When ultrafast electrons are deflected, they emit light – synchrotron radiation. This is used in so called storage rings in which magnets force the particles onto a closed path. This light is longitudinally incoherent and consists of a broad spectrum of wavelengths. Its high brilliance makes it an excellent tool for materials research. Monochromators can be used to pick out individual wavelengths from the spectrum, but this reduces the radiant power by many orders of magnitude to values of a few watts only.
Credit: HZB/ Communications Physics
When ultrafast electrons are deflected, they emit light – synchrotron radiation. This is used in so called storage rings in which magnets force the particles onto a closed path. This light is longitudinally incoherent and consists of a broad spectrum of wavelengths. Its high brilliance makes it an excellent tool for materials research. Monochromators can be used to pick out individual wavelengths from the spectrum, but this reduces the radiant power by many orders of magnitude to values of a few watts only.
Size matters
But what if a storage ring were instead to deliver monochromatic, coherent light with outputs of several kilowatts, analogous to a high-power laser? Physicist Alexander Chao and his doctoral student Daniel Ratner found an answer to this challenge in 2010: if the electron bunches orbiting in a storage ring become shorter than the wavelength of the light they emit, the emitted radiation becomes coherent and therefore millions of times more powerful.
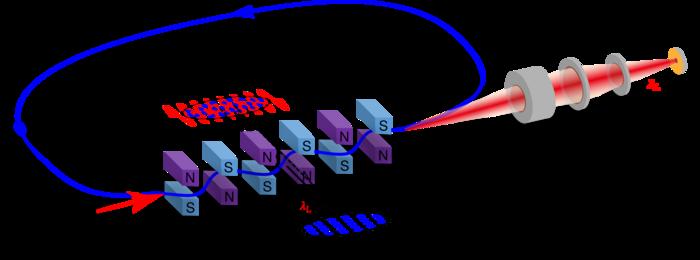
“You need to know that the electrons in a storage ring are not homogeneously distributed,” explains Arnold Kruschinski, PhD student at HZB and lead author of the paper. “They move in bunches with a typical length of about a centimetre and a distance around 60 centimetres. That is six orders of magnitude more than the micro-bunches proposed by Alexander Chao.” Chinese theorist Xiujie Deng has defined a set of settings for a specific type of circular accelerator, the isochrone or “low-alpha” rings, for the Steady-State Micro-Bunching project (SSMB). After interacting with a laser, these create short particle bunches that are only one micrometre long.
The research team from HZB, Tsinghua University and PTB already demonstrated that this works in a proof-of-principle experiment in 2021. They used the Metrology Light Source (MLS) in Adlershof – the first storage ring ever designed for low-alpha operation. The team has now been able to fully verify Deng’s theory for generating micro-bunches in extensive experiments. “For us, this is an important step on the way to a new type of SSMB radiation source,” says Arnold Kruschinski.
The long road to success
However, HZB project manager Jörg Feikes is certain that it will take some time until then. He sees some parallels between the SSMB and the development of free-electron lasers. “After initial experiments and decades of development work, this idea turned into kilometre-long, superconducting accelerator,” he says. “Such developments are very long-term. It starts with an idea, then a theory, and then there are experimenters who gradually realise it and I think that SSMB will develop in the same way.”
Text by Kai Dürfeld / Science writer
Journal
Communications Physics
DOI
10.1038/s42005-024-01657-y
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Confirming the theoretical foundation of steady-state microbunching
Article Publication Date
21-May-2024
COI Statement
none




