A new peer-reviewed study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington; the University of Nevada, Reno; Mokwon University in Daejeon, Korea; and Texas A&M University at Corpus Christi shows the Deepwater Horizon (DWH) oil spill of 2010 affected wildlife and their habitat much more than previously understood.
Credit: Photo courtesy Masoud Rostami at UT Arlington
A new peer-reviewed study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington; the University of Nevada, Reno; Mokwon University in Daejeon, Korea; and Texas A&M University at Corpus Christi shows the Deepwater Horizon (DWH) oil spill of 2010 affected wildlife and their habitat much more than previously understood.
“Overall, we found the area of deep-sea floor affected by the DWH spill was significantly larger than previously thought,” said Masoud Rostami, an author of the study and assistant professor of instruction in UTA’s Division of Data Science.
In recent decades, deep-water ecosystems in lakes, oceans, and seas around the world have faced pressures from offshore oil and gas production, including frequent contamination from oil and other pollutants. The DWH oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico that started on April 20, 2010, was the largest marine oil spill in U.S. history, releasing nearly 5 million barrels of crude oil and hydrocarbon gases over 87 days, with 3.2 million barrels of oil remaining in the water after cleanup efforts.
This spill greatly exceeded the amount of natural discharge of oil that seeps in the Gulf each year, and up to 35% of the pollutants were trapped below the surface, severely impacting the lives and habitats of the plants, animals, and microorganisms (like bacteria and fungi) that live deep in the ocean. For this study, the researchers focused on the harpacticoid copepods, a type of crustacean that lives near the bottom of the ocean, to better understand the DWH spill’s effects on the deep-sea ecosystem in the Gulf of Mexico. Copepods are good for this type of study because they live in several different deep-sea habitats and are known to be sensitive to pollution.
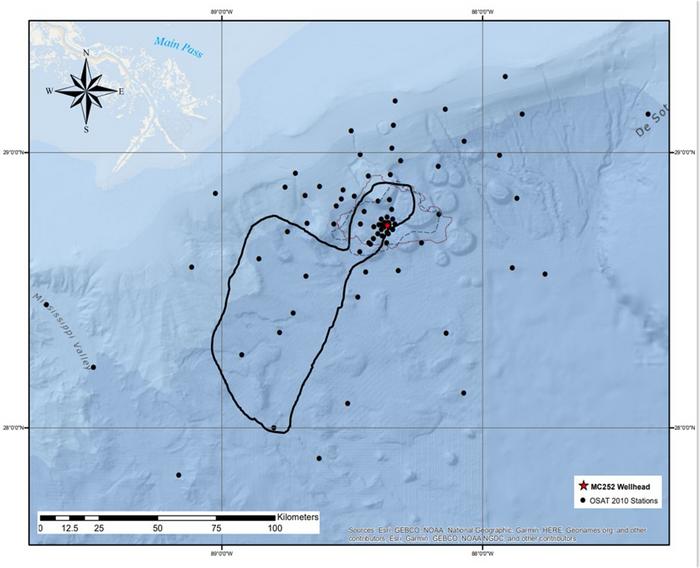
Researchers found the spill affected biodiversity over an area of 1,100 square miles—a area nearly nine times larger than earlier studies on DWH. Using advanced methodologies, including remote sensing, multivariate statistical analysis, and machine-learning approaches, the team detected subtle changes in the deep-sea copepod community composition.
“This study demonstrates that harpacticoid copepod diversity dramatically declined because of DWH oil pollution,” said Rostami.
***
This work was supported by BP, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the U.S. Department of Interior’s Deepwater Horizon National Resource Damage Assessment.
Journal
Marine Pollution Bulletin
DOI
10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116343
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Harpacticoid copepods expand the scope and provide family-level indicators of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill deep-sea impacts
Article Publication Date
1-May-2024
COI Statement
This manuscript is derived from the authors’ participation in the DWH Natural Resource Damage Assessment (NRDA). The authors thank Christopher Lewis (Industrial Economics, Inc.), Rob Ricker (NOAA), Jeff Hyland (NOAA, retired), and Cynthia Cooksey (NOAA) for their contributions to the NRDA process and prior related manuscripts. A very special thanks to Ms. Heejin Moon for assistance with taxonomic identification. Many undergraduate and graduate students assisted with sample sorting and picking, including: Tony Kamikawa, Paul Bennetts, Colin Morrison, Grey Saiyo, Nate Conrad-Forrest, Erin Parsons, and Elizabeth Everest.




