit: Yokohama National University
Clathrate hydrates are complex water structures that contain foreign guest molecules inside a host water-molecule shell. A predicted clathrate hydrate phase structure has been stably synthesized in the lab and may play an important role in future material science research.
Water molecules are made up of just three atoms: two hydrogen atoms bound to a single oxygen atom. Individual water molecules can weakly bind to one another and other molecules, changing their collective physicochemical properties.
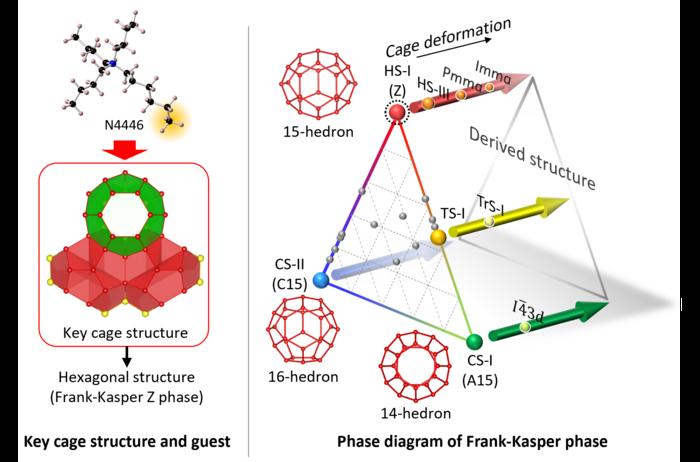
Clathrate hydrates, in particular, are lattices of water molecules that self-assemble around guest substances to create hydrogen-bonded frameworks. These frameworks belong to Frank-Kasper (FK) phases because of their geometric arrangement as close-packed tetrahedra. Remarkably, the framework is made entirely of weak bonds between water and guest molecules, making some predicted clathrate hydrate structures very difficult to synthesize.
The HS-I structure is one such clathrate hydrate phase that generates hexagonal crystals. A prior study had reported a metastable form of the HS-I structure, but a stable form eluded researchers. To address this issue, a team of chemical engineers and crystallographers from Yokohama National University and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial and Science Technology (AIST) in Japan generated a stable form of HS-I clathrate hydrate and analyzed the true structure of the HS-I form.
The team published the study in the July 24th issue of Science Advances.
“The hexagonal structure, one of the three primitive [FK] structures of clathrate hydrates, can be geometrically arranged but is thermodynamically unstable and had not been created in practice. We created a substance which fits the key part of this structure and succeeded in stabilizing the hexagonal structure using this material,” said Sanehiro Muromachi, associate professor in the Graduate School of Engineering at Yokohama National University.
Specifically, the research team created stable HS-I clathrate hydrate by fine-tuning the guest molecule, tri-n-butyl, n-hexylammonium chloride (N4446Cl). The n-hexyl chain, in particular, was the only guest molecule capable of stabilizing the true form of a pentakaidecahedron (12 pentagons + 3 hexagons) water-molecule cage required for the HS-I structure.
Stable forms were produced under gas pressures of both methane and carbon dioxide and also atmospheric pressure. The hexagonal crystal structure was made up of individual dodecahedrons (12 pentagons), tetrakaidecahedrons (12 pentagons + 2 hexagons) and pentakaidecahedrons composed of pentagonal and/or hexagonal faces.
Carefully tuning the guest molecule to generate stable HS-I clathrate hydrate may allow researchers to generate a combination of mixed FK phases to engineer clathrate hydrate with properties ideal for a variety of applications. “Discovering the final primitive structure of clathrate hydrates opens material science exploration. We expect these findings to be applied to storage and transportation technologies for natural gas and synthetic fuels, carbon dioxide separation and recovery technologies, and to the creation of new materials,” said Muromachi.
One important aspect of the team’s research was their ability to synthesize HS-I clathrate hydrate under conditions similar to ambient temperature and pressure. A trend of earlier studies designed to create new water structures focused on extreme conditions, such as ultrahigh pressure, vacuum or ultracold temperatures. This most recent finding highlights the ability to apply the physicochemical properties of different water lattices to ecological research and simplified material development.
The synthesis of stable HS-I clathrate hydrate will have a broad impact on many different fields and will likely spur the synthesis of additional FK phase structures for other compounds by finely tuning guest molecule structures. “The HS-I structure is expected to be applied to storage and transportation technologies for natural gas and synthetic fuels and CO2 capture technologies based on the clathrate hydrates. We will also continue to develop new materials that incorporate mixed phases,” said Muromachi.
Satoshi Takeya, chief senior researcher from the Energy Process Research Institute (EPRI) at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial and Science Technology (AIST) in Tsukuba, Japan also contributed to this research.
This research was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) for a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists: Grant No. 18K13710.
##
Yokohama National University (YNU or Yokokoku) is a Japanese national university founded in 1949. YNU provides students with a practical education utilizing the wide expertise of its faculty and facilitates engagement with the global community. YNU’s strength in the academic research of practical application sciences leads to high-impact publications and contributes to international scientific research and the global society. For more information, please see: https://www.ynu.ac.jp/english/
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.adp4384
Article Title
Discovery of the final primitive Frank-Kasper phase of clathrate hydrates
Article Publication Date
24-Jul-2024




