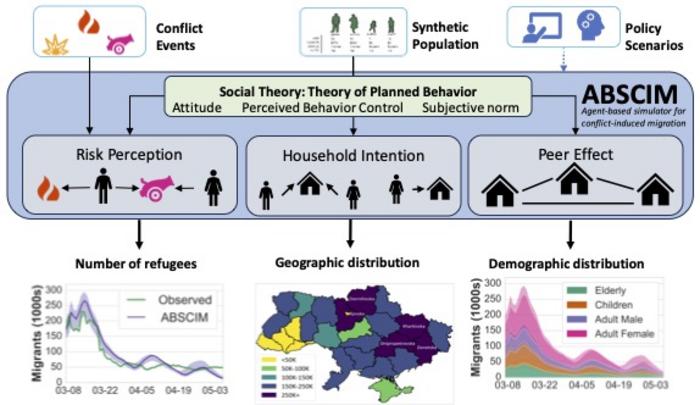
Researchers built a model, using insights from social and behavioral theory, that estimates daily flows of refugees from conflict. Forced migration, in contrast to planned migration, is a sudden choice made in response to an unexpected event. The United Nations High Commission for Refugees estimates that as of June 2023, there are some 110 million people worldwide who have been forced to move because of violence or natural disaster. Aid agencies and national governments need accurate and timely information to assist these migrants. Zakaria Mehrab and colleagues developed ABSCIM (Agent-based simulator for conflict-induced migration), a model to capture forced migration dynamics during the Ukraine War. The model simulates the behavior of a synthetic population of 46 million individuals, each of whom either migrates or remains at home according to rules derived from social theory. Age, gender, and household composition are key variables for deriving an individual’s attitude toward conflict (e.g., families may leave earlier than single adults). The authors’ model incorporates data on conflict events such as explosions, battles, and violence against civilians, which then drives individual choices and movements. ABSCIM was able to estimate daily migrant outflows from Ukraine between March 1, 2022, and May 15, 2022, with high accuracy. Along with the number of refugees, the model estimates the age, gender, and geographic origin of the migrants, including those that were internally displaced—information that can be used to tailor aid responses. ABSCIM also highlights its policy-relevant use cases by analyzing counterfactual conflict settings and estimating wartime sexual assault. According to the authors, the model can be used by humanitarian agencies responding to refugee crises around the world.
Credit: Zakaria Mehrab, Srini Venkatramanan, Bryan Lewis, Henning Mortveit
Researchers built a model, using insights from social and behavioral theory, that estimates daily flows of refugees from conflict. Forced migration, in contrast to planned migration, is a sudden choice made in response to an unexpected event. The United Nations High Commission for Refugees estimates that as of June 2023, there are some 110 million people worldwide who have been forced to move because of violence or natural disaster. Aid agencies and national governments need accurate and timely information to assist these migrants. Zakaria Mehrab and colleagues developed ABSCIM (Agent-based simulator for conflict-induced migration), a model to capture forced migration dynamics during the Ukraine War. The model simulates the behavior of a synthetic population of 46 million individuals, each of whom either migrates or remains at home according to rules derived from social theory. Age, gender, and household composition are key variables for deriving an individual’s attitude toward conflict (e.g., families may leave earlier than single adults). The authors’ model incorporates data on conflict events such as explosions, battles, and violence against civilians, which then drives individual choices and movements. ABSCIM was able to estimate daily migrant outflows from Ukraine between March 1, 2022, and May 15, 2022, with high accuracy. Along with the number of refugees, the model estimates the age, gender, and geographic origin of the migrants, including those that were internally displaced—information that can be used to tailor aid responses. ABSCIM also highlights its policy-relevant use cases by analyzing counterfactual conflict settings and estimating wartime sexual assault. According to the authors, the model can be used by humanitarian agencies responding to refugee crises around the world.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
An agent-based framework to study forced migration: A case study of Ukraine
Article Publication Date
19-Mar-2024




