“[…] our findings support the hypothesis that the intrauterine environment, particularly essential and non-essential metals, affect epigenetic aging biomarkers across the life course.”
Credit: 2024 Bozack et al.
“[…] our findings support the hypothesis that the intrauterine environment, particularly essential and non-essential metals, affect epigenetic aging biomarkers across the life course.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 12, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 4, entitled, “Associations of prenatal one-carbon metabolism nutrients and metals with epigenetic aging biomarkers at birth and in childhood in a US cohort.”
Epigenetic gestational age acceleration (EGAA) at birth and epigenetic age acceleration (EAA) in childhood may be biomarkers of the intrauterine environment. In this new study, researchers Anne K. Bozack, Sheryl L. Rifas-Shiman, Andrea A. Baccarelli, Robert O. Wright, Diane R. Gold, Emily Oken, Marie-France Hivert, and Andres Cardenas from Stanford University School of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Columbia University, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai investigated the extent to which first-trimester folate, B12, 5 essential and 7 non-essential metals in maternal circulation are associated with EGAA and EAA in early life.
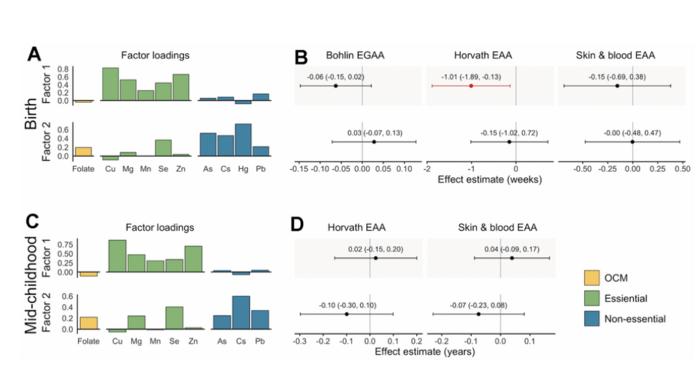
“[…] we hypothesized that OCM [one-carbon metabolism] nutrients and essential metals would be positively associated with EGAA and non-essential metals would be negatively associated with EGAA. We also investigated nonlinear associations and associations with mixtures of micronutrients and metals.”
Bohlin EGAA and Horvath pan-tissue and skin and blood EAA were calculated using DNA methylation measured in cord blood (N=351) and mid-childhood blood (N=326; median age = 7.7 years) in the Project Viva pre-birth cohort. A one standard deviation increase in individual essential metals (copper, manganese, and zinc) was associated with 0.94-1.2 weeks lower Horvath EAA at birth, and patterns of exposures identified by exploratory factor analysis suggested that a common source of essential metals was associated with Horvath EAA. The researchers also observed evidence of nonlinear associations of zinc with Bohlin EGAA, magnesium and lead with Horvath EAA, and cesium with skin and blood EAA at birth. Overall, associations at birth did not persist in mid-childhood; however, arsenic was associated with greater EAA at birth and in childhood.
“Prenatal metals, including essential metals and arsenic, are associated with epigenetic aging in early life, which might be associated with future health.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205602
Corresponding Author: Andres Cardenas
Corresponding Email: [email protected]
Keywords: epigenetic age acceleration, metals, folate, B12, prenatal exposures
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205602
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Associations of prenatal one-carbon metabolism nutrients and metals with epigenetic aging biomarkers at birth and in childhood in a US cohort
Article Publication Date
26-Feb-2024



