SAN ANTONIO — May 28, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute has created a comprehensive data analysis tool to help metropolitan areas curb urban heat islands (UHIs) and pursue mitigation methods for especially vulnerable populations. This internally funded project was a collaboration with the City of San Antonio.
UHIs occur when dense concentrations of pavement and buildings absorb heat and raise surrounding temperatures. Without green spaces to provide a cooling effect, UHI temperatures can exceed other areas by as much as 20 degrees Fahrenheit, which could be dangerous to residents during summer.
“Tackling UHIs goes beyond simply analyzing spatial temperature differences,” said SwRI Senior Environmental Engineer Justin Long. “A comprehensive analysis of UHIs must also identify vulnerable populations, as well as viable mitigation methods in the areas where they reside.”
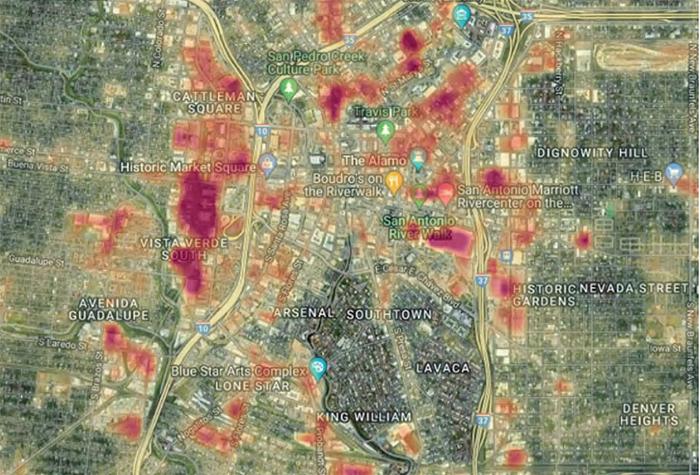
SwRI has created a data fusion tool that compiled and combined more than 230 datasets collected from several different city departments and public databases. The tool allows city leaders to analyze and explore several scenarios at once.
“Before the City of San Antonio can prioritize resources to address UHIs, it needs to identify all their characteristics, particularly zones where conditions are the most severe and that have a direct impact on the public,” Long said. “We discovered, for example, that many areas that experience extreme heat are also zones with historically high bus ridership. On hot summer days, pedestrians in these areas may be at higher risk of prolonged heat exposure and related illnesses.”
The tool could show city leaders where bus stops and high surface temperatures overlap and locations where planting trees or erecting artificial structures to mitigate the heat could be most effective.
To demonstrate how the data fusion tool could inform UHI policy making, SwRI created a hypothetical case study, merging multiple datasets from different sources for comparison. The scenario focused on locating regions with concentrated UHI effects that could pose a health hazard to bus riders and reduce the use of public transportation. Equipped with this knowledge, city officials could select locations to implement UHI mitigation strategies based on local socioeconomic, environmental and infrastructure characteristics.
“Mitigation strategies must be tailored to the specific characteristics of locations experiencing extreme heat from UHIs,” Long said. “The tool integrates data from multidisciplinary sources and enables users to rapidly identify candidate sites for mitigation strategies.”
While the tool was developed to address UHI, SwRI is working with the City of San Antonio to explore ways it can address other challenges as well. This project is one of many UHI-related studies that are part of a collaboration between SwRI, the City of San Antonio and The University of Texas at San Antonio.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/industries/fluids-engineering.
Credit: Southwest Research Institute
SAN ANTONIO — May 28, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute has created a comprehensive data analysis tool to help metropolitan areas curb urban heat islands (UHIs) and pursue mitigation methods for especially vulnerable populations. This internally funded project was a collaboration with the City of San Antonio.
UHIs occur when dense concentrations of pavement and buildings absorb heat and raise surrounding temperatures. Without green spaces to provide a cooling effect, UHI temperatures can exceed other areas by as much as 20 degrees Fahrenheit, which could be dangerous to residents during summer.
“Tackling UHIs goes beyond simply analyzing spatial temperature differences,” said SwRI Senior Environmental Engineer Justin Long. “A comprehensive analysis of UHIs must also identify vulnerable populations, as well as viable mitigation methods in the areas where they reside.”
SwRI has created a data fusion tool that compiled and combined more than 230 datasets collected from several different city departments and public databases. The tool allows city leaders to analyze and explore several scenarios at once.
“Before the City of San Antonio can prioritize resources to address UHIs, it needs to identify all their characteristics, particularly zones where conditions are the most severe and that have a direct impact on the public,” Long said. “We discovered, for example, that many areas that experience extreme heat are also zones with historically high bus ridership. On hot summer days, pedestrians in these areas may be at higher risk of prolonged heat exposure and related illnesses.”
The tool could show city leaders where bus stops and high surface temperatures overlap and locations where planting trees or erecting artificial structures to mitigate the heat could be most effective.
To demonstrate how the data fusion tool could inform UHI policy making, SwRI created a hypothetical case study, merging multiple datasets from different sources for comparison. The scenario focused on locating regions with concentrated UHI effects that could pose a health hazard to bus riders and reduce the use of public transportation. Equipped with this knowledge, city officials could select locations to implement UHI mitigation strategies based on local socioeconomic, environmental and infrastructure characteristics.
“Mitigation strategies must be tailored to the specific characteristics of locations experiencing extreme heat from UHIs,” Long said. “The tool integrates data from multidisciplinary sources and enables users to rapidly identify candidate sites for mitigation strategies.”
While the tool was developed to address UHI, SwRI is working with the City of San Antonio to explore ways it can address other challenges as well. This project is one of many UHI-related studies that are part of a collaboration between SwRI, the City of San Antonio and The University of Texas at San Antonio.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/industries/fluids-engineering.




