A new study shows how organic molecules greatly influence the redox potential of gold nanoparticles, with differences up to 71 mV. Using experiments and computer simulations, the study highlights the important role of capping agents in controlling the nanoparticles’ electrochemical properties and also identifies how kinetic effects impact these interactions. These findings have practical uses in areas like nanoparticle dispersion, monitoring ligand exchange, and advancements in fields such as catalysis, electronics, and drug delivery, showing the potential for customizing nanoparticle behavior for specific applications.
Credit: Din Zelikovich (PhD student), Pavel Savchenko (MSc student) and Hadassah Elgavi Sinai (Senior Researcher).
A new study shows how organic molecules greatly influence the redox potential of gold nanoparticles, with differences up to 71 mV. Using experiments and computer simulations, the study highlights the important role of capping agents in controlling the nanoparticles’ electrochemical properties and also identifies how kinetic effects impact these interactions. These findings have practical uses in areas like nanoparticle dispersion, monitoring ligand exchange, and advancements in fields such as catalysis, electronics, and drug delivery, showing the potential for customizing nanoparticle behavior for specific applications.
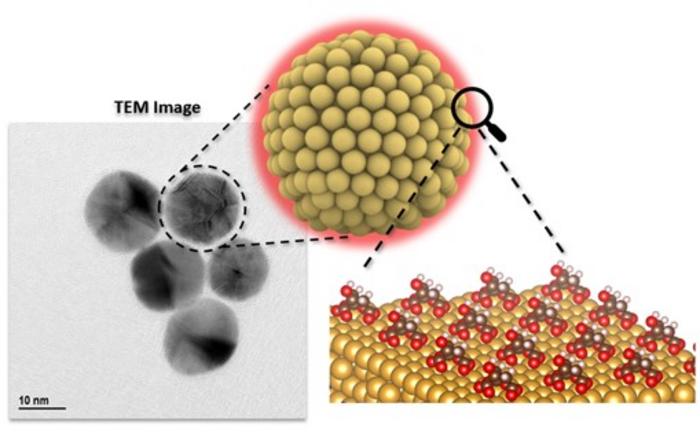
A recent study led by Prof. Daniel Mandler with Prof. Roi Baer and Dr. Hadassah Elgavi Sinai and a team at Hebrew University, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, reveals how organic molecules affect the behavior of tiny gold particles absorbed on surfaces. Their research deepens our understanding of how these nanoparticles absorbed on surfaces interact with their surroundings, offering important insights for various uses. The research was conducted jointly by PhD student Din Zelikovich, who carried out very careful experiments and MSc student Pavel Savchenko, who conducted the theoretical calculations.
The study found that different molecules, like 2- and 4-mercaptobenzoic acid, can cause gold nanoparticles to have significantly different electrical properties, with differences up to 71 Mv (millivolts). This highlights how crucial these molecules are in determining how nanoparticles behave.
Using advanced computer simulations and experiments, the collaboration between the experimental and theoretical teams showed that some molecules stick to gold surfaces in predictable ways, matching what they saw experimentally. However, they also found that the kinetics, namely, the rate the nanoparticles are oxidized adds more complexity to how they interact.
For instance, they discovered that gold nanoparticles stabilized by 4-mercaptobenzoic acid reacted twice as quickly as those with citrate. This finding, backed by scientific theories, shows just how much the right molecule can change how these nanoparticles act.
Prof. Daniel Mandler emphasized the significance of the research, stating, “Our study demonstrates the profound impact that capping agents have on the redox properties of nanoparticles. This understanding allows us to fine-tune nanoparticle behavior for specific applications, potentially leading to significant impact in fields ranging from catalysis to drug delivery.”
As the scientific community continues to explore the intricate world of nanoparticles, this research contributes valuable knowledge to the field of nanoparticle chemistry. By shedding light on the complex interactions between nanoparticles and their capping agents, this study opens new avenues for designing and optimizing nanoparticles for a wide range of applications, promising exciting developments in nanotechnology in the years to come.
Journal
Journal of the American Chemical Society
DOI
10.1021/jacs.4c02524
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
The Effect of the Capping Agents of Nanoparticles on Their Redox Potential
Article Publication Date
3-Jul-2024




