If fruit fly wings do not develop into the right shape, the flies will die. UC Riverside researchers have learned how fly embryo cells develop as they need to, opening a window into human development and possible treatments for birth defects.
Credit: Mark Alber/UCR
If fruit fly wings do not develop into the right shape, the flies will die. UC Riverside researchers have learned how fly embryo cells develop as they need to, opening a window into human development and possible treatments for birth defects.
Biologists often investigate tissue development by studying parts of individual cells. In contrast, the UCR team used some of the most powerful supercomputers in California to simulate many cells working together.
The team examined the mechanical properties of the cells, such as their elasticity and fluid pressure. They also studied how a group of different cell types called a ‘wing disc’ divide and eventually become wing tissue. Their findings are detailed in the journal Nature Communications.
“We modeled hundreds of cells, trying to figure out how they interact with each other, in this case to become the wing of a fruit fly,” said Mark Alber, UCR distinguished mathematics professor and senior co-author of the study.
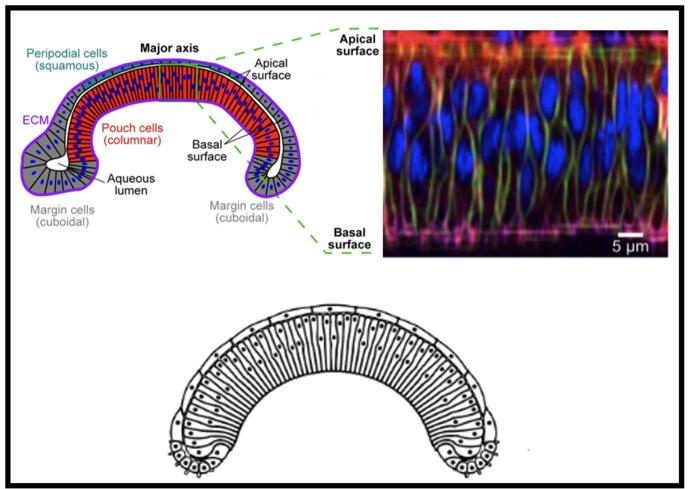
In close collaboration with bioengineers and quantitative biologists from the University of Notre Dame, the researchers saw that in the earlier stages of development the wing disc is uniformly curved. But in later stages, the top keeps its curvature while the bottom flattens.
“The disc, in a cross-section view, begins as something flat that transitions into a rainbow-like shape. Later, the top keeps the shape, but the middle bottom flattens out, so we have a top and bottom that don’t mirror each other anymore,” said Jennifer Rangel Ambriz, UCR mathematics doctoral student and paper co-first author.
“We wanted to understand what causes this shape, because the flies won’t fly, or survive, if development doesn’t happen properly,” Rangel Ambriz said.
The group found that a subcellular structure called actomyosin drives much of the development process, especially the lower wing disc flattening. This structure is a dynamic network of actin fibers that affects how stiff or tall the cells become.
During cell division and growth, actomyosin pushes the nuclei of different cells back and forth to influence the shapes of individual cells that make up the wing disc.
“For a cell to divide, the nucleus has to move into the top region of a cell, and it does so based on the actomyosin network,” Rangel Ambriz said. “It’s like a fist on a tube of toothpaste. When you squeeze the bottom, it moves everything to the top.”
Actomyosin also connects to a key component called the extracellular matrix, or ECM, which is composed of collagen. The cells in the wing disc adhere to the ECM, which keeps them from drifting too far from one another, especially when cells are dividing. The relative flexibility or stiffness of the ECM also has an important effect on tissue shape and development.
Going forward, the researchers hope to gain a better understanding of the genetic and chemical signals that affect actomyosin. While mechanical factors, such as pressure and membrane surface tension in the cells, also influence tissue shape, different chemical signals likely play an important role.
This project is funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation on which Alber is the principal investigator, along with co-investigators Weitao Chen of UCR, and Jeremiah J. Zartman and Alexander Dowling of UND. The team is working toward the goal of determining mechanisms that help restore damaged tissues to their normal function.
“In the embryo, if you cut a cell or even several cells, the tissue still goes on to develop as it should,” Alber said. “What we know now about factors that affect tissue development could have applications beyond fruit flies and might enable tissue regeneration in humans or animals.”
Furthermore, the team is hopeful their findings also can be used to correct defects in human tissue formation.
“Our fly models may allow us to connect the factors that control tissue development to specific genes, identify ones that are promoting certain birth defects, and eventually reprogram or correct them,” Rangel Ambriz said.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-024-46698-7
Article Title
Balancing competing effects of tissue growth and cytoskeletal regulation during Drosophila wing disc development
Article Publication Date
20-Mar-2024




