WASHINGTON, April 23, 2024 – Oil spills are deadly disasters for ocean ecosystems. They can have lasting impacts on fish and marine mammals for decades and wreak havoc on coastal forests, coral reefs, and the surrounding land. Chemical dispersants are often used to break down oil, but they often increase toxicity in the process.
Credit: Yuchun He
WASHINGTON, April 23, 2024 – Oil spills are deadly disasters for ocean ecosystems. They can have lasting impacts on fish and marine mammals for decades and wreak havoc on coastal forests, coral reefs, and the surrounding land. Chemical dispersants are often used to break down oil, but they often increase toxicity in the process.
In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Central South University, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and Ben-Gurion University of the Negev used laser treatments to transform ordinary cork into a powerful tool for treating oil spills.
They wanted to create a nontoxic, effective oil cleanup solution using materials with a low carbon footprint, but their decision to try cork resulted from a surprising discovery.
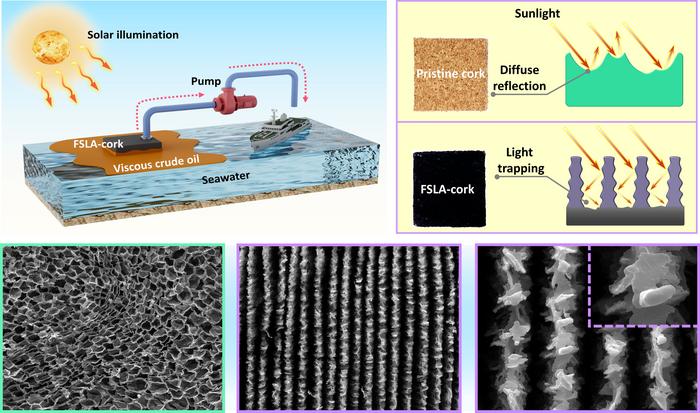
“In a different laser experiment, we accidentally found that the wettability of the cork processed using a laser changed significantly, gaining superhydrophobic (water-repelling) and superoleophilic (oil-attracting) properties,” author Yuchun He said. “After appropriately adjusting the processing parameters, the surface of the cork became very dark, which made us realize that it might be an excellent material for photothermal conversion.”
“Combining these results with the eco-friendly, recyclable advantages of cork, we thought of using it for marine oil spill cleanup,” author Kai Yin said. “To our knowledge, no one else has tried using cork for cleaning up marine oil spills.”
Cork comes from the bark of cork oak trees, which can live for hundreds of years. These trees can be harvested about every seven years, making cork a renewable material. When the bark is removed, the trees amplify their biological activity to replace it and increase their carbon storage, so harvesting cork helps mitigate carbon emissions.
The authors tested variations of a fast-pulsing laser treatment to achieve the optimal balance of characteristics in the cork that can be achieved at low cost. They closely examined nanoscopic structural changes and measured the ratio of oxygen and carbon in the material, changes in the angles with which water and oil contact the surface, and the material’s light wave absorption, reflection, and emission across the spectrum to determine its durability after multiple cycles of warming and cooling.
The photothermal properties endowed in cork through this laser processing allow the cork to warm quickly in the sun. The deep grooves also increase the surface area exposed to sunlight, so the cork can be warmed by just a little sunlight in 10-15 seconds. This energy is used to heat up spilled oil, lowering its viscosity and making it easier to collect. In experiments, the laser-treated cork collected oil out of water within 2 minutes.
The laser treatments not only help to better absorb oil, but also work to keep water out.
“When the cork undergoes a fast-pulsing laser treatment, its surface microstructure becomes rougher,” Yin said. “This micro- to nano-level roughness enhances hydrophobicity.”
As a result, the cork collects the oil without absorbing water, so the oil can be extracted from the cork and possibly even reused.
“Oil recovery is a complex and systematic task, and participating in oil recovery throughout its entire life cycle is our goal,” Yuchun He said. “The next step is to prepare electrothermal materials using polyurethane foam as the skeleton for oil adsorption, combining photothermal and electrothermal techniques to form an all-weather oil recovery system.”
###
The article “Femtosecond laser structured black superhydrophobic cork for efficient solar-driven cleanup of crude oil” is authored by Yuchun He, Kai Yin, Lingxiao Wang, Tingni Wu, Yu Chen, and Christopher J. Arnusch. It will appear in Applied Physics Letters on April 23, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0199291). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0199291.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Letters features rapid reports on significant discoveries in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/apl.
###
Journal
Applied Physics Letters
DOI
10.1063/5.0199291
Article Title
Femtosecond laser structured black superhydrophobic cork for efficient solar-driven cleanup of crude oil
Article Publication Date
23-Apr-2024




