Philadelphia, March 28, 2024 – Although the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially life-threatening ventricular cardiomyopathies and channelopathies may initially present with AF.
AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with increased risks of heart failure, stroke, and death. It is not traditionally considered to be a heritable form of heart disease, however, a growing body of literature over the past 25 years has shown that genetics contribute importantly to susceptibility for arrhythmias, including AF.
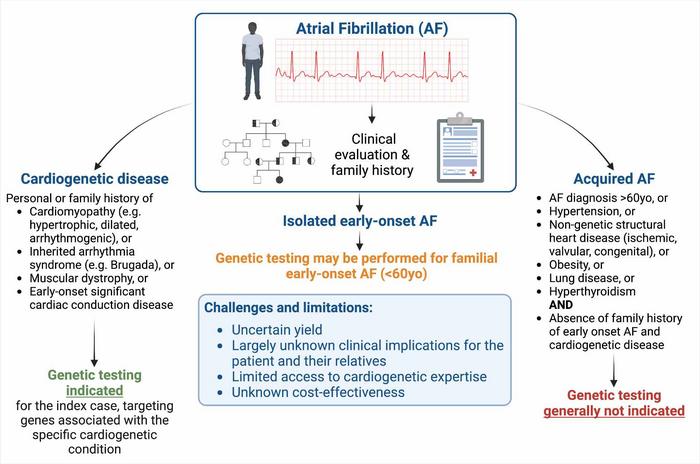
Our understanding of the genetics underlying AF remains in the relatively early stages, although it has become clear that the majority of cases likely develop secondary to a complex interaction between environmental and genetic contributors. In a minority of AF cases, powerful single rare genetic variants can be the primary drivers of arrhythmia development.
Beyond accounting for why AF has developed, identification of these powerful single genetic culprits can be important because – in addition to AF – many can also cause life-threatening ventricular cardiomyopathy and channelopathy syndromes. At present, it remains unclear why the same genetic variant may manifest with AF in isolation, a ventricular cardiomyopathy/channelopathy syndrome, or both.
Lead author of the White Paper Jason D. Roberts, MD, MAS, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, and Hamilton Health Sciences, says, “Given this recognition, we recommend that all early onset AF cases undergo careful clinical screening for evidence of a co-existing ventricular cardiomyopathy or channelopathy syndrome associated with a risk of sudden cardiac death. Should one be identified, appropriate genetic testing for the ventricular syndrome is recommended.”
Coauthor Rafik Tadros, MD, PhD, Cardiovascular Genetics Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, adds, “In the absence of clinical evidence of a co-existing ventricular cardiomyopathy or channelopathy syndrome, genetic testing may be considered in early onset AF cases, particularly if there is a positive family history and an absence of conventional clinical risk factors. However, clinicians should be aware that the yield of genetic testing in these instances is anticipated to be low (<10%), and this should only be pursued in settings equipped to interpret and appropriately manage genetic testing results."
Dr. Roberts states, “The vast majority of clinicians do not view AF as a genetic disorder and, except for certain specialty clinics, clinical genetic testing for AF is rarely performed. The notion that AF may have underlying genetic contributors will hopefully encourage clinicians to perform careful family histories, particularly in early onset forms of the condition wherein genetic contributors may be more prominent. Recognition that AF may potentially arise secondary to genetic variants that can also cause life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy syndromes will hopefully guide clinicians to carefully clinically screen for these conditions, particularly in early onset AF cases that develop in the absence of identifiable clinical risk factors.”
This White Paper was written by a group assembled by the CCS AF Guidelines Committee, which judged that the area of clinical application of AF genetics merited particular consideration. The writing group consisted of the chairs of the most recent AF Guidelines Committee, along with experts in clinical arrhythmia genetics and AF pathophysiology.
Credit: Canadian Journal of Cardiology
Philadelphia, March 28, 2024 – Although the vast majority of clinicians do not view atrial fibrillation (AF) as a genetic disorder, a White Paper in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, analyzes the current understanding of genetics and the role of genetic testing in AF and concludes there is an increasing appreciation that genetic culprits for potentially life-threatening ventricular cardiomyopathies and channelopathies may initially present with AF.
AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with increased risks of heart failure, stroke, and death. It is not traditionally considered to be a heritable form of heart disease, however, a growing body of literature over the past 25 years has shown that genetics contribute importantly to susceptibility for arrhythmias, including AF.
Our understanding of the genetics underlying AF remains in the relatively early stages, although it has become clear that the majority of cases likely develop secondary to a complex interaction between environmental and genetic contributors. In a minority of AF cases, powerful single rare genetic variants can be the primary drivers of arrhythmia development.
Beyond accounting for why AF has developed, identification of these powerful single genetic culprits can be important because – in addition to AF – many can also cause life-threatening ventricular cardiomyopathy and channelopathy syndromes. At present, it remains unclear why the same genetic variant may manifest with AF in isolation, a ventricular cardiomyopathy/channelopathy syndrome, or both.
Lead author of the White Paper Jason D. Roberts, MD, MAS, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, and Hamilton Health Sciences, says, “Given this recognition, we recommend that all early onset AF cases undergo careful clinical screening for evidence of a co-existing ventricular cardiomyopathy or channelopathy syndrome associated with a risk of sudden cardiac death. Should one be identified, appropriate genetic testing for the ventricular syndrome is recommended.”
Coauthor Rafik Tadros, MD, PhD, Cardiovascular Genetics Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, adds, “In the absence of clinical evidence of a co-existing ventricular cardiomyopathy or channelopathy syndrome, genetic testing may be considered in early onset AF cases, particularly if there is a positive family history and an absence of conventional clinical risk factors. However, clinicians should be aware that the yield of genetic testing in these instances is anticipated to be low (<10%), and this should only be pursued in settings equipped to interpret and appropriately manage genetic testing results."
Dr. Roberts states, “The vast majority of clinicians do not view AF as a genetic disorder and, except for certain specialty clinics, clinical genetic testing for AF is rarely performed. The notion that AF may have underlying genetic contributors will hopefully encourage clinicians to perform careful family histories, particularly in early onset forms of the condition wherein genetic contributors may be more prominent. Recognition that AF may potentially arise secondary to genetic variants that can also cause life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy syndromes will hopefully guide clinicians to carefully clinically screen for these conditions, particularly in early onset AF cases that develop in the absence of identifiable clinical risk factors.”
This White Paper was written by a group assembled by the CCS AF Guidelines Committee, which judged that the area of clinical application of AF genetics merited particular consideration. The writing group consisted of the chairs of the most recent AF Guidelines Committee, along with experts in clinical arrhythmia genetics and AF pathophysiology.
Journal
Canadian Journal of Cardiology
DOI
10.1016/j.cjca.2023.11.022
Method of Research
Literature review
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Clinical Genetic Testing for Atrial Fibrillation: Are We There Yet? A CJC White Paper
Article Publication Date
28-Mar-2024




