This study is led by Prof. Qiang Deng (Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University), Prof. Ke Lan (State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan University), and Prof. Yueqiu Gao (Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine).
Credit: ©Science China Press
This study is led by Prof. Qiang Deng (Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University), Prof. Ke Lan (State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan University), and Prof. Yueqiu Gao (Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine).
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection can lead to advanced liver pathology. HBV has been infecting humans for over 10,000 years, with coordinated viral gene expression to establish persistent infection. It is generally believed that HBV is not directly cytopathic in infected hepatocytes; chronic hepatitis and associated liver injury progress due to the complex interplay between virus-infected cells and the host immune response. However, this notion requires re-examination in pathophysiological settings. Naturally occurring double mutation C1766T/T1768A in HBV basal core promoter (BCP) was associated with a fatal outbreak of fulminant hepatitis and led to an enhanced HBc production up to 15-fold. In this study, Su and colleagues established a transgenic murine model expressing a BCP-mutated HBV genome. Unlike previous studies on the wild-type virus, the BCP-mutated HBV transgenic mice manifested chronic liver injury that culminated in cirrhosis and tumor development with age. Notably, agonistic anti-Fas treatment induced fulminant hepatitis in these mice even at a negligible dose, reminiscent of mitochondria-regulated death signal amplification.
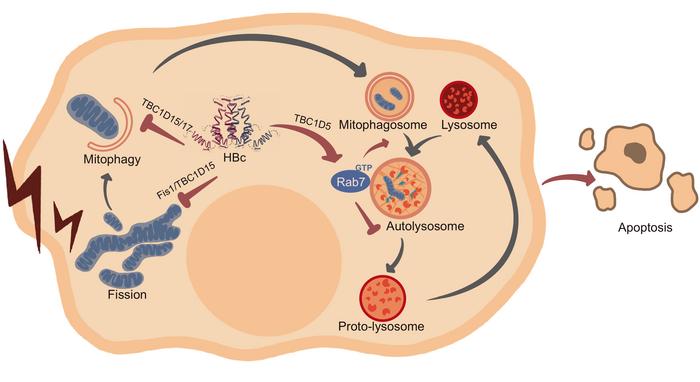
The BCP-mutated HBV transgenic mice provide a valuable model for understanding chronic hepatitis B progression. As the BCP mutant exhibits a striking increase in HBV core protein (HBc) expression, it is speculated that HBc is actively involved in hepatocellular injury. Consistent with this idea, the authors found that HBc interferes with Fis1-stimulated mitochondrial recruitment of Tre-2/Bub2/Cdc16 domain family member 15 (TBC1D15). HBc may also inhibit multiple Rab GTPase-activating proteins, including Rab7-specific TBC1D15 and TBC1D5, by binding to their conserved catalytic domain. In cells under mitochondrial stress, HBc thus perturbs mitochondrial dynamics and prevents the recycling of damaged mitochondria. Moreover, sustained HBc expression causes lysosomal consumption via Rab7 hyperactivation, which further hampers late-stage autophagy and substantially increases apoptotic cell death. In line with the in vitro results, adenoviral vector-delivered HBc expression caused profound liver injury in immune-deficient SCID mice. The above study showed for the first time that HBc can be directly cytopathic independent of immune-mediated cytotoxicity.
Collectively, the present study highlights an unexpected cytopathic role of HBc and may provide a new mechanistic insight into fatal HBV BCP mutation-associated hepatitis. Accordingly, the HBV BCP mutant may stimulate excessive oxidative stress while HBc overexpression concomitantly inhibits the disposal of damaged mitochondria, thereby causing irreversible cellular injury and fulminant hepatitis. In the scenario of chronic viral infection, the immunopathological damage and the direct cytopathic effect of the virus jointly promote the progression of chronic liver disease, and eventually lead to the development of hepatocellular cancer. In this regard, antivirals with the potential to inhibit HBc expression or promote HBc degradation may have promising prospects for treatment of chronic hepatitis B.
Journal
Science Bulletin
DOI
10.1016/j.scib.2024.04.014




