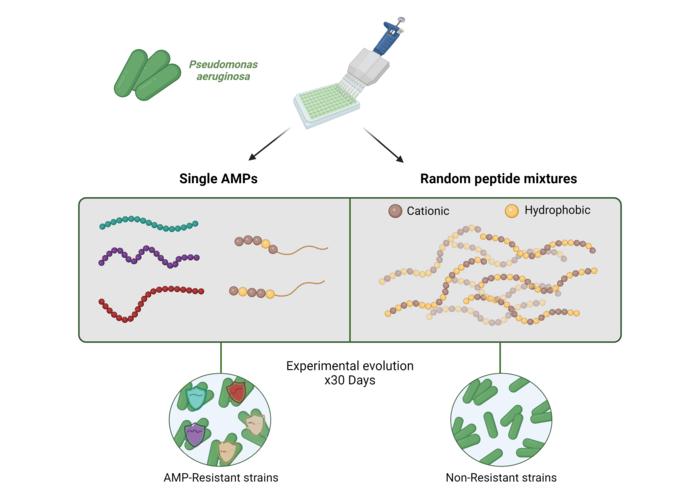
A common infection-causing bacteria was much less likely to evolve antibiotic resistance when treated with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides rather than a single peptide, making these mixtures a viable strategy for developing new antibiotic treatments. Jens Rolff of the Freie Universitat Berlin, Germany, and colleagues report these findings in a new study publishing July 2nd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Credit: Bar Manon (CC-BY 4.0, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
A common infection-causing bacteria was much less likely to evolve antibiotic resistance when treated with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides rather than a single peptide, making these mixtures a viable strategy for developing new antibiotic treatments. Jens Rolff of the Freie Universitat Berlin, Germany, and colleagues report these findings in a new study publishing July 2nd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria have become a major threat to public health. The World Health Organization estimates that 1.27 million people died directly from drug-resistant strains in 2019 and these strains contributed to 4.95 million deaths. While bacteria naturally evolve resistance to antibiotics, misuse and overuse of these drugs has accelerated the problem, rendering many antibiotics ineffective. One emerging strategy to combat antibiotic resistance is the use of antimicrobial peptides, which are chains of amino acids that function as broad-spectrum antimicrobial compounds and are key components of the innate immune system in animals, fungi and plants.
In the new study, researchers investigated whether antimicrobial peptide mixtures synthesized in the lab could reduce the risk of the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa from evolving antimicrobial resistance, compared to exposure to a single antimicrobial peptide. They found that using antimicrobial peptide mixtures carried a much lower risk of the bacteria developing resistance. The mixtures also helped prevent the bacteria from developing cross-resistance to other antimicrobial drugs, while maintaining – or even improving – drug sensitivity.
Overall, the findings suggest that the use of antimicrobial peptide mixtures is a strategy worth pursuing in the search for new, longer-lasting treatments for bacteria. The researchers suspect that using a cocktail of multiple antimicrobial peptides creates a larger set of challenges for bacteria to overcome, which can potentially delay the evolution of resistance, compared to traditional antibiotics. Furthermore, these cocktails can be synthesized affordably, and previous studies have shown them to be non-toxic in mice.
Lead author Bernardo Antunes adds, “Even after four weeks of exposure, a usual treatment duration for Pseudomonas infections, we could not find resistance against our new random peptide, but against other antimicrobials.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002692
Citation: Antunes B, Zanchi C, Johnston PR, Maron B, Witzany C, Regoes RR, et al. (2024) The evolution of antimicrobial peptide resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is severely constrained by random peptide mixtures. PLoS Biol 22(7): e3002692. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002692
Author Countries: Israel, Germany, United Kingdom, Switzerland
Funding: This work was funded by the Joint Berlin-Jerusalem Postdoctoral Fellowship Program offered by the Freie Universität Berlin (FUB) and Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI) to BA. The project was further supported by a grant from the Volkswagen Foundation (grant no. 96517) to JR. CZ was funded by the DFG (FOR 5026). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS Biology
DOI
10.1371/journal.pbio.3002692
COI Statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.




