The pressing need for effective greenhouse gas emission reduction strategies has intensified the focus on converting CO2 and methane (CH4) into useful chemicals like syngas. The dry reforming of methane (DRM) reaction is a promising avenue for this conversion. However, the efficiency of this process is heavily dependent on the catalyst used, with Ni-based catalysts being of particular interest due to their comparable activity to precious metals and their economic viability. The size of the active metal particles in these catalysts is known to influence their performance, but the detailed mechanisms behind this size-dependency have been elusive.
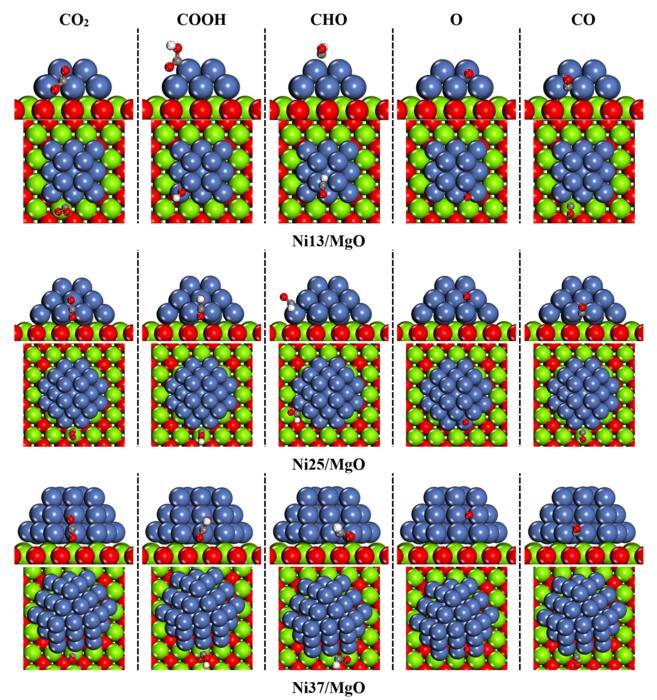
A research group of Juntian Niu from Taiyuan University of Technology studied the impact of metal particle size on CO2 activation and CO formation within the DRM reaction. They construct Nix/MgO (x = 13, 25, 37) models to investigate the activation pathways and identify how the particle size significantly influences the DRM reaction’s efficiency and the catalyst’s resistance to carbon formation.
The findings reveal that CO2 is more likely to undergo chemisorption on Nix/MgO before activation. As the particle size varies, so does the primary activation pathway of CO2. Notably, the smallest Ni13/MgO favors direct dissociation, while larger particles, Ni25/MgO and Ni37/MgO, are more inclined toward hydrogenation dissociation. The oxidation of surface carbon atoms and CH is more readily facilitated on Ni25/MgO, suggesting superior resistance to carbon formation compared to other particle sizes studied.
This study’s theoretical insights are pivotal for the development of highly efficient Ni-based catalysts for the DRM reaction. By understanding the role of Ni particle size, researchers can potentially enhance the catalyst’s performance and stability, thereby contributing to more effective greenhouse gas utilization and cleaner energy production.
Credit: HIGHER EDUCATION PRESS
The pressing need for effective greenhouse gas emission reduction strategies has intensified the focus on converting CO2 and methane (CH4) into useful chemicals like syngas. The dry reforming of methane (DRM) reaction is a promising avenue for this conversion. However, the efficiency of this process is heavily dependent on the catalyst used, with Ni-based catalysts being of particular interest due to their comparable activity to precious metals and their economic viability. The size of the active metal particles in these catalysts is known to influence their performance, but the detailed mechanisms behind this size-dependency have been elusive.
A research group of Juntian Niu from Taiyuan University of Technology studied the impact of metal particle size on CO2 activation and CO formation within the DRM reaction. They construct Nix/MgO (x = 13, 25, 37) models to investigate the activation pathways and identify how the particle size significantly influences the DRM reaction’s efficiency and the catalyst’s resistance to carbon formation.
The findings reveal that CO2 is more likely to undergo chemisorption on Nix/MgO before activation. As the particle size varies, so does the primary activation pathway of CO2. Notably, the smallest Ni13/MgO favors direct dissociation, while larger particles, Ni25/MgO and Ni37/MgO, are more inclined toward hydrogenation dissociation. The oxidation of surface carbon atoms and CH is more readily facilitated on Ni25/MgO, suggesting superior resistance to carbon formation compared to other particle sizes studied.
This study’s theoretical insights are pivotal for the development of highly efficient Ni-based catalysts for the DRM reaction. By understanding the role of Ni particle size, researchers can potentially enhance the catalyst’s performance and stability, thereby contributing to more effective greenhouse gas utilization and cleaner energy production.
Journal
Frontiers in Energy
DOI
10.1007/s11708-024-0952-6
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Impact of Ni particle size on CO2 activation and CO formation during reforming process: A density functional theory study
Article Publication Date
16-Jul-2024




